The Power of Diversification in Investment
Diversification is a cornerstone of investment strategy, allowing investors to mitigate risk and increase potential returns. By spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies, investors can reduce their exposure to any one particular market or sector, thereby minimizing risk. This approach is rooted in the concept that as diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, making it an essential component of any investment strategy. In essence, diversification enables investors to create a portfolio that is greater than the sum of its parts, where the whole is more resilient and stable than the individual components. By adopting a diversified approach, investors can navigate the complexities of the market with greater confidence, positioning themselves for long-term success.
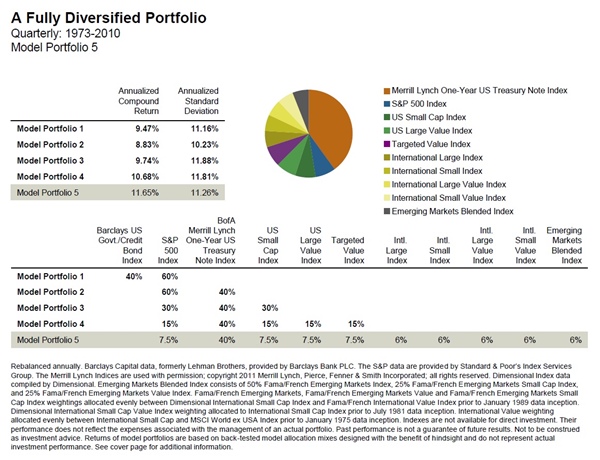
As Diversification Increases, Portfolio Volatility Decreases
Academic research and real-world examples consistently demonstrate that diversification leads to a reduction in portfolio volatility. This is because a diversified portfolio is less susceptible to market fluctuations, as the performance of one asset is offset by the performance of another. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. For instance, a study by Vanguard found that a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds reduced volatility by up to 40% compared to a portfolio invested solely in stocks. Similarly, a diversified portfolio of international and domestic stocks can reduce exposure to country-specific risks, leading to a more stable performance. By spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors, investors can create a portfolio that is more resilient to market shocks, ultimately reducing portfolio volatility and increasing potential returns.
How to Build a Diversified Portfolio that Minimizes Risk
Building a diversified portfolio that minimizes risk requires a thoughtful and strategic approach. One key step is to allocate assets effectively, dividing investments across different classes such as stocks, bonds, and alternatives. This helps to reduce exposure to any one market or sector, thereby minimizing risk. Sector rotation is another important strategy, involving the periodic rebalancing of the portfolio to maintain an optimal mix of sectors and industries. Security selection is also critical, as it involves choosing individual stocks or bonds that are likely to perform well over the long term. Additionally, investors should consider diversifying across different geographic regions, such as developed and emerging markets, to further reduce risk. By following these principles, investors can create a diversified portfolio that is well-positioned to achieve long-term success. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. By taking a proactive and informed approach to portfolio construction, investors can minimize risk and maximize potential returns.
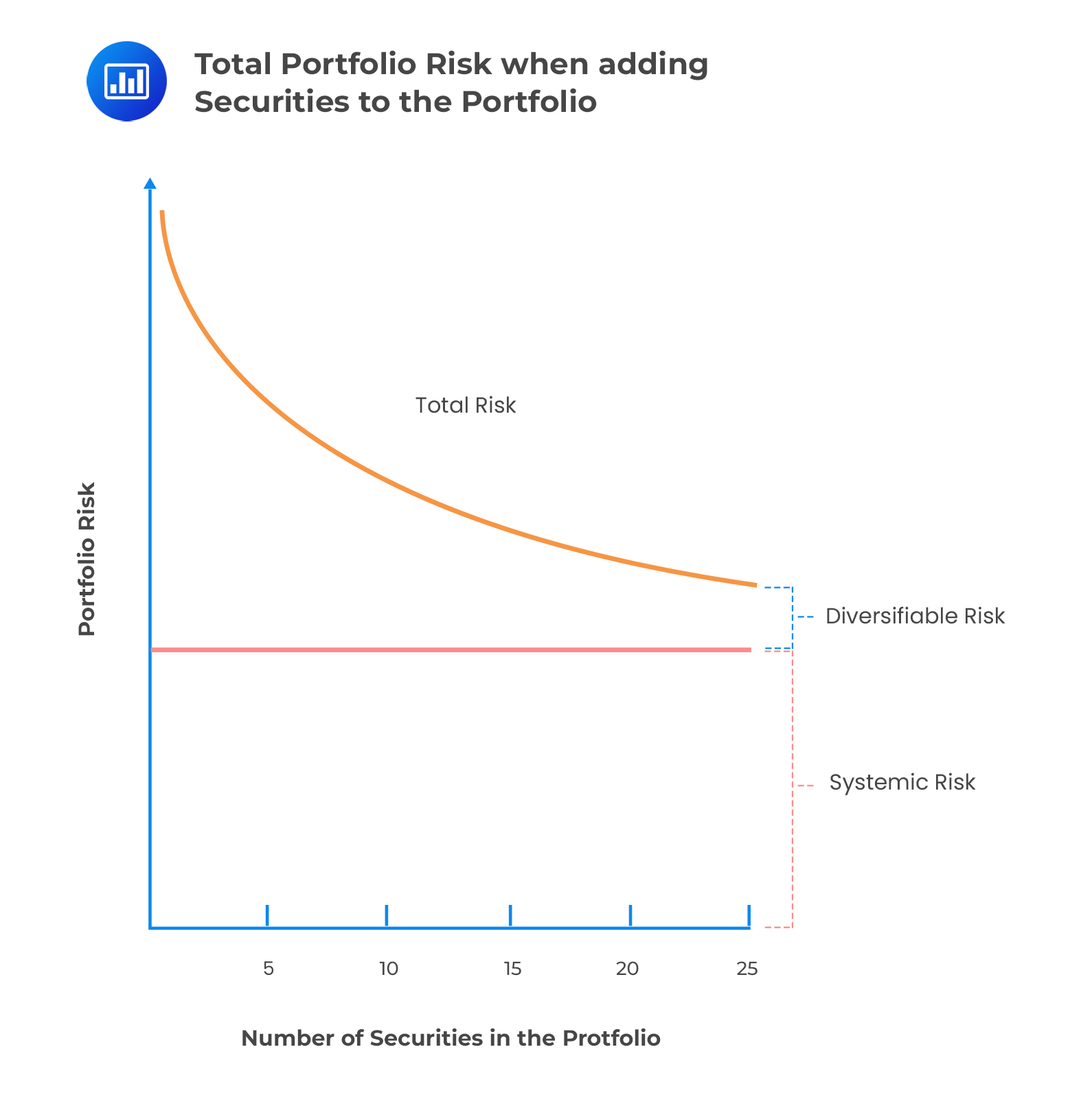
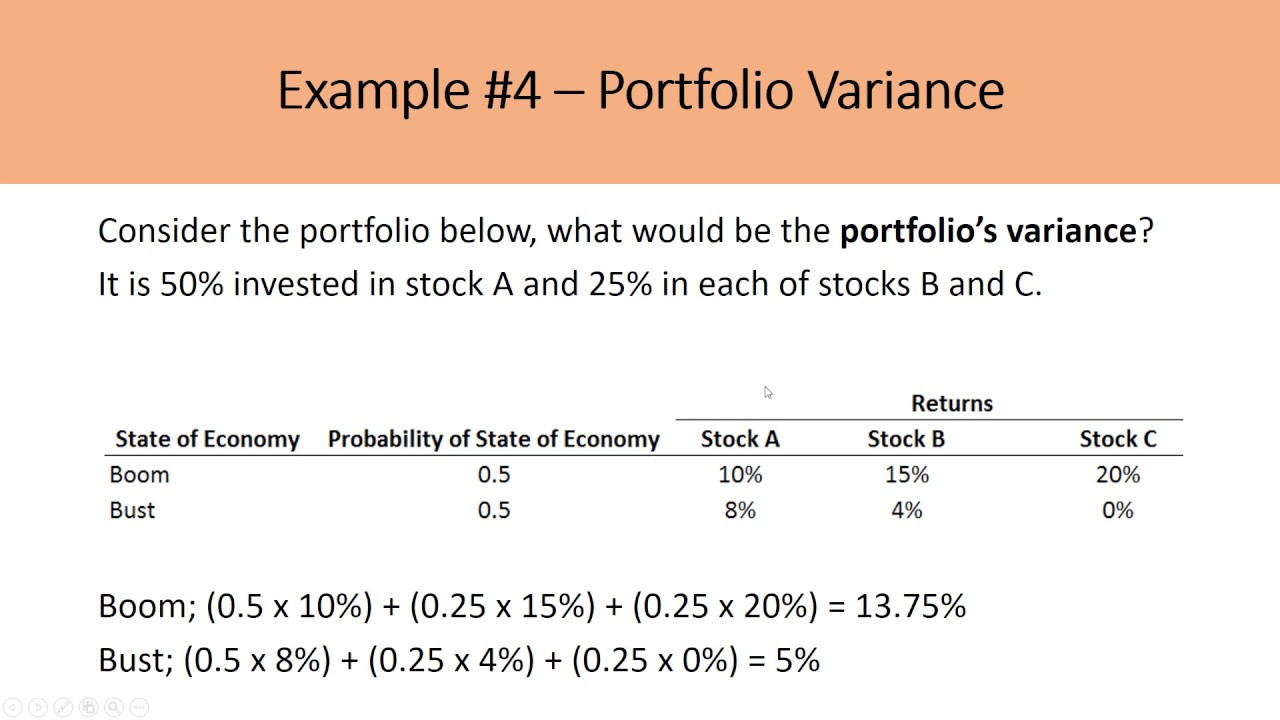
The Relationship Between Diversification and Portfolio Variance
At its core, diversification is a mathematical concept that relies on the principles of probability theory. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. This is because the returns of individual assets are not perfectly correlated, meaning that they do not move in perfect sync with one another. By combining assets with low correlation, investors can reduce the overall risk of their portfolio, as the gains of one asset can offset the losses of another. Mathematically, this can be expressed as the portfolio variance formula: σp² = ∑(wi²σi²) + 2∑∑(wiwjσij), where σp² is the portfolio variance, wi is the weight of asset i, σi² is the variance of asset i, and σij is the covariance between assets i and j. By minimizing the portfolio variance, investors can create a more stable and consistent portfolio that is better positioned to achieve long-term success. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. This mathematical relationship is the foundation of diversification, and it is the key to building a portfolio that minimizes risk and maximizes potential returns.
Why a Diversified Portfolio is Essential for Long-Term Success
A diversified portfolio is essential for long-term investment success, as it provides a foundation for stable and consistent returns. By reducing risk through diversification, investors can increase their potential for long-term success, as they are better positioned to weather market fluctuations and economic downturns. This is because a diversified portfolio is less reliant on any one asset or sector, reducing the impact of market volatility on overall performance. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. Furthermore, a diversified portfolio provides investors with the opportunity to capitalize on growth opportunities across different asset classes and sectors, increasing their potential for long-term returns. By adopting a diversified investment approach, investors can create a portfolio that is well-positioned to achieve their long-term investment goals, while minimizing the risk of significant losses. In essence, a diversified portfolio is a key component of a successful long-term investment strategy, providing investors with the stability and consistency they need to achieve their financial objectives.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Diversifying Your Portfolio
While diversification is a powerful tool for reducing risk and increasing potential returns, it’s not without its pitfalls. Investors must be aware of common mistakes that can undermine the effectiveness of their diversification strategy. One common mistake is over-diversification, where investors spread their portfolio too thin, resulting in a lack of focus and increased transaction costs. Another mistake is a lack of rebalancing, where investors fail to periodically review and adjust their portfolio to ensure it remains aligned with their investment objectives. This can lead to a drift in the portfolio’s risk profile, undermining its ability to achieve long-term success. Additionally, investors may fail to consider the correlation between assets, leading to a portfolio that is not as diversified as they think. By avoiding these common mistakes, investors can ensure that their diversification strategy is effective in reducing risk and increasing potential returns. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. By being mindful of these common mistakes, investors can create a diversified portfolio that is well-positioned to achieve their long-term investment goals.
The Role of Correlation in Portfolio Diversification
Correlation plays a crucial role in portfolio diversification, as it measures the degree to which two or more assets move in tandem. When building a diversified portfolio, it’s essential to select assets with low correlation, as this helps to reduce overall portfolio risk. Assets with high correlation tend to move together, increasing the portfolio’s exposure to market fluctuations. On the other hand, assets with low correlation can help to offset each other’s movements, resulting in a more stable portfolio. For example, a portfolio that combines stocks and bonds can benefit from the low correlation between these two asset classes, reducing overall portfolio volatility. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. By selecting assets with low correlation, investors can create a diversified portfolio that is better equipped to navigate market uncertainty and achieve long-term success. Furthermore, correlation analysis can also help investors to identify potential risks and opportunities within their portfolio, enabling them to make more informed investment decisions.
Putting it All Together: A Real-World Example of Diversification in Action
Let’s consider a real-world example of a diversified portfolio to illustrate how the concepts discussed in this article can be applied in practice. Suppose we have an investor with a $100,000 portfolio, seeking to balance risk and potential returns. The investor decides to allocate 40% to stocks, 30% to bonds, and 30% to alternative investments, such as real estate and commodities. Within the stock allocation, the investor selects a mix of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks from various sectors, including technology, healthcare, and finance. The bond allocation includes a mix of government and corporate bonds with varying maturities. The alternative investment allocation includes a real estate investment trust (REIT) and a commodity index fund. By diversifying across asset classes, sectors, and securities, the investor has created a portfolio that is well-positioned to reduce risk and increase potential returns. As diversification increases, the total variance of a portfolio approaches a lower level, resulting in a more stable and consistent performance. This example demonstrates how a diversified portfolio can be tailored to an investor’s specific goals and risk tolerance, providing a powerful tool for achieving long-term investment success.