Unlocking the Secrets of the Forward Curve
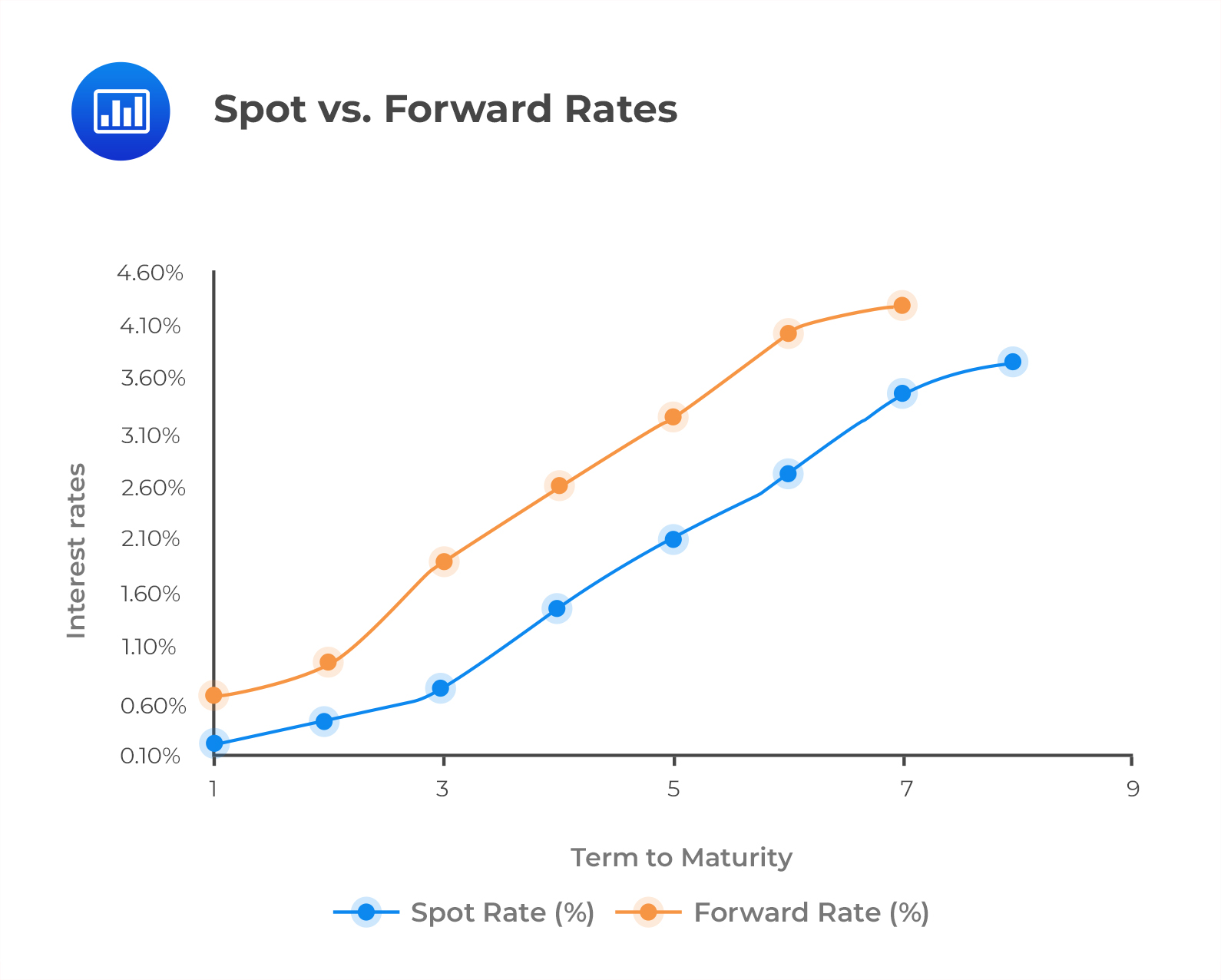
The bond market is a complex and dynamic system, with numerous factors influencing the yields of government securities. One of the most powerful tools for understanding this market is the forward curve, a graphical representation of the expected yields on a bond at a series of future dates. The forward curve is distinct from the yield curve, which displays the current yields of bonds with different maturities. While the yield curve provides a snapshot of current market conditions, the forward curve offers a forward-looking perspective, enabling users to anticipate changes in interest rates and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. This makes the forward curve an essential component of investment decisions, risk management, and economic forecasting. In the context of the 10-year treasury market, the forward 10 year treasury curve is particularly important, as it provides insights into the expected direction of interest rates and the overall health of the economy.
How to Interpret the Forward 10 Year Treasury Curve
Interpreting the forward 10 year treasury curve requires a deep understanding of its components and the factors that influence its shape. The curve is typically plotted with the x-axis representing time and the y-axis representing the expected yield. A steepening curve indicates that market participants expect interest rates to rise in the future, while a flattening curve suggests that rates are expected to remain stable or decline. To accurately interpret the forward 10 year treasury curve, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
Firstly, the slope of the curve provides insights into market expectations of future interest rates. A steep slope indicates that investors expect rates to rise significantly, while a shallow slope suggests that rates will remain stable. Secondly, the level of the curve is also important, as it reflects the overall direction of interest rates. A high level indicates that rates are expected to be high, while a low level suggests that rates will be low.
In addition to these factors, it’s also important to consider the implications of steepening and flattening curves. A steepening curve can indicate a strong economy, with rising interest rates reflecting increased borrowing demand. On the other hand, a flattening curve may suggest a slowing economy, with declining interest rates reflecting reduced borrowing demand. By understanding these dynamics, investors and economists can use the forward 10 year treasury curve to make informed decisions about investment strategies and economic forecasts.
The Role of Market Expectations in Shaping the Forward Curve
Market expectations play a crucial role in shaping the forward 10 year treasury curve, as they reflect the collective views of investors, economists, and other market participants on the future direction of interest rates. The forward curve is not simply a reflection of current market conditions, but rather a forward-looking indicator that incorporates market expectations of future events. As such, changes in market expectations can have a significant impact on the shape and slope of the forward curve.
One of the key factors that influences market expectations is inflation expectations. When inflation expectations rise, the forward curve tends to steepen, as investors expect higher interest rates to combat inflationary pressures. Conversely, when inflation expectations fall, the forward curve tends to flatten, as investors expect lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. Monetary policy decisions, such as changes in central bank interest rates, also have a significant impact on market expectations and the forward curve.
Economic growth expectations also play a critical role in shaping the forward curve. When economic growth expectations are strong, the forward curve tends to steepen, as investors expect higher interest rates to reflect a strong economy. Conversely, when economic growth expectations are weak, the forward curve tends to flatten, as investors expect lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. By understanding the impact of market expectations on the forward 10 year treasury curve, investors and economists can gain valuable insights into the future direction of interest rates and make informed investment decisions.
What the Forward Curve Reveals About Future Interest Rates
The forward 10 year treasury curve is a powerful tool for predicting future interest rates, providing valuable insights for investors, economists, and policymakers. By analyzing the shape and slope of the curve, market participants can gain a better understanding of the future direction of interest rates, which has significant implications for borrowing costs, investment decisions, and economic growth.
The forward curve reveals information about future interest rates by reflecting market expectations of future economic conditions. A steepening curve, for example, suggests that market participants expect interest rates to rise in the future, which can be indicative of a strong economy with rising inflation pressures. Conversely, a flattening curve suggests that market participants expect interest rates to remain stable or decline, which can be indicative of a slowing economy with reduced inflation pressures.
The implications of the forward curve for borrowing costs are significant. When the curve suggests that interest rates will rise in the future, borrowers may be incentivized to lock in lower interest rates now, while lenders may be more cautious in their lending activities. Conversely, when the curve suggests that interest rates will remain stable or decline, borrowers may be more likely to take on debt, while lenders may be more willing to lend.
The forward curve also has significant implications for investment decisions. By analyzing the curve, investors can gain insights into the future direction of interest rates, which can inform their investment strategies. For example, if the curve suggests that interest rates will rise in the future, investors may be more likely to invest in shorter-term bonds or other fixed-income securities. Conversely, if the curve suggests that interest rates will remain stable or decline, investors may be more likely to invest in longer-term bonds or other securities with higher yields.
Overall, the forward 10 year treasury curve is a valuable tool for predicting future interest rates, providing insights that can inform investment decisions, borrowing costs, and economic growth. By understanding the forward curve, market participants can gain a better understanding of the future direction of interest rates and make more informed decisions.
The Relationship Between the Forward Curve and Economic Indicators
The forward 10 year treasury curve is closely tied to various economic indicators, providing valuable insights into the overall health of the economy. By analyzing the correlation between the forward curve and key economic indicators, investors and economists can gain a better understanding of the complex relationships between interest rates, economic growth, and inflation.
One of the most significant correlations between the forward curve and economic indicators is with GDP growth. When the forward curve is steepening, it often indicates that market participants expect stronger economic growth, which can lead to higher interest rates. Conversely, when the forward curve is flattening, it may suggest that market participants expect slower economic growth, which can lead to lower interest rates.
Inflation is another key economic indicator that is closely tied to the forward curve. When inflation expectations rise, the forward curve tends to steepen, as market participants expect higher interest rates to combat inflationary pressures. Conversely, when inflation expectations fall, the forward curve tends to flatten, as market participants expect lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth.
Unemployment rates are also closely correlated with the forward curve. When unemployment rates are falling, the forward curve may steepen, as market participants expect stronger economic growth and higher interest rates. Conversely, when unemployment rates are rising, the forward curve may flatten, as market participants expect slower economic growth and lower interest rates.
Other economic indicators, such as consumer spending, business confidence, and housing market activity, also have a significant impact on the forward curve. By analyzing the correlation between these indicators and the forward curve, investors and economists can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the economy and make more informed decisions.
In conclusion, the forward 10 year treasury curve is a valuable tool for understanding the complex relationships between interest rates, economic growth, and inflation. By analyzing the correlation between the forward curve and key economic indicators, investors and economists can gain valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and make more informed decisions.
Using the Forward Curve to Inform Investment Decisions
Investors can leverage the forward 10 year treasury curve to make informed investment decisions, optimizing their portfolios and managing risk. By analyzing the forward curve, investors can gain valuable insights into the future direction of interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, enabling them to adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
One key application of the forward curve is in bond allocation. By analyzing the shape and slope of the curve, investors can determine the optimal bond allocation for their portfolio. For example, if the forward curve is steepening, investors may want to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to shorter-term bonds, as interest rates are expected to rise in the future. Conversely, if the forward curve is flattening, investors may want to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to longer-term bonds, as interest rates are expected to remain stable or decline.
The forward curve can also be used to inform duration management strategies. By analyzing the forward curve, investors can determine the optimal duration for their bond portfolio, taking into account the expected changes in interest rates and inflation. For example, if the forward curve suggests that interest rates will rise in the future, investors may want to shorten the duration of their bond portfolio to minimize losses.
Risk assessment is another key application of the forward curve. By analyzing the forward curve, investors can gain insights into the potential risks and opportunities associated with different investment strategies. For example, if the forward curve suggests that interest rates will rise in the future, investors may want to reduce their exposure to long-term bonds and increase their exposure to shorter-term bonds or other fixed-income securities.
In addition to these strategies, the forward curve can also be used to inform investment decisions in other asset classes, such as stocks and commodities. By analyzing the forward curve, investors can gain insights into the overall direction of the economy and make more informed investment decisions.
Overall, the forward 10 year treasury curve is a powerful tool for investors, providing valuable insights into the future direction of interest rates, inflation, and economic growth. By leveraging the forward curve, investors can optimize their portfolios, manage risk, and make more informed investment decisions.
Common Misconceptions About the Forward 10 Year Treasury Curve
Despite its importance in understanding the bond market, the forward 10 year treasury curve is often shrouded in misconceptions and myths. It is essential to address these misconceptions to ensure that investors and economists can accurately interpret the forward curve and make informed decisions.
One common misconception is that the forward curve is identical to the yield curve. While both curves are related to interest rates, they are distinct concepts. The yield curve represents the current interest rates for different bond maturities, whereas the forward curve represents the expected future interest rates. This distinction is crucial, as the forward curve provides valuable insights into market expectations and future interest rate movements.
Another misconception is that central banks have direct control over the forward curve. While central banks can influence the forward curve through monetary policy decisions, they do not have direct control over the curve. The forward curve is shaped by market expectations, which are influenced by a wide range of factors, including economic indicators, inflation expectations, and monetary policy.
Some investors also believe that the forward curve is only relevant for bond investors. However, the forward curve has implications for investors across various asset classes, including stocks, commodities, and currencies. By analyzing the forward curve, investors can gain insights into the overall direction of the economy and make more informed investment decisions.
Additionally, some economists believe that the forward curve is a perfect predictor of future interest rates. While the forward curve provides valuable insights into market expectations, it is not a perfect predictor of future interest rates. The forward curve is subject to various risks and uncertainties, including changes in market expectations, economic shocks, and monetary policy surprises.
By addressing these common misconceptions, investors and economists can gain a deeper understanding of the forward 10 year treasury curve and its significance in the bond market. By accurately interpreting the forward curve, investors can make more informed investment decisions and navigate the complex world of treasury yields with confidence.
The Future of the Forward Curve: Trends and Predictions
The forward 10 year treasury curve is a dynamic and constantly evolving concept, influenced by a wide range of factors, including technological advancements, demographic changes, and shifting global economic dynamics. As the global economy continues to evolve, it is essential to consider the potential trends and predictions for the forward curve.
One potential trend is the increasing importance of artificial intelligence and machine learning in shaping the forward curve. As AI and machine learning algorithms become more prevalent in financial markets, they are likely to play a larger role in shaping market expectations and influencing the forward curve. This could lead to more accurate predictions of future interest rates and improved investment decisions.
Another trend is the impact of demographic changes on the forward curve. As the global population ages, it is likely to lead to changes in consumption patterns, savings rates, and investment decisions. This could result in shifts in the forward curve, as investors adapt to changing demographic trends.
The rise of sustainable investing is also likely to influence the forward curve. As investors increasingly focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, it could lead to changes in the forward curve, as investors prioritize investments that align with their values.
In terms of predictions, many experts believe that the forward 10 year treasury curve will continue to play a critical role in shaping investment decisions and economic growth. As the global economy continues to evolve, the forward curve will remain an essential tool for investors and economists, providing valuable insights into market expectations and future interest rates.
Some experts also predict that the forward curve will become more volatile in the future, as investors respond to changing market conditions and shifting global economic dynamics. This could lead to increased uncertainty and risk in financial markets, highlighting the importance of careful analysis and interpretation of the forward curve.
Overall, the future of the forward 10 year treasury curve is likely to be shaped by a complex interplay of technological, demographic, and economic factors. By understanding these trends and predictions, investors and economists can better navigate the complex world of treasury yields and make more informed investment decisions.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=71JP8dtzD8U