Understanding the Power of Return on Investment
In the world of investing, understanding the power of return on investment (ROI) is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving long-term financial goals. ROI is a fundamental concept in portfolio management, as it helps investors evaluate their portfolio’s performance and determine whether their investments are generating the desired returns. By grasping the significance of ROI, investors can refine their investment strategies, optimize their portfolios, and ultimately, maximize their returns. In essence, ROI serves as a benchmark for measuring the success of an investment, enabling investors to compare the performance of different assets and make data-driven decisions. As investors navigate the complex landscape of portfolio management, understanding ROI is essential for unlocking portfolio performance and achieving financial success. To effectively manage a portfolio, it’s essential to know how to calculate return on a portfolio, which involves understanding the intricacies of ROI and its applications.
Defining Portfolio Return: A Closer Look
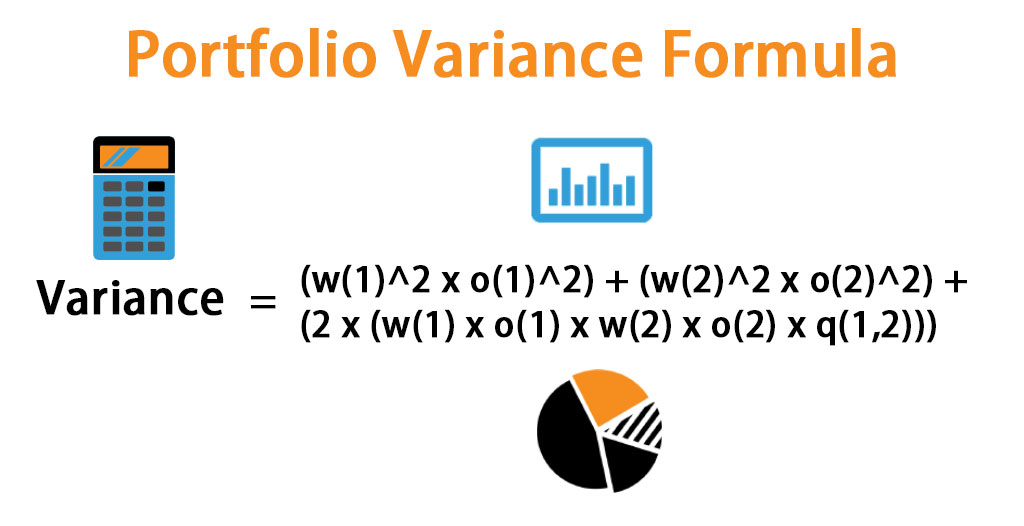
When it comes to evaluating portfolio performance, understanding the different types of returns is crucial. A portfolio’s return can be measured in various ways, including total return, rate of return, and return on equity. Total return, for instance, takes into account the capital appreciation and income generated by an investment, providing a comprehensive picture of an investment’s performance. Rate of return, on the other hand, focuses solely on the percentage change in an investment’s value over a specific period. Return on equity, meanwhile, measures a company’s profitability by comparing its net income to shareholder equity. Grasping these distinct concepts is essential for accurately calculating portfolio return and making informed investment decisions. By understanding the nuances of each return type, investors can better navigate the complexities of portfolio management and optimize their investment strategies. To effectively calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to understand these different return types and how they impact overall portfolio performance.
How to Calculate Portfolio Return: A Simple Formula
Calculating portfolio return is a crucial step in evaluating investment performance and making informed decisions. Fortunately, the process is relatively straightforward, and can be broken down into a simple formula. To calculate return on a portfolio, investors can use the following formula: (Ending Portfolio Value – Beginning Portfolio Value) / Beginning Portfolio Value. This formula takes into account the change in portfolio value over a specific period, providing a clear picture of investment performance. For example, if an investor’s portfolio was worth $100,000 at the beginning of the year and $120,000 at the end of the year, the return on the portfolio would be 20%. By understanding how to calculate return on a portfolio, investors can gain valuable insights into their investment performance and make data-driven decisions to optimize their portfolios. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, learning how to calculate return on a portfolio is an essential skill for achieving long-term financial success.
Factors Affecting Portfolio Return: What You Need to Know
When it comes to calculating return on a portfolio, several factors can impact the outcome. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions and optimizing portfolio performance. One of the most significant factors affecting portfolio return is risk. The level of risk an investor is willing to take on can significantly impact returns, with higher-risk investments potentially yielding higher returns, but also increasing the likelihood of losses. Diversification is another critical factor, as spreading investments across different asset classes and industries can help reduce risk and increase potential returns. Market conditions, such as economic downturns or upswings, can also have a significant impact on portfolio return. Additionally, fees and taxes can eat into returns, making it essential to consider these costs when calculating portfolio return. By understanding how these factors interact and impact portfolio return, investors can make more informed decisions and develop strategies to maximize returns. For instance, investors may choose to diversify their portfolios to reduce risk, or adjust their investment strategies in response to changing market conditions. By considering these factors, investors can gain a more accurate picture of their portfolio’s performance and make data-driven decisions to optimize returns. When learning how to calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to consider these factors and their impact on investment performance.
The Role of Time in Calculating Portfolio Return
Time plays a critical role in calculating portfolio return, as it can significantly impact investment growth and returns. One of the key concepts to understand is compounding, which refers to the effect of earning returns on previous returns. Over time, compounding can lead to significant growth in portfolio value, making it an essential factor to consider when calculating return on a portfolio. For example, if an investor earns a 10% return on a $100,000 portfolio in year one, and then earns a 10% return on the new portfolio value of $110,000 in year two, the compounding effect can lead to a significant increase in portfolio value over time. Additionally, time can also impact investment decisions, as investors may need to adjust their strategies in response to changing market conditions or personal financial goals. By understanding the role of time in calculating portfolio return, investors can make more informed decisions and develop strategies to maximize returns over the long term. When learning how to calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to consider the impact of time and compounding on investment performance. By doing so, investors can gain a more accurate picture of their portfolio’s performance and make data-driven decisions to optimize returns.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Portfolio Return
When learning how to calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results and poor investment decisions. One of the most significant mistakes investors make is ignoring fees and taxes, which can significantly eat into returns. For example, if an investor earns a 10% return on a portfolio, but pays 2% in fees and 1% in taxes, the net return would be only 7%. Another common mistake is failing to account for inflation, which can erode the purchasing power of returns over time. Additionally, investors may also make the mistake of not considering the impact of compounding, which can lead to significant differences in portfolio value over the long term. By being aware of these common mistakes, investors can take steps to avoid them and ensure accurate calculations of portfolio return. This includes carefully reviewing investment fees and taxes, accounting for inflation, and considering the impact of compounding on investment growth. By doing so, investors can gain a more accurate picture of their portfolio’s performance and make informed decisions to optimize returns.
Real-World Examples: Calculating Return on a Portfolio
To illustrate how to calculate return on a portfolio, let’s consider a few real-world examples. Suppose an investor has a portfolio consisting of 60% stocks and 40% bonds, with a total value of $100,000. Over the course of a year, the stocks earn a 12% return, while the bonds earn a 4% return. To calculate the portfolio return, the investor would need to weight the returns of each asset class by their respective allocations. In this case, the portfolio return would be (0.6 x 12%) + (0.4 x 4%) = 8.8%. Another example might involve an investor with a portfolio consisting of 80% domestic stocks and 20% international stocks, with a total value of $50,000. If the domestic stocks earn a 10% return and the international stocks earn a 15% return, the portfolio return would be (0.8 x 10%) + (0.2 x 15%) = 11.5%. By working through these examples, investors can gain a better understanding of how to calculate return on a portfolio and apply this knowledge to their own investment decisions. When learning how to calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to consider the specific asset allocation and investment strategy in place, as these factors can significantly impact portfolio performance.
Maximizing Portfolio Return: Strategies for Success
To maximize portfolio return, investors can employ a range of strategies that help optimize performance and minimize risk. One key approach is diversification, which involves spreading investments across different asset classes and industries to reduce exposure to any one particular market or sector. Regular portfolio rebalancing is another essential strategy, as it helps maintain an optimal asset allocation and prevents drift over time. Tax-efficient investing is also crucial, as it can help minimize tax liabilities and maximize after-tax returns. Additionally, investors can consider implementing a dollar-cost averaging strategy, which involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach can help reduce timing risks and avoid emotional decision-making. By incorporating these strategies into their investment approach, investors can increase their chances of achieving their financial goals and maximizing portfolio return. When learning how to calculate return on a portfolio, it’s essential to consider these strategies and how they can be used to optimize portfolio performance. By doing so, investors can make more informed decisions and achieve greater success in their investment endeavors.