What is a Bid-Ask Spread?
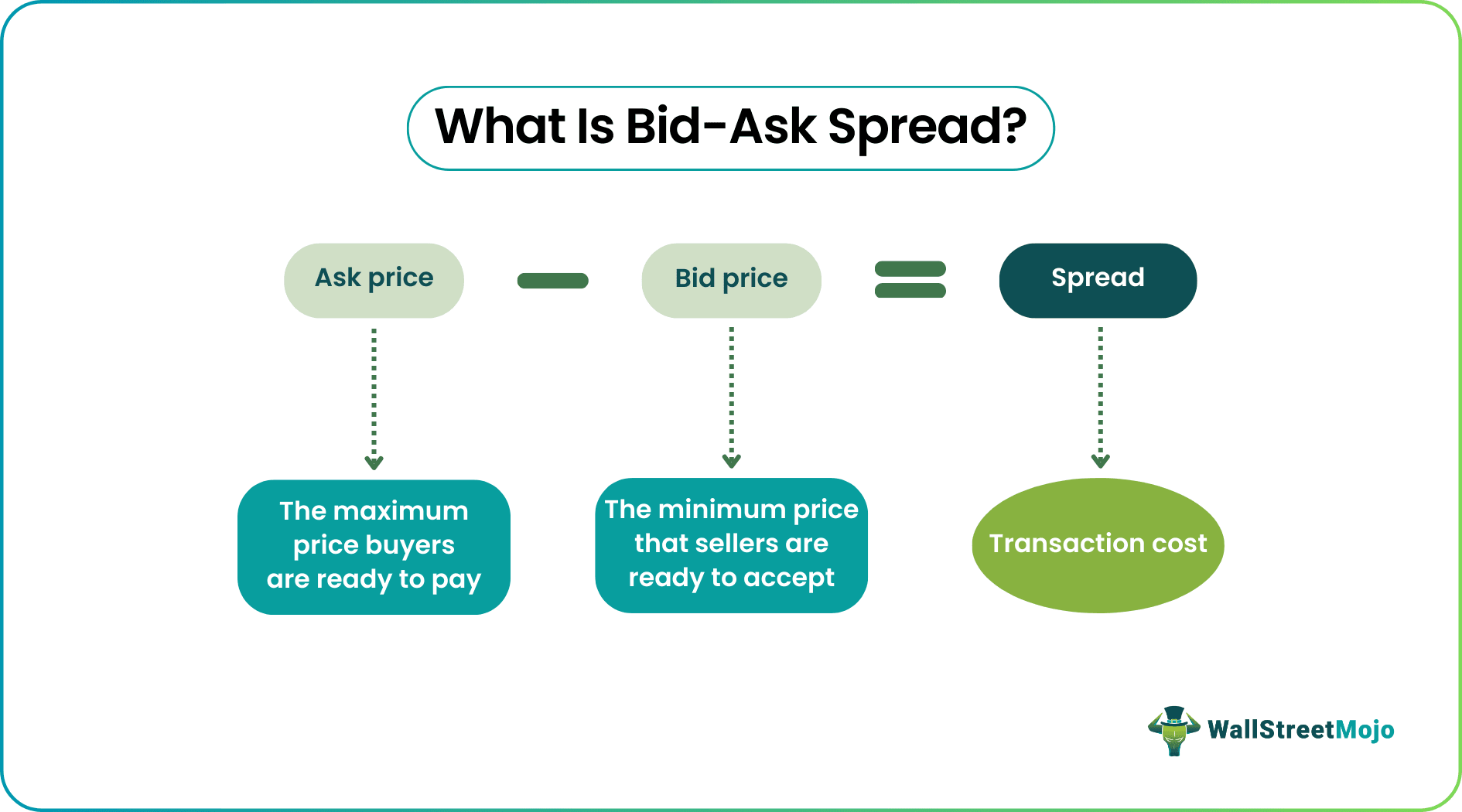
The bid-ask spread is a fundamental concept in trading. It represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for an asset (the bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (the ask). Understanding this spread is crucial for anyone involved in buying or selling financial instruments.
To illustrate, imagine selling a used car. Several potential buyers might offer different prices. The highest offer is your “bid.” Simultaneously, you, as the seller, have a minimum price you are willing to accept. This is your “ask.” The difference between these two prices is analogous to the bid-ask spread in financial markets. This difference reflects the cost of executing a trade immediately.
The bid-ask spread impacts profitability. Knowing how to calculate bid offer spread is essential to making informed trading decisions. The formula to calculate bid offer spread is simple: (Ask Price – Bid Price = Bid-Ask Spread). For example, if a stock has a bid price of $50.00 and an ask price of $50.05, the bid-ask spread is $0.05. This $0.05 represents the cost a trader incurs to enter and exit a position immediately. This is how to calculate bid offer spread and factor it into your trading strategy.
Dissecting the Components of the Spread
The bid-ask spread isn’t a static entity. It’s a dynamic reflection of market forces. Understanding its components is crucial for informed trading decisions. Several factors interplay to determine the width of the spread. Order book dynamics are a primary influence. The order book lists all outstanding buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders for a specific asset. A large number of orders clustered near the current price suggests high liquidity and a tighter spread. Conversely, a sparse order book can indicate lower liquidity and a wider spread. This highlights how to calculate bid offer spread.
Supply and demand also significantly impact the spread. High demand and limited supply typically push the ask price higher, widening the spread. Conversely, high supply and limited demand can lower the bid price, also widening the spread. Market makers play a vital role in providing liquidity and narrowing spreads. They simultaneously quote bid and ask prices, profiting from the spread. Their presence ensures there are always buyers and sellers available, facilitating trading. The competition among market makers also contributes to tighter spreads. Therefore, one can learn how to calculate bid offer spread by having this information.
The interaction of these factors constantly reshapes the bid-ask spread. Liquidity, referring to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price, is paramount. Highly liquid assets tend to have tighter spreads. This is because there are many participants willing to trade at or near the current market price. Illiquid assets, on the other hand, often exhibit wider spreads due to the difficulty of finding willing counterparties. Market volatility is another key determinant. During periods of high volatility, uncertainty increases, and market makers widen spreads to compensate for the increased risk. Understanding how these elements interact allows traders to better grasp how to calculate bid offer spread and navigate the markets more effectively. Additionally, learning how to calculate bid offer spread can be achieved by understanding what order book dynamics are and using that knowledge to your advantage.
How to Determine the Bid Offer Spread: A Step-by-Step Approach
Understanding how to calculate bid offer spread is crucial for any trader or investor. The bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay (the bid) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (the ask). Knowing how to calculate bid offer spread allows individuals to understand transaction costs and assess market liquidity.
The process of how to calculate bid offer spread is straightforward. First, identify the ask price, which is the lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell an asset. Next, determine the bid price, representing the highest price a buyer is willing to purchase the same asset. Once these values are identified, apply the following formula: Ask Price – Bid Price = Bid-Ask Spread. This simple calculation reveals the cost of executing a round-trip trade, buying and then immediately selling, or vice-versa. For instance, if the ask price for a stock is $100.10 and the bid price is $100.00, then how to calculate bid offer spread would be $100.10 – $100.00 = $0.10. The bid-ask spread is $0.10. This amount represents the transaction cost incurred for immediately buying and selling the asset.
It’s important to remember that the bid-ask spread is typically expressed in currency units, such as dollars, cents, or pips, depending on the asset being traded. Factors influencing the spread’s width include market volatility, trading volume, and the presence of market makers. Actively monitoring the bid-ask spread for assets is an important step in understanding how to calculate bid offer spread, and in turn, can help traders make informed decisions and manage their trading costs effectively. A narrow spread generally indicates high liquidity and lower transaction costs, while a wider spread suggests lower liquidity and higher costs. Learning how to calculate bid offer spread provides a foundational understanding of market dynamics and their impact on trading profitability.
The Impact of Spread on Trading Profitability
The bid-ask spread directly influences trading costs and, consequently, profitability. It represents a transaction cost that every trader must account for. A wider spread means a higher cost to enter and exit a trade, reducing potential profits or increasing potential losses. Understanding how to calculate bid offer spread is crucial for assessing the true cost of trading.
When a trader buys an asset at the ask price and immediately sells it at the bid price, they will incur a loss equal to the bid-ask spread, even before considering commissions or other fees. This highlights the importance of minimizing the spread’s impact. Several strategies can be employed to achieve this. Trading during peak liquidity hours, when more buyers and sellers are active, typically results in tighter spreads. This is because increased competition among market participants narrows the gap between the bid and ask prices. How to calculate bid offer spread also becomes important when assessing different trading times.
Another common strategy involves the use of limit orders. Instead of accepting the prevailing market price, a limit order allows a trader to specify the price they are willing to buy or sell at. While this doesn’t guarantee execution, it provides the opportunity to obtain a better price and potentially reduce the impact of the spread. Traders may also analyze spreads across different brokers or trading platforms, as some offer tighter spreads than others. Being able to determine how to calculate bid offer spread efficiently allows traders to compare different assets quickly and make better decisions. Moreover, assets with higher trading volumes generally exhibit narrower spreads, making them more cost-effective to trade. Volatility also influences spreads; higher volatility often leads to wider spreads as market makers increase their compensation for the increased risk.
Analyzing Spreads Across Different Assets
Bid-ask spreads vary significantly across different asset classes. Understanding these differences is crucial for informed trading decisions. For example, stocks of large, well-established companies typically have tighter spreads than those of smaller, less liquid companies. This is because there are more buyers and sellers actively trading the former, leading to greater competition and narrower price differences.
In the foreign exchange (forex) market, spreads are generally very tight for major currency pairs like EUR/USD and USD/JPY. This high liquidity stems from the massive trading volume in these pairs, involving banks, institutions, and individual traders worldwide. However, exotic currency pairs, such as USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR, often exhibit wider spreads due to lower trading volume and increased volatility. The concept of how to calculate bid offer spread remains the same, but the resulting value differs significantly.
Cryptocurrencies present another unique case. While some cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin (BTC) and Ethereum (ETH) have relatively liquid markets and tighter spreads on major exchanges, smaller altcoins can experience significantly wider spreads. Factors influencing cryptocurrency spreads include exchange volume, market sentiment, and regulatory uncertainty. Moreover, the cost to how to calculate bid offer spread may incorporate exchange fees that can eat into potential profits more than traditional markets. The volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies also contributes to wider spreads, as market makers demand a larger premium to compensate for the increased risk. Different assets such as bonds, commodities, and derivatives also display varying spreads, influenced by factors such as credit risk, storage costs, and time to expiration.
Factors That Widen or Narrow a Spread
The bid-ask spread is not static; it fluctuates based on various market conditions and events. Several factors can cause the spread to widen, indicating decreased liquidity and increased risk, while others can narrow it, reflecting improved liquidity and stability. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders aiming to optimize their trading strategies. Learning how to calculate bid offer spread during different events, will improve any trader capabilities.
News announcements and economic data releases are prime examples of events that can significantly widen the bid-ask spread. Prior to major announcements, uncertainty increases, leading market makers to widen spreads to compensate for the heightened risk of adverse price movements. For instance, before the release of inflation data or a central bank interest rate decision, spreads in related currency pairs or stock indices typically expand. Similarly, unexpected geopolitical events or company-specific news (e.g., earnings reports, regulatory changes) can trigger a widening of spreads due to increased volatility and uncertainty. Periods of high market volatility, often measured by indicators like the VIX, are also associated with wider spreads. Increased volatility makes it more challenging for market makers to accurately price assets, leading them to widen the gap between the bid and ask prices to protect themselves from potential losses. Conversely, periods of low volatility and stable market conditions tend to result in narrower spreads. A key component for any trader is how to calculate bid offer spread.
Conversely, increased trading volume and participation can narrow the bid-ask spread. Higher trading volume generally indicates greater liquidity, making it easier for market makers to match buyers and sellers without having to offer wide spreads. For example, actively traded stocks or currency pairs during peak trading hours often exhibit tighter spreads compared to less liquid assets or off-peak hours. Furthermore, the presence of more market participants, including high-frequency traders and algorithmic trading firms, can contribute to tighter spreads by providing continuous liquidity and price discovery. These participants often compete to offer the best bid and ask prices, narrowing the spread and benefiting other traders. Understanding how to calculate bid offer spread and how different factors influence its width enables traders to make more informed decisions about when and how to execute their trades. This knowledge helps in minimizing transaction costs and maximizing potential profitability.
Strategies to Navigate Bid-Ask Spreads Effectively
Effectively managing bid-ask spreads is crucial for successful trading. Several strategies can minimize their impact on profitability. Traders seeking to understand how to calculate bid offer spread, should consider the nuances of each technique. Limit orders are a primary tool. They allow traders to specify the price at which they are willing to buy or sell. By setting a limit price, traders avoid the risk of accepting an unfavorable price within the spread. This is particularly useful in volatile markets. A trader places an order, which guarantees execution at the desired price or better. However, there’s no guarantee the order will be filled, especially if the market moves away from the limit price.
Stop-loss orders are another essential risk management tool. While primarily designed to limit potential losses, they can also influence execution prices relative to the bid-ask spread. A stop-loss order becomes a market order. This happens once the price reaches a specified stop price. This can lead to execution within the spread, possibly at a less favorable price. However, the primary goal is to exit a losing position and control losses, which outweighs the spread’s impact. Traders should carefully consider the placement of stop-loss orders. This considers typical market volatility to avoid premature triggering. Understanding how to calculate bid offer spread helps to make informed decisions about stop-loss placement.
Selecting a trading platform with tight spreads is also important. Some brokers are known for offering more competitive spreads than others. Interactive Brokers and IG are examples of platforms often cited for their tight spreads. These brokers aggregate liquidity from multiple sources. This allows them to offer tighter spreads, reducing transaction costs. Furthermore, trading during peak liquidity hours can help. Higher trading volumes typically lead to tighter spreads. This is because there are more buyers and sellers actively participating in the market. This increased competition narrows the gap between the bid and ask prices. Therefore, understanding how to calculate bid offer spread, is key to minimizing trading costs and enhancing overall profitability.
Beyond the Basics: Understanding Spread and Market Liquidity
The bid-ask spread is intrinsically linked to market liquidity. A narrow bid-ask spread generally signifies high market liquidity. High liquidity means there are many buyers and sellers actively participating. This allows traders to execute orders quickly and at desired prices. When many participants are willing to trade, the difference between the bid and ask prices tightens. Conversely, wider spreads often indicate lower liquidity. This can occur in less actively traded assets or during times of market uncertainty. In such scenarios, fewer buyers and sellers are present. This leads to a larger gap between the highest bid and the lowest ask.
Liquidity plays a crucial role in efficient price discovery. When a market is liquid, new information is rapidly reflected in prices. This is because numerous participants are constantly evaluating and trading based on the available data. Tight spreads facilitate this process. They allow for smoother price adjustments. This makes it easier to enter and exit positions without significantly impacting the market price. The ability to quickly execute trades at predictable prices is vital for traders and investors. Therefore, the bid-ask spread serves as a valuable indicator of market efficiency. Knowing how to calculate bid offer spread and understanding its implications is crucial.
Market stability also depends on liquidity, which is reflected in the bid-ask spread. A liquid market can absorb large orders without experiencing significant price swings. This reduces the risk of market manipulation and promotes fair pricing. When spreads are tight, it becomes more difficult for large traders to exploit price discrepancies. This contributes to a more stable and transparent trading environment. Understanding the relationship between the bid-ask spread and liquidity is essential for anyone involved in financial markets. It allows for a more informed assessment of trading costs and potential risks. Recognizing how to calculate bid offer spread is key to navigating the markets successfully and making informed trading decisions. The ability to understand how to calculate bid offer spread empowers traders to minimize costs and maximize profitability.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/YenETFMeaningProsandConsExamplesGettyImages-504133765-898e895ff3b547448648f356220dfad9.jpg)