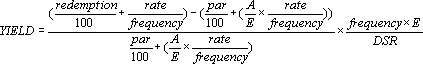Understanding Government Bond Yields: An Introduction
Treasury securities, encompassing T-bills, notes, and bonds, are vital instruments through which the government finances its operations. These securities represent a loan made by investors to the government, which promises to repay the principal along with interest. Investors are drawn to Treasury securities due to their perceived safety and reliability, backed by the full faith and credit of the government. When considering investments in these securities, understanding the concept of “yield” is paramount. Yield, in simple terms, is the return an investor receives on the security. It represents the income earned from the investment, usually expressed as an annual percentage of the amount invested. Accurately determining the yield on treasury securities requires a sophisticated yield on treasury securities calculator that considers market dynamics.
Several types of yields provide different perspectives on the return potential of Treasury securities. The nominal yield is the stated interest rate or coupon rate at the time the bond is issued. The current yield is a more immediate measure, reflecting the bond’s annual income relative to its current market price. A yield on treasury securities calculator can quickly show how yields vary. The yield to maturity (YTM) offers the most comprehensive view, projecting the total return an investor can expect if the bond is held until maturity, taking into account both interest payments and any difference between the purchase price and the face value. A sophisticated yield on treasury securities calculator is essential for those seeking to understand potential returns.
The yield on treasury securities calculator becomes an indispensable tool for investors seeking to make informed decisions in the bond market. While the nominal yield provides a baseline, the current yield and, more importantly, the yield to maturity offer a more realistic assessment of the investment’s potential profitability. Investors use these metrics to compare different Treasury securities, assess their attractiveness relative to other investment options, and gauge the overall health and stability of the government bond market. Understanding these different facets of yield, especially with the help of a yield on treasury securities calculator, is critical for anyone looking to invest in Treasury securities. These calculations become simple with a proper yield on treasury securities calculator.
How to Calculate the Yield of Treasury Securities
Calculating the current yield of a Treasury security offers a quick snapshot of its return. This calculation focuses on the annual income generated relative to its current market price. It’s a straightforward method to gauge immediate income, although it does not reflect the total return if the bond is held to maturity. To determine the current yield, you’ll need three key pieces of information: the current market price of the Treasury security, its coupon rate, and its face value.
The formula for calculating the current yield is simple: (Annual Coupon Payments / Current Market Price) x 100. The annual coupon payment is determined by multiplying the coupon rate by the face value of the Treasury security. For example, consider a Treasury note with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 5%. This note pays $50 annually ($1,000 x 0.05). If the current market price of this note is $950, the current yield would be ($50 / $950) x 100 = 5.26%. This indicates that, based on the current market price, the investor would receive a 5.26% return annually. While this calculation is simple, it’s important to remember that current yield provides only a partial view of the potential return from a Treasury security, and to get a more precise calculation it is recommended to use a yield on treasury securities calculator.
Keep in mind that the current yield doesn’t account for any capital gains or losses that may occur if the Treasury security is held until maturity. Furthermore, it does not consider the time value of money. For a more comprehensive analysis, especially when assessing long-term investments, it’s essential to explore the Yield to Maturity (YTM), which considers these additional factors. Utilizing a yield on treasury securities calculator designed for YTM calculations provides a more accurate assessment of the total return potential. The current yield serves as a preliminary indicator, while YTM offers a more complete picture of a Treasury security’s investment performance and both are usually provided when using a yield on treasury securities calculator.
Exploring Yield to Maturity (YTM) for Treasury Bonds
Yield to Maturity (YTM) represents the total return anticipated on a bond, assuming it is held until maturity. It is a more comprehensive measure than current yield. YTM considers the time value of money. It also accounts for any premium or discount on the bond’s purchase price. For investors seeking a complete picture of potential returns, YTM is an invaluable metric. This metric related to the yield on treasury securities calculator assists the investor to estimate profitability.
Unlike current yield, YTM factors in the difference between the purchase price and the face value of the bond. If a bond is purchased at a discount (below face value), the YTM will be higher than the current yield. This happens because the investor will receive the face value at maturity, which is more than they paid. Conversely, if a bond is purchased at a premium (above face value), the YTM will be lower than the current yield. The investor will receive the face value at maturity, which is less than they paid. Therefore, YTM offers a more accurate representation of the expected return over the bond’s lifetime.
Calculating YTM manually involves a complex formula. This formula takes into account the current market price, face value, coupon rate, and time to maturity. Due to the complexity of this calculation, using a yield on treasury securities calculator is highly recommended. These calculators are readily available online. They provide a quick and accurate YTM calculation, simplifying the investment analysis process. By utilizing such a tool, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments in Treasury securities. Understanding YTM is crucial for investors to accurately assess the potential return and make informed decisions, and the yield on treasury securities calculator is there to help.
Factors Influencing Treasury Security Yields
Several macroeconomic factors exert significant influence on Treasury security yields. These factors interact in complex ways, pushing yields up or down based on prevailing economic conditions. One of the most important factors is inflation. Generally, rising inflation leads to higher Treasury yields, as investors demand a greater return to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, lower inflation often results in lower yields. Interest rate policies enacted by the Federal Reserve (also known as the Fed) also play a crucial role. The Fed’s decisions regarding the federal funds rate directly impact short-term Treasury yields. When the Fed raises rates, yields on Treasury securities typically increase, and vice versa. Economic growth is another key determinant of Treasury yields. Strong economic growth tends to push yields higher, as increased demand for capital leads to higher interest rates. Slower economic growth, or even a recession, often results in lower yields as investors seek safe-haven assets like Treasury securities. Investor sentiment also has a notable impact. During times of economic uncertainty or market volatility, investors often flock to Treasury securities, driving up their prices and pushing yields lower. Conversely, when investors are optimistic about the economy, they may shift their investments to riskier assets, causing Treasury prices to fall and yields to rise. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to use a yield on treasury securities calculator.
The yield curve, which plots the yields of Treasury securities with different maturities, provides valuable insights into the market’s expectations for future economic conditions. A normal yield curve, where longer-term yields are higher than short-term yields, typically indicates a healthy, growing economy. An inverted yield curve, where short-term yields are higher than long-term yields, has historically been a predictor of economic recession. Monitoring the yield curve can help investors anticipate changes in Treasury yields and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. This, in turn, influences decisions when using a yield on treasury securities calculator. The interplay of these macroeconomic forces makes predicting Treasury yields a challenging, but essential, aspect of fixed-income investing.
Keeping abreast of economic news and understanding the Federal Reserve’s policy decisions are paramount for anyone interested in investing in Treasury securities. The yield on treasury securities calculator provides a snapshot, but contextual awareness amplifies its value. Awareness of the forces that shape the yield is key. By understanding how inflation, interest rates, economic growth, and investor sentiment affect Treasury yields, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments and better utilize tools like a yield on treasury securities calculator. This knowledge helps them to assess the potential risks and rewards of investing in government bonds in different market conditions. Also, understanding the effect of such factors allows for strategic choices of investment to consider the time horizon or diversification of investment.
Using Online Bond Calculators to Determine Returns
The task of calculating returns on Treasury securities can seem daunting. Fortunately, a wealth of online tools are available to simplify the process. These online Treasury security yield calculators offer a user-friendly interface. They swiftly determine both the current yield and Yield to Maturity (YTM). Using a Treasury security yield calculator eliminates manual calculations. It reduces the risk of errors and saves valuable time.
These calculators typically request specific inputs. This usually includes the Treasury security’s face value, coupon rate, current market price, and maturity date. The face value represents the amount the investor will receive at maturity. The coupon rate is the annual interest rate paid on the face value. The current market price is the price at which the Treasury security is being traded. The maturity date is the date when the principal is repaid. Once these details are entered, the Treasury security yield calculator instantly computes the relevant yields. Some calculators also provide additional metrics. These might include accrued interest and estimated after-tax returns. A Treasury security yield calculator makes complex bond calculations accessible to everyone.
The advantages of using an online Treasury security yield calculator are numerous. The primary benefit is speed. Manual calculations, especially for YTM, can be time-consuming. They also require a strong understanding of financial mathematics. Accuracy is another crucial advantage. Online calculators use precise algorithms. This eliminates the potential for human error. This is particularly important when making investment decisions. Using a Treasury security yield calculator empowers investors. It gives them the information they need to make informed choices about their investments. A reliable Treasury security yield calculator is an indispensable tool. It’s useful for anyone investing in government bonds. This enhances both efficiency and confidence in investment strategies.
Interpreting Treasury Yield Results: What Does the Data Mean?
Understanding the results from a yield on treasury securities calculator is crucial for informed investment decisions. A higher yield generally suggests a greater return on investment. Conversely, a lower yield indicates a smaller return. However, yield must be considered in the context of the prevailing market conditions. Comparing the yield on treasury securities calculator output to historical averages can provide valuable perspective. For instance, a yield significantly higher than the norm might signal an attractive investment opportunity. Conversely, a yield markedly lower could suggest that the security is overvalued.
It’s important to link the yield back to the inherent risk associated with the investment. A high yield could reflect a higher perceived risk, although government bonds, particularly U.S. Treasury securities, are considered among the safest investments globally. The yield on treasury securities calculator doesn’t directly quantify risk, but the market’s assessment of risk is embedded in the yield. A significant spike in yield might indicate concerns about inflation, economic stability, or government fiscal policy. While the risk of the U.S. government defaulting on its debt is extremely low, a slightly elevated yield compared to other government bonds with similar maturities could be a sign to investigate further.
Consider the current market environment when analyzing the yield on treasury securities calculator results. In a period of rising interest rates, bond yields tend to increase as well. This is because newly issued bonds need to offer higher yields to compete with existing bonds. Conversely, during periods of falling interest rates, bond yields typically decline. Therefore, understanding the broader economic context is essential for accurately interpreting the data. Keep in mind that the yield on treasury securities calculator provides a snapshot in time and that yields can fluctuate based on market conditions. Analyzing trends of yield on treasury securities calculator results is an important element for potential investors seeking insight for a more informed investment strategy. The yield on treasury securities calculator is a tool, but financial understanding turns data into informed choices.
Strategies for Investing in Treasury Securities Based on Yield
Several investment strategies can be implemented based on Treasury yields, aligning with different financial goals and risk tolerances. Treasury securities, with their varying yields, can be strategically utilized for portfolio diversification, income generation, or as a safe haven during periods of economic uncertainty. However, it’s crucial to remember that this information is not financial advice, and consulting with a qualified financial advisor is always recommended before making any investment decisions.
For investors seeking diversification, Treasury securities can provide a counterbalance to riskier assets like stocks. When equity markets decline, investors often flock to the safety of Treasury bonds, potentially driving up their prices and lowering their yields, thus offsetting losses in other parts of the portfolio. Income-seeking investors might focus on Treasury bonds with higher yields, aiming to generate a steady stream of income. The current yield on treasury securities calculator can be a helpful tool in identifying these bonds. It’s important to consider the investor’s time horizon. Short-term investors might prefer Treasury bills, while those with longer time horizons might opt for Treasury notes or bonds. Actively monitoring the yield on treasury securities calculator is crucial for making informed decisions.
Treasury securities can also serve as a safe haven during economic downturns. In times of recession or market volatility, investors often seek the security of government-backed bonds, increasing demand and potentially lowering yields. While lower yields may seem unattractive, the principal protection offered by Treasury securities can be particularly valuable during turbulent times. It’s important to understand that a high yield on a Treasury security, while seemingly attractive, could indicate a higher perceived risk, though the risk of the U.S. government defaulting is extremely low. This is where tools like a yield on treasury securities calculator become invaluable, providing insights into potential returns based on current market conditions. The yield on treasury securities calculator assists in determining potential returns, offering clarity in the market. Carefully consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon before investing in Treasury securities. Utilizing a yield on treasury securities calculator can help in assessing the potential risks and rewards associated with these investments. Keep in mind, a proper evaluation using a yield on treasury securities calculator, complemented by professional advice, is key for strategic investing.
Comparing iBonds and Treasury ETFs: An Overview
Individual Treasury securities, Treasury ETFs, and iBonds each offer unique avenues for investing in government debt. Understanding their differences is crucial for aligning investment choices with financial goals. Individual Treasury securities, like notes and bonds, provide a direct claim on government debt. Investors receive fixed interest payments (coupon rate) and the face value at maturity. A Treasury ETF, on the other hand, is a fund that holds a basket of Treasury securities. The ETF’s price fluctuates based on the underlying securities’ market values. The yield on treasury securities calculator can be useful for estimating potential returns, but keep in mind that ETF returns also depend on fund management and expense ratios.
iBonds are specifically designed to protect against inflation. Their interest rate is a combination of a fixed rate and an inflation rate that adjusts twice a year. This feature makes them attractive during periods of rising inflation. Liquidity also varies significantly across these investment vehicles. Individual Treasury securities can be sold on the secondary market before maturity, but their price may fluctuate. Treasury ETFs are highly liquid. They can be bought and sold throughout the trading day. iBonds are less liquid. They cannot be sold within the first year and have a penalty for early redemption within the first five years.
Expense ratios are another key consideration. Individual Treasury securities have no ongoing expenses, while Treasury ETFs charge expense ratios to cover management costs. These fees, though often small, can impact overall returns over time. Tax implications also differ. Interest earned from individual Treasury securities and Treasury ETFs is subject to federal income tax, but is exempt from state and local taxes. iBonds have the same federal tax advantage. Furthermore, iBond interest is exempt from federal income tax if used for qualified education expenses. When assessing investments, the yield on treasury securities calculator can help project returns. The choice between individual Treasury securities, Treasury ETFs, and iBonds depends on an investor’s risk tolerance, time horizon, and need for liquidity and inflation protection. Understanding these nuances allows for informed decisions and a well-diversified investment portfolio.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/bond-final-f7932c780bc246cbad6c254febe2d0cd.png)