Understanding the Volatility of Stocks and Bonds
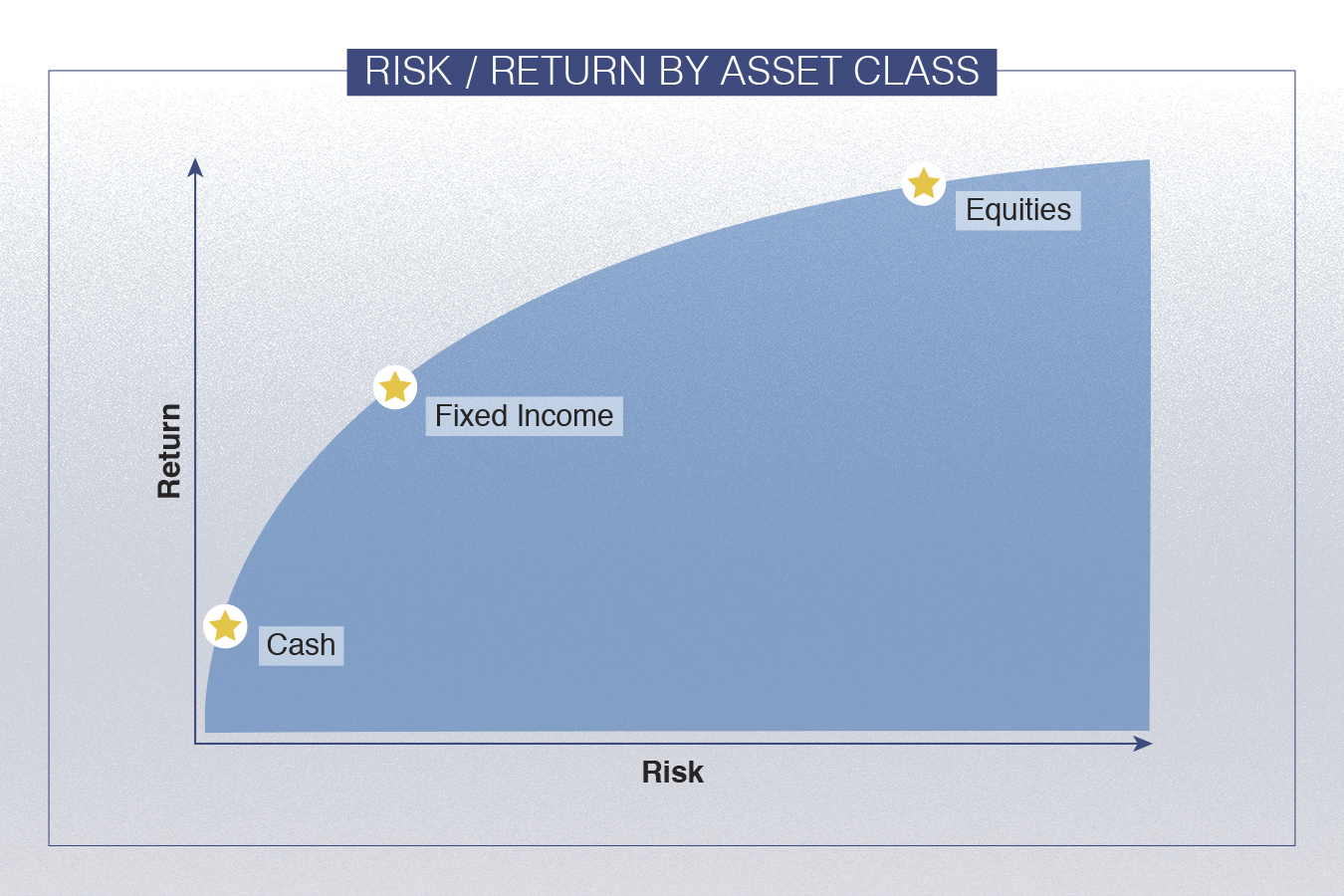
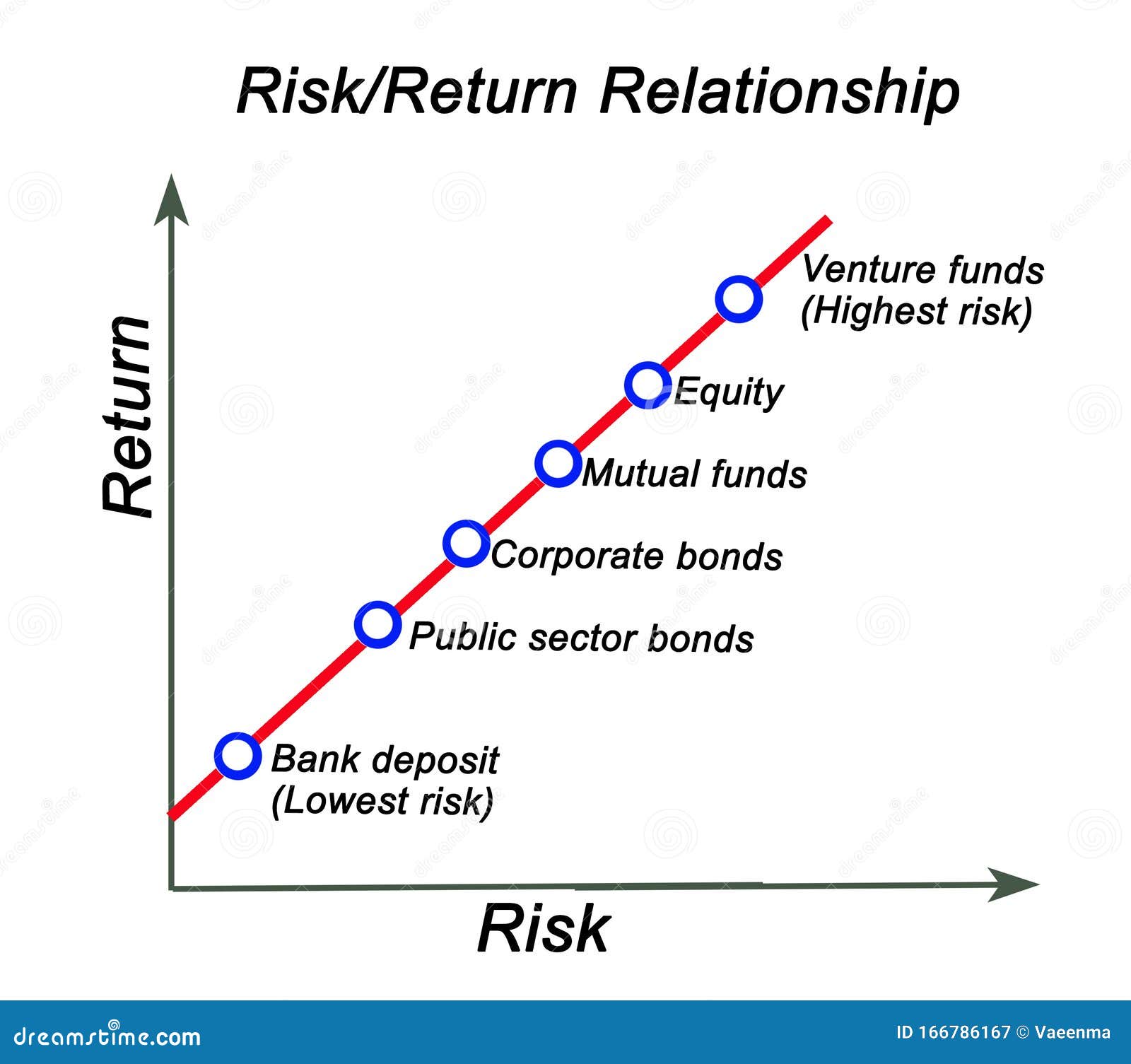
Investing in stocks and bonds can be a lucrative way to grow wealth, but it’s essential to understand the common risk factors that affect returns on these investments. Risk and volatility are inherent in the investment landscape, and failing to comprehend their implications can lead to significant losses. The common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds can be broadly categorized into two types: systematic and unsystematic risks. Systematic risks, such as market risk and interest rate risk, affect the entire market, while unsystematic risks, like company-specific risks, are specific to individual companies or industries. By grasping the concept of risk and volatility, investors can develop a robust investment strategy that minimizes potential losses and maximizes returns.
Identifying the Key Drivers of Investment Risk
When it comes to investing in stocks and bonds, understanding the key drivers of investment risk is crucial for making informed decisions. The common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds can be broadly categorized into four main types: market risk, credit risk, liquidity risk, and interest rate risk. Market risk refers to the potential losses resulting from changes in the overall market, such as a decline in stock prices or a rise in bond yields. Credit risk, on the other hand, arises from the possibility of borrowers defaulting on their debt obligations. Liquidity risk occurs when investors are unable to quickly sell their securities without significantly affecting their prices. Finally, interest rate risk affects the value of bonds, as changes in interest rates can impact their yields and prices. By recognizing these key drivers of investment risk, investors can develop strategies to mitigate potential losses and optimize their returns.
How to Mitigate Risk through Diversification
Diversification is a powerful tool for mitigating investment risk and increasing the potential for consistent returns. By spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, investors can reduce their exposure to the common risk factors that affect returns on stocks and bonds. This strategy is based on the principle that different investments perform differently in various market conditions, thereby reducing the overall risk of the portfolio. For instance, a portfolio that combines stocks and bonds can reduce the impact of market risk, as bonds tend to perform better during market downturns. Similarly, investing in different industries and sectors can minimize the impact of company-specific risks. By diversifying their investments, investors can create a more stable and resilient portfolio that is better equipped to navigate the complexities of the market. This, in turn, can lead to more consistent returns and a reduced risk of significant losses.
The Impact of Economic Indicators on Investment Returns
Economic indicators play a crucial role in shaping the performance of stocks and bonds. Understanding the relationship between these indicators and investment returns is essential for making informed investment decisions. Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation, and unemployment rates are three key economic indicators that have a significant impact on the returns on stocks and bonds. A growing GDP, for instance, can boost stock prices as companies’ revenues and profits increase. On the other hand, high inflation can lead to higher interest rates, which can negatively affect bond prices. Unemployment rates, meanwhile, can influence consumer spending and confidence, which can in turn affect stock prices. By analyzing these economic indicators, investors can gain valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and make more informed investment decisions. This, in turn, can help mitigate the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds, such as market risk and interest rate risk, and increase the potential for consistent returns.
Company-Specific Risks: Understanding the Role of Management and Industry
Company-specific risks are a critical component of the common risk factors that affect returns on stocks and bonds. These risks are unique to individual companies and can have a significant impact on investment returns. Management quality, for instance, plays a crucial role in shaping a company’s performance. A strong and experienced management team can make informed decisions that drive growth and profitability, while a weak management team can lead to poor decision-making and declining stock prices. Industry trends are another important factor to consider. Companies operating in growing industries tend to perform better than those in declining industries. Additionally, the competitive landscape of an industry can also affect a company’s performance. Companies with a strong competitive advantage tend to perform better than those with weak competitive positions. By understanding these company-specific risks, investors can make more informed investment decisions and mitigate the impact of these risks on their returns. This, in turn, can help reduce the overall risk of their investment portfolio and increase the potential for consistent returns.
Market Sentiment and Its Influence on Investment Decisions
Market sentiment plays a significant role in driving investment decisions, and understanding its impact is crucial for mitigating the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds. Fear, greed, and herd behavior are three key emotions that can influence investor decisions. When investors are fearful, they may sell their stocks and bonds at low prices, leading to a decline in market values. On the other hand, when investors are greedy, they may buy stocks and bonds at high prices, leading to a surge in market values. Herd behavior, where investors follow the crowd, can also lead to market volatility. By understanding market sentiment, investors can avoid making emotional decisions and instead focus on making informed investment decisions based on fundamental analysis. This can help reduce the impact of market sentiment on investment returns and increase the potential for consistent returns. Additionally, investors can use market sentiment to their advantage by buying undervalued stocks and bonds during periods of fear and selling overvalued ones during periods of greed. By doing so, investors can increase their returns and reduce their exposure to the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds.
Long-Term Investing: A Strategy for Consistent Returns
A long-term investment strategy is essential for mitigating the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds. By adopting a long-term approach, investors can reduce the impact of short-term market volatility and focus on achieving their financial goals. One key benefit of long-term investing is dollar-cost averaging, which involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of the market’s performance. This strategy helps reduce the impact of market timing and can lead to lower average costs over time. Regular portfolio rebalancing is another important aspect of long-term investing. By periodically reviewing and adjusting their investment portfolio, investors can ensure that it remains aligned with their risk tolerance and financial goals. This can help reduce the risk of overexposure to a particular asset class or industry. Tax-efficient investing is also crucial for long-term investors. By minimizing tax liabilities, investors can increase their returns and achieve their financial goals more quickly. By adopting a long-term investment strategy, investors can increase their potential for consistent returns and reduce their exposure to the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds. This, in turn, can help investors achieve their financial goals and build wealth over time.
Monitoring and Adjusting Your Investment Portfolio
Regularly reviewing and adjusting an investment portfolio is crucial for ensuring that it remains aligned with an investor’s risk tolerance and financial goals. This process involves monitoring the performance of individual stocks and bonds, as well as the overall portfolio, to identify any deviations from the target asset allocation. By doing so, investors can mitigate the common risk factors in the returns on stocks and bonds and increase their potential for consistent returns. One key tip is to set a regular review schedule, such as quarterly or annually, to assess the portfolio’s performance and make adjustments as needed. Another important aspect is to rebalance the portfolio by selling assets that have become overvalued and buying those that have become undervalued. This can help maintain an optimal asset allocation and reduce the risk of overexposure to a particular asset class or industry. Additionally, investors should consider tax implications when making adjustments to their portfolio, aiming to minimize tax liabilities and maximize returns. By regularly monitoring and adjusting their investment portfolio, investors can increase their confidence in their investment decisions and achieve their long-term financial goals.