What is Maturity Risk Premium and Why Does it Matter?
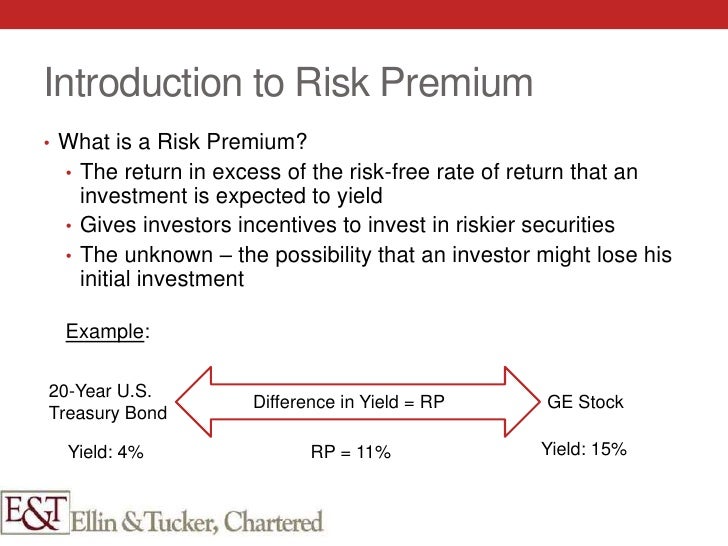
In the world of finance, maturity risk premium is a crucial concept that plays a significant role in investment decisions. It refers to the additional return investors demand for tying up their capital in a long-term investment. This premium is a critical component of the overall return on investment, as it compensates investors for taking on the risk of uncertainty associated with long-term investments. The formula for maturity risk premium is essential in calculating this premium, and understanding its significance is vital for investors seeking to maximize their returns. By grasping the concept of maturity risk premium, investors can make informed decisions about their investments and optimize their portfolios.
Understanding the Components of Maturity Risk Premium
The maturity risk premium is a complex concept that comprises several components, each contributing to the overall premium. The four primary components are the risk-free rate, credit risk premium, liquidity premium, and term premium. The risk-free rate represents the return on a risk-free investment, such as a U.S. Treasury bond. The credit risk premium accounts for the likelihood of default by the borrower, while the liquidity premium reflects the ease with which an investment can be bought or sold. The term premium, on the other hand, is the compensation for tying up capital in a long-term investment. Understanding each of these components is crucial in calculating the formula for maturity risk premium, as it enables investors to make informed decisions about their investments. By breaking down the components of maturity risk premium, investors can better appreciate the intricacies of this critical concept and optimize their investment strategies accordingly.
How to Calculate Maturity Risk Premium: A Step-by-Step Guide
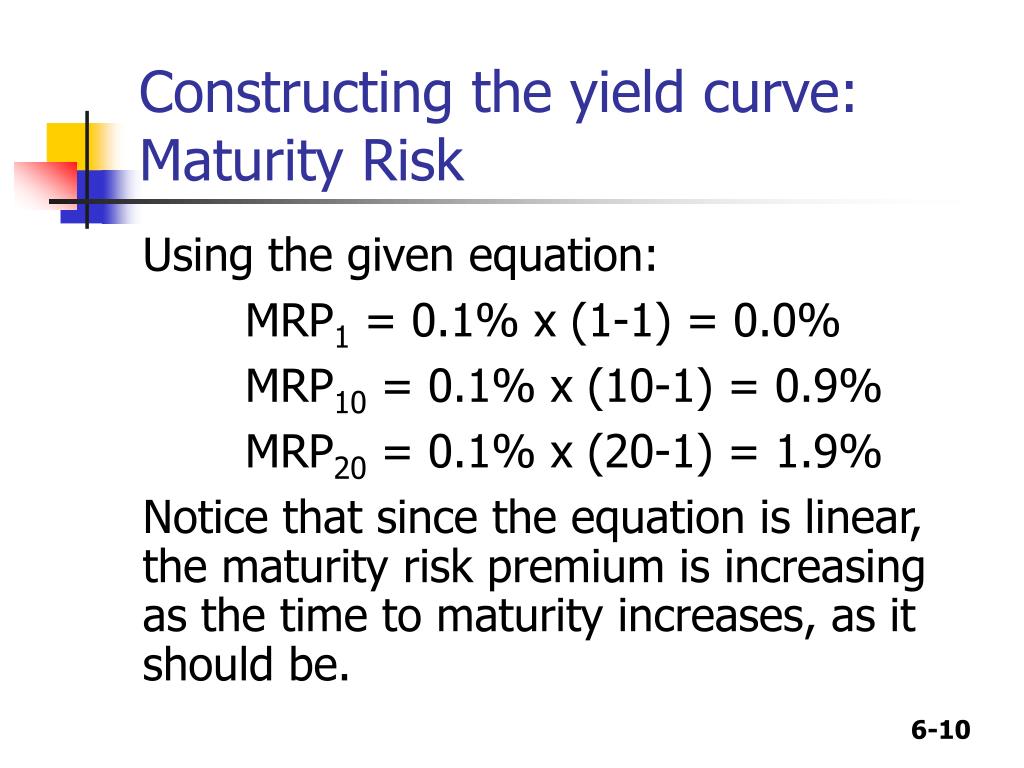
Calculating the maturity risk premium is a crucial step in investment decision-making. The formula for maturity risk premium is a complex equation that takes into account various factors, including the risk-free rate, credit risk premium, liquidity premium, and term premium. To calculate the maturity risk premium, follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the risk-free rate, which is typically represented by the yield on a long-term government bond.
Step 2: Calculate the credit risk premium, which is the additional return required to compensate for the borrower’s credit risk.
Step 3: Determine the liquidity premium, which reflects the ease with which an investment can be bought or sold.
Step 4: Calculate the term premium, which is the compensation for tying up capital in a long-term investment.
Step 5: Combine the components to calculate the overall maturity risk premium using the formula for maturity risk premium.
For example, let’s say the risk-free rate is 2%, the credit risk premium is 1%, the liquidity premium is 0.5%, and the term premium is 1.5%. Using the formula for maturity risk premium, the overall maturity risk premium would be 5%. This means that investors would require a 5% return above the risk-free rate to invest in a long-term bond with a certain level of credit risk and liquidity.
By following these steps and using the formula for maturity risk premium, investors can accurately calculate the maturity risk premium and make informed investment decisions.
The Role of Time to Maturity in Maturity Risk Premium
Time to maturity plays a critical role in calculating the maturity risk premium. The length of time to maturity affects the risk premium, as investors require a higher return for tying up their capital for an extended period. The formula for maturity risk premium takes into account the time to maturity, as it is a key factor in determining the overall risk premium.
A longer time to maturity typically results in a higher maturity risk premium, as investors face a greater degree of uncertainty and risk. This is because the likelihood of default, changes in interest rates, and other market fluctuations increases over time. Conversely, a shorter time to maturity typically results in a lower maturity risk premium, as the risk of default and market fluctuations is lower.
For example, a 10-year bond typically carries a higher maturity risk premium than a 5-year bond, as investors are exposed to a greater degree of risk over the longer time period. To adjust for this, investors can use the formula for maturity risk premium to calculate the required return for the bond, taking into account the time to maturity.
In addition, the shape of the yield curve also plays a role in determining the maturity risk premium. A steepening yield curve, where long-term rates are higher than short-term rates, indicates a higher maturity risk premium, as investors require a higher return for tying up their capital for an extended period. Conversely, a flattening yield curve, where long-term rates are lower than short-term rates, indicates a lower maturity risk premium.
By understanding the role of time to maturity in maturity risk premium, investors can make more informed investment decisions and adjust their calculations to reflect the unique characteristics of each investment opportunity.
Real-World Applications of Maturity Risk Premium Formula
The formula for maturity risk premium has numerous real-world applications in finance, including bond pricing, portfolio management, and risk assessment. By understanding how to calculate the maturity risk premium, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
In bond pricing, the formula for maturity risk premium is used to determine the required return on a bond. This takes into account the credit risk premium, liquidity premium, and term premium, allowing investors to accurately price bonds and make informed investment decisions. For example, a bond with a higher credit risk premium will require a higher return to compensate for the increased risk of default.
In portfolio management, the formula for maturity risk premium is used to optimize portfolio returns and minimize risk. By calculating the maturity risk premium for each asset in the portfolio, investors can identify areas of high risk and adjust their portfolio accordingly. This can help to reduce overall portfolio risk and increase returns.
In risk assessment, the formula for maturity risk premium is used to evaluate the risk of different investments. By calculating the maturity risk premium, investors can identify investments with high levels of risk and adjust their investment decisions accordingly. This can help to minimize losses and maximize returns.
For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, investors who understood the formula for maturity risk premium were better equipped to navigate the complex and volatile market conditions. By accurately pricing bonds and assessing risk, they were able to make more informed investment decisions and minimize losses.
In conclusion, the formula for maturity risk premium is a powerful tool that has numerous real-world applications in finance. By understanding how to calculate the maturity risk premium, investors can make more informed investment decisions, optimize their portfolios, and minimize risk.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Maturity Risk Premium
When calculating the maturity risk premium, investors often make common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results and poor investment decisions. By understanding these mistakes, investors can avoid them and ensure that their calculations are accurate and reliable.
One common mistake is ignoring credit risk premium. Credit risk premium is a critical component of the maturity risk premium, and ignoring it can lead to underestimating the risk of default. Investors should always include credit risk premium in their calculations to ensure that they are accurately pricing bonds and assessing risk.
Another common mistake is neglecting liquidity premium. Liquidity premium is the compensation investors require for holding illiquid assets, and ignoring it can lead to underestimating the risk of holding such assets. Investors should always consider liquidity premium when calculating the maturity risk premium.
Additionally, investors often fail to adjust the formula for maturity risk premium to reflect changing market conditions. For example, during economic downturns, investors may need to adjust the credit risk premium to reflect the increased risk of default. By failing to adjust the formula, investors may underestimate the risk of their investments.
Furthermore, investors may use incorrect or outdated data when calculating the maturity risk premium. This can lead to inaccurate results and poor investment decisions. Investors should always use reliable and up-to-date data when calculating the maturity risk premium.
To avoid these mistakes, investors should carefully follow the formula for maturity risk premium and ensure that they are including all relevant components. They should also stay up-to-date with changing market conditions and adjust their calculations accordingly. By doing so, investors can ensure that their calculations are accurate and reliable, and make informed investment decisions.
By understanding the common mistakes to avoid when calculating the maturity risk premium, investors can ensure that they are accurately pricing bonds, assessing risk, and making informed investment decisions. The formula for maturity risk premium is a powerful tool, and by using it correctly, investors can optimize their portfolios and achieve their investment goals.
Maturity Risk Premium in Different Market Conditions
The formula for maturity risk premium is not a one-size-fits-all solution. In fact, the maturity risk premium behaves differently in various market conditions, and investors need to adjust their calculations accordingly. Understanding how the maturity risk premium responds to changing market conditions is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
During economic downturns, the maturity risk premium tends to increase as investors become more risk-averse. This means that investors require a higher return to compensate for the increased risk of default. In such scenarios, investors should adjust the credit risk premium and term premium components of the formula to reflect the higher risk environment.
On the other hand, during periods of high inflation, the maturity risk premium may decrease as investors become more focused on returns that keep pace with inflation. In such scenarios, investors should adjust the risk-free rate component of the formula to reflect the higher inflation environment.
In addition, changes in monetary policy can also impact the maturity risk premium. For example, during periods of quantitative easing, the maturity risk premium may decrease as investors become more optimistic about the economy. In such scenarios, investors should adjust the liquidity premium component of the formula to reflect the increased liquidity in the market.
By understanding how the maturity risk premium behaves in different market conditions, investors can adjust their calculations to reflect the changing risk environment. This can help investors make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios. The formula for maturity risk premium is a powerful tool, and by using it correctly, investors can navigate different market conditions with confidence.
Ultimately, the key to successfully using the formula for maturity risk premium is to stay flexible and adapt to changing market conditions. By doing so, investors can ensure that their calculations are accurate and reliable, and make informed investment decisions that drive long-term success.
Conclusion: Mastering the Formula for Maturity Risk Premium
In conclusion, the formula for maturity risk premium is a powerful tool that investors can use to make informed investment decisions. By understanding the components of maturity risk premium, including the risk-free rate, credit risk premium, liquidity premium, and term premium, investors can accurately calculate the risk premium and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Moreover, by grasping the impact of time to maturity on maturity risk premium and understanding how to adjust the formula for different market conditions, investors can optimize their portfolios and achieve their investment goals. It is essential to avoid common mistakes, such as ignoring credit risk or liquidity premiums, and to stay up-to-date with changing market conditions.
The formula for maturity risk premium is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and investors need to adapt it to their specific investment needs and market conditions. By mastering the formula for maturity risk premium, investors can gain a competitive edge in the market and make informed investment decisions that drive long-term success.
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing financial landscape, understanding the formula for maturity risk premium is crucial for investors who want to stay ahead of the curve. By incorporating this powerful tool into their investment strategies, investors can navigate complex market conditions with confidence and achieve their investment goals.
Ultimately, the key to successful investing lies in understanding the intricacies of the formula for maturity risk premium and applying it effectively in real-world scenarios. By doing so, investors can unlock the secrets of risk premium calculation and achieve long-term success in the world of finance.