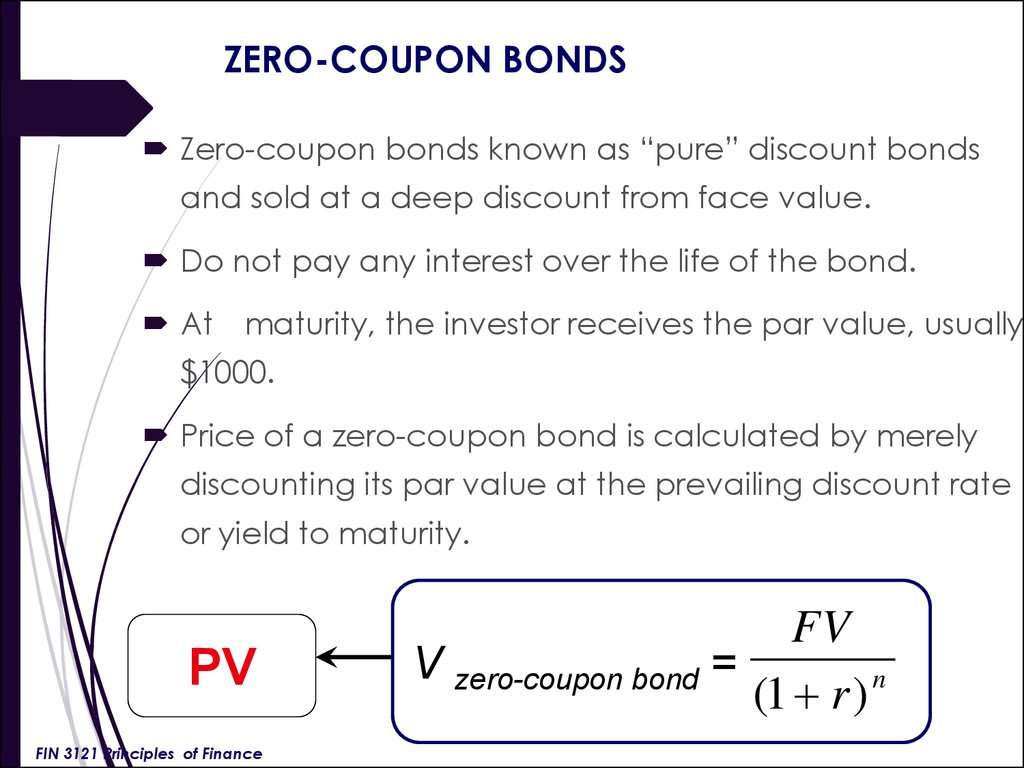
What is a Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curve?
In the realm of bond investing, the zero coupon bond yield curve is a vital tool that provides valuable insights into the bond market. It is a graphical representation of the relationship between the yield of a zero coupon bond and its maturity. Unlike traditional yield curves, which are based on coupon-bearing bonds, zero coupon bond yield curves reflect the yields of bonds that do not make regular interest payments. This distinction is significant, as it allows investors to isolate the effect of time on bond yields, unaffected by coupon payments.
The zero coupon bond yield curve is essential in bond investing, as it enables investors to assess the term structure of interest rates, identify opportunities for profit, and manage risk. By analyzing the curve, investors can determine the market’s expectations of future interest rates, identify undervalued or overvalued bonds, and adjust their portfolios accordingly. In essence, the zero coupon bond yield curve is a powerful tool for investors seeking to optimize their returns and minimize their risk in the bond market.
How to Interpret the Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curve
Interpreting the zero coupon bond yield curve is a crucial step in unlocking its secrets and making informed investment decisions. The curve provides a visual representation of the relationship between the yield of a zero coupon bond and its maturity, allowing investors to identify patterns and trends that can inform their investment strategies.
To read and interpret the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors must understand the relationship between bond prices, yields, and maturities. The curve typically slopes upward, indicating that longer-term bonds offer higher yields to compensate investors for the increased risk of holding the bond for a longer period. However, the curve can also be flat or even inverted, indicating changes in market sentiment and expectations of future interest rates.
By analyzing the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can identify opportunities for profit and manage risk. For example, a steepening curve may indicate that short-term interest rates are expected to rise, making short-term bonds more attractive. Conversely, a flattening curve may suggest that long-term interest rates are expected to fall, making long-term bonds more appealing. By understanding these relationships and trends, investors can make informed decisions about their bond investments and optimize their portfolios.
The Benefits of Zero Coupon Bonds in a Portfolio
Incorporating zero coupon bonds into a portfolio can provide several benefits to investors. One of the primary advantages is the reduction of interest rate risk. Since zero coupon bonds do not make regular interest payments, their prices are more sensitive to changes in interest rates. By including zero coupon bonds in a portfolio, investors can reduce their exposure to interest rate fluctuations, thereby minimizing the risk of losses.
Another benefit of zero coupon bonds is their potential to increase returns. Because they do not make regular interest payments, zero coupon bonds typically offer higher yields than traditional coupon-bearing bonds. This is especially true for longer-term zero coupon bonds, which can provide a higher total return over their lifetime. By including zero coupon bonds in a portfolio, investors can potentially increase their returns and achieve their investment goals.
Zero coupon bonds can also provide a hedge against inflation. Since their prices are more sensitive to changes in interest rates, zero coupon bonds can serve as a natural hedge against inflation. When inflation rises, interest rates tend to increase, causing the prices of zero coupon bonds to decrease. By including zero coupon bonds in a portfolio, investors can reduce their exposure to inflation risk and protect their purchasing power.
Furthermore, zero coupon bonds can be used to match liabilities and assets. For example, a pension fund may use zero coupon bonds to match its long-term liabilities, ensuring that it has sufficient funds to meet its future obligations. By including zero coupon bonds in a portfolio, investors can better manage their cash flows and ensure that they have sufficient funds to meet their financial obligations.
Understanding the Factors that Influence the Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curve
The zero coupon bond yield curve is influenced by a range of factors, including economic indicators, monetary policy, and market sentiment. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors seeking to make informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, play a significant role in shaping the zero coupon bond yield curve. For example, a strong economy with low unemployment and rising inflation may lead to higher interest rates, causing the yield curve to steepen. Conversely, a slowing economy with high unemployment and low inflation may lead to lower interest rates, causing the yield curve to flatten.
Monetary policy, set by central banks, also has a profound impact on the zero coupon bond yield curve. Changes in interest rates, quantitative easing, and forward guidance can all influence the shape and slope of the yield curve. For instance, a central bank may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, causing the yield curve to flatten, or raise interest rates to combat inflation, causing the yield curve to steepen.
Market sentiment, including investor expectations and risk appetite, also plays a crucial role in shaping the zero coupon bond yield curve. For example, if investors are risk-averse and seeking safe-haven assets, they may drive up demand for long-term bonds, causing the yield curve to flatten. Conversely, if investors are seeking higher returns and are willing to take on more risk, they may drive up demand for short-term bonds, causing the yield curve to steepen.
In addition to these factors, the zero coupon bond yield curve can also be influenced by supply and demand imbalances, credit ratings, and regulatory changes. By understanding these factors and their impact on the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
Furthermore, the zero coupon bond yield curve can also be influenced by the term premium, which is the extra return investors demand for holding long-term bonds. The term premium can be affected by a range of factors, including economic uncertainty, inflation expectations, and monetary policy. By understanding the term premium and its impact on the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can better navigate the bond market and make more informed investment decisions.
How to Use the Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curve for Investment Decisions
The zero coupon bond yield curve is a powerful tool for investors seeking to make informed investment decisions. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can identify undervalued or overvalued bonds, optimize their portfolios, and maximize returns.
One way to use the zero coupon bond yield curve is to identify mispricings in the bond market. For example, if the yield curve suggests that a particular bond is undervalued, investors may consider purchasing it to capitalize on the potential upside. Conversely, if the yield curve suggests that a bond is overvalued, investors may consider selling it to avoid potential losses.
Another way to use the zero coupon bond yield curve is to optimize portfolio construction. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can identify the optimal mix of short-term and long-term bonds to achieve their investment objectives. For instance, if the yield curve is steepening, investors may consider shifting their portfolio towards shorter-term bonds to take advantage of the higher yields.
The zero coupon bond yield curve can also be used to identify opportunities for arbitrage. For example, if the yield curve suggests that a particular bond is trading at a premium to its fair value, investors may consider selling the bond and buying a similar bond at a lower price. This can help investors generate profits through arbitrage opportunities.
In addition, the zero coupon bond yield curve can be used to evaluate the performance of bond managers. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can determine whether a bond manager is generating alpha through their investment decisions or simply riding the wave of market trends.
Furthermore, the zero coupon bond yield curve can be used to inform asset allocation decisions. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can determine the optimal allocation of their portfolio between bonds and other asset classes, such as stocks or commodities.
By using the zero coupon bond yield curve in these ways, investors can make more informed investment decisions, optimize their portfolios, and maximize returns. The zero coupon bond yield curve is a powerful tool that can help investors navigate the complexities of the bond market and achieve their investment objectives.
Comparing Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curves Across Different Markets
Zero coupon bond yield curves can vary significantly across different markets, reflecting unique economic conditions, monetary policies, and market sentiments. Comparing zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets can provide valuable insights for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on opportunities.
In the US, the zero coupon bond yield curve is often seen as a benchmark for other markets. The US yield curve is typically upward-sloping, reflecting the country’s strong economy and low unemployment rates. In contrast, the European zero coupon bond yield curve has been flatter in recent years, reflecting the region’s slower economic growth and negative interest rates.
In Asia, the zero coupon bond yield curve can vary significantly across countries. For example, Japan’s yield curve is often downward-sloping, reflecting the country’s low inflation and deflationary concerns. In contrast, China’s yield curve is often steeper, reflecting the country’s rapid economic growth and rising inflation.
Comparing zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets can help investors identify opportunities for arbitrage and diversification. For example, if the US yield curve is steeper than the European yield curve, investors may consider investing in US bonds to capitalize on the higher yields. Similarly, if the Japanese yield curve is flatter than the Chinese yield curve, investors may consider investing in Chinese bonds to capitalize on the higher yields.
Moreover, comparing zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets can provide insights into the relative attractiveness of different markets. For example, if the zero coupon bond yield curve in a particular market is steeper than in other markets, it may indicate that the market is more attractive to investors, reflecting higher growth prospects or lower credit risk.
Furthermore, comparing zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets can help investors identify potential risks and opportunities. For example, if the zero coupon bond yield curve in a particular market is flattening, it may indicate that the market is becoming more vulnerable to interest rate risk, and investors may need to adjust their portfolios accordingly.
In conclusion, comparing zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets is an essential tool for investors seeking to diversify their portfolios and capitalize on opportunities. By analyzing the similarities and differences between zero coupon bond yield curves across different markets, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
The Role of Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curves in Risk Management
Risk management is a critical component of bond investing, and zero coupon bond yield curves play a vital role in this process. By analyzing the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can gain valuable insights into the interest rate risk associated with their bond portfolios.
One of the primary ways that zero coupon bond yield curves contribute to risk management is by helping investors mitigate interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with lower yields decreases, resulting in potential losses for investors. By analyzing the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can identify the bonds that are most sensitive to interest rate changes and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
For example, if the zero coupon bond yield curve is steepening, it may indicate that interest rates are expected to rise in the future. In this scenario, investors may consider reducing their exposure to long-term bonds and shifting their portfolio towards shorter-term bonds with lower durations. This can help to minimize potential losses and optimize returns.
Zero coupon bond yield curves can also help investors optimize their portfolios by identifying opportunities for diversification. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can identify bonds with different maturities and yields that can help to reduce overall portfolio risk. For instance, if the yield curve is flat, investors may consider investing in a mix of short-term and long-term bonds to reduce interest rate risk.
In addition, zero coupon bond yield curves can be used to evaluate the performance of bond managers. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can determine whether a bond manager is generating alpha through their investment decisions or simply riding the wave of market trends. This can help investors to make more informed decisions about their investments and optimize their portfolios.
Furthermore, zero coupon bond yield curves can be used to develop hedging strategies that mitigate interest rate risk. For example, investors can use the yield curve to identify bonds that are most sensitive to interest rate changes and then hedge their exposure using derivatives or other instruments. This can help to reduce potential losses and optimize returns.
In conclusion, zero coupon bond yield curves play a critical role in risk management by helping investors to mitigate interest rate risk, optimize their portfolios, and develop hedging strategies. By analyzing the zero coupon bond yield curve, investors can gain valuable insights into the bond market and make more informed investment decisions.
Real-World Applications of Zero Coupon Bond Yield Curves
In practice, zero coupon bond yield curves are used in a variety of ways to inform investment decisions and manage risk. One common application is in asset liability management, where institutions use zero coupon bond yield curves to manage their asset and liability portfolios.
For example, a pension fund may use a zero coupon bond yield curve to determine the present value of its future liabilities, such as pension payments. By analyzing the yield curve, the fund can identify the bonds that are most suitable for its investment portfolio, taking into account factors such as duration, credit risk, and yield.
In hedge fund strategies, zero coupon bond yield curves are used to identify arbitrage opportunities and optimize returns. By analyzing the yield curve, hedge funds can identify mispricings in the bond market and take advantage of them through various trading strategies.
In addition, zero coupon bond yield curves are used in risk management to quantify and manage interest rate risk. For instance, a bank may use a zero coupon bond yield curve to determine the sensitivity of its bond portfolio to changes in interest rates, and then adjust its portfolio accordingly to minimize potential losses.
Another real-world application of zero coupon bond yield curves is in the valuation of complex financial instruments, such as derivatives and structured products. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can determine the fair value of these instruments and make more informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, zero coupon bond yield curves are used in central banks’ monetary policy decisions. By analyzing the yield curve, central banks can gauge the market’s expectations of future interest rates and inflation, and adjust their monetary policy accordingly.
In the corporate world, zero coupon bond yield curves are used to evaluate the cost of capital and optimize capital structure. By analyzing the yield curve, companies can determine the optimal mix of debt and equity financing, and make more informed decisions about their capital allocation.
In conclusion, zero coupon bond yield curves have a wide range of real-world applications, from asset liability management to hedge fund strategies, risk management, and central banks’ monetary policy decisions. By understanding how to interpret and apply zero coupon bond yield curves, investors and financial professionals can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.