Understanding the Wasting Asset: Option’s Time Component
An option is a contract that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a predetermined price (strike price) on or before a specific date (expiration date). The price of an option, known as the premium, comprises two key components: intrinsic value and extrinsic value. Understanding these components is crucial for anyone involved in options trading. Intrinsic value is the profit an option holder would realize if they exercised the option immediately. Extrinsic value, also known as time value, represents the portion of the option’s premium that exceeds its intrinsic value. In essence, the time value reflects the potential for the option to become more profitable before expiration. Therefore, what is time value of an option? It’s the market’s assessment of the possibility that the option will move into a more profitable position before it expires.
The time value of an option is influenced by several factors, with time to expiration being paramount. As the expiration date approaches, the time value erodes, a phenomenon known as time decay. This decay accelerates as the option nears expiration. Volatility also plays a significant role. Higher volatility generally translates to higher time value, as there’s a greater chance of the underlying asset price moving favorably. Conversely, lower volatility implies lower time value. What is time value of an option also depends on these elements. The interplay between time decay and volatility is a central consideration for options traders.
To further illustrate, consider an example: A call option on a stock trading at $50 with a strike price of $45 has an intrinsic value of $5 ($50 – $45). If the option premium is $7, the time value is $2 ($7 – $5). This $2 represents the market’s expectation that the stock price may rise further before expiration, making the option even more valuable. What is time value of an option in this context? It’s the extra premium investors are willing to pay for the possibility of increased profitability. Options are wasting assets because of this time value decay. Understanding and estimating time value is, therefore, essential for developing informed and effective option trading strategies.
What Contributes to an Option’s Erosion?
An option’s time value decays over time. This decay is a key characteristic of options. Understanding it is vital for successful trading. The rate at which this time value diminishes isn’t constant. It accelerates as the option nears its expiration date. A metric called “theta” measures this rate of decay. Theta indicates how much an option’s price will decrease each day, assuming other factors remain constant.
Several factors influence the pace of this decay. Time to expiration is a primary driver. Options with longer times until expiration possess greater time value. This is because there’s more opportunity for the underlying asset’s price to move favorably. Conversely, options closer to expiration experience faster time value erosion. Volatility also plays a significant role. Higher volatility generally leads to higher time value. This reflects the increased uncertainty and potential for price swings. However, the relationship isn’t always straightforward. High volatility can also accelerate time decay under certain circumstances.
To truly understand what is time value of an option, one must consider how time erodes it. The closer an option gets to its expiration date, the more rapidly its time value declines. This concept is critical for option buyers and sellers alike. Sellers of options, such as in covered call strategies, benefit from this decay. As the option’s time value decreases, the option becomes less expensive to buy back, increasing the seller’s profit. Conversely, option buyers need the underlying asset to move quickly to offset this decay. Understanding theta and the factors influencing it allows traders to make informed decisions. This ultimately leads to better risk management and potentially higher returns in options trading.
The Volatility Connection: How Market Swings Influence Time Value
The relationship between volatility and the time value of an option is crucial for understanding option pricing. Implied volatility, which reflects the market’s expectation of future price swings, directly impacts an option’s premium. Higher implied volatility translates to a greater time value. This occurs because there’s an increased probability of the underlying asset’s price moving significantly in a favorable direction before the option’s expiration date. Therefore, options traders closely monitor implied volatility when assessing the fair price of an option, and what is time value of an option.
To illustrate this point, consider two scenarios involving call options on the same stock, with identical strike prices and expiration dates. In the first scenario, the implied volatility is relatively low, say 20%. Consequently, the option’s time value will also be lower, reflecting the market’s expectation of limited price movement. However, in the second scenario, if the implied volatility surges to 40%, the option’s time value will increase substantially. This reflects the market’s anticipation of potentially large price fluctuations, making the option more valuable to a prospective buyer, who speculates what is time value of an option. The term “Vega” quantifies the sensitivity of an option’s price to changes in implied volatility. A higher Vega indicates that the option’s price will be more responsive to fluctuations in implied volatility.
Understanding the interplay between implied volatility and time value is essential for making informed trading decisions. Options with high implied volatility offer the potential for significant gains if the underlying asset’s price moves favorably. But they also come with a higher premium, reflecting the increased risk and uncertainty. Conversely, options with lower implied volatility are less expensive. However, they may not provide sufficient leverage if the underlying asset’s price does not move as anticipated. Therefore, traders must carefully consider their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and market outlook when evaluating options with different levels of implied volatility, and what is time value of an option represents.
How to Estimate Time Value for Informed Option Strategies
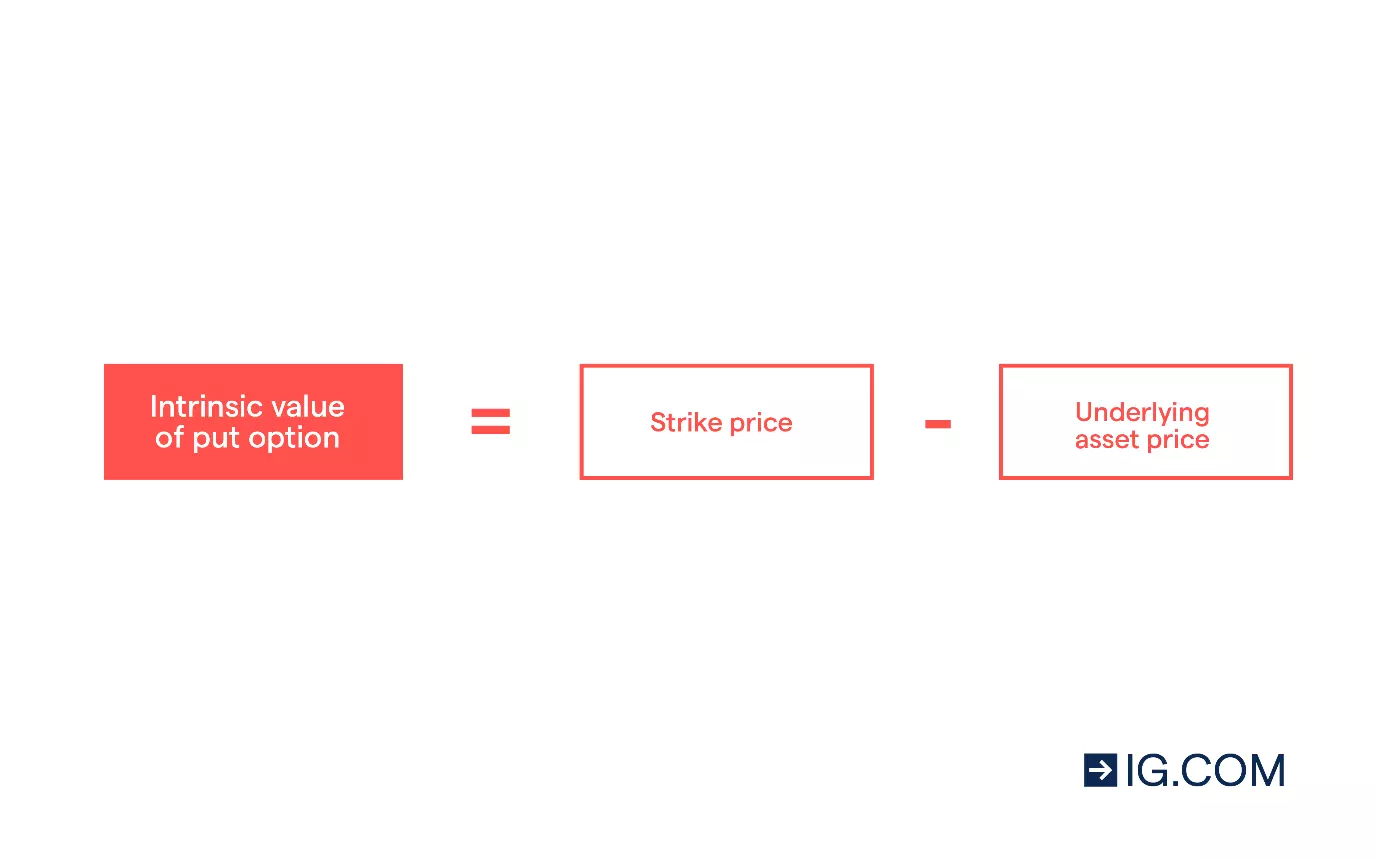
A practical method for estimating what is time value of an option involves subtracting the intrinsic value from the option’s premium. The intrinsic value is the difference between the underlying asset’s price and the option’s strike price, if that difference favors the option holder. If the option is out-of-the-money, meaning it would not be profitable to exercise it immediately, its intrinsic value is zero. The formula for estimating what is time value of an option is: Time Value = Option Premium – Intrinsic Value. This calculation provides an *estimation*, not a precise determination of what is time value of an option.
For example, consider a call option with a premium of $5 on a stock trading at $55, with a strike price of $50. The intrinsic value of this option is $5 ($55 – $50). Therefore, the estimated what is time value of an option is $0 ($5 – $5). Now, consider a call option with a premium of $3 on a stock trading at $48, with a strike price of $50. The intrinsic value of this option is $0 because the option is out-of-the-money. In this case, the estimated what is time value of an option is $3 ($3 – $0). This highlights that even out-of-the-money options have time value, reflecting the possibility of the stock price moving above the strike price before expiration. The estimation is based on current market conditions and doesn’t guarantee future outcomes.
It’s crucial to remember that this is a simplified approach. More sophisticated models, like the Black-Scholes model, consider additional factors such as volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates to provide a more precise valuation. However, understanding this basic calculation allows traders to quickly assess the time value component of an option’s price. This quick assessment assists in evaluating whether an option is overpriced or underpriced relative to its intrinsic value and potential for future price movement. By understanding what is time value of an option, traders can make more informed decisions when buying or selling options, understanding the potential for time decay to impact their profitability. It’s essential to consider what is time value of an option in the construction and management of various options trading strategies.
Decoding Time Decay: Understanding the Option Expiration Curve
The concept of an “expiration curve,” also known as a “time decay curve,” is crucial for understanding how an option’s time value diminishes. What is time value of an option? It represents the portion of an option’s premium that reflects the potential for future price movement in the underlying asset. This time value doesn’t decay linearly; instead, the rate of decay accelerates significantly as the option approaches its expiration date.
Imagine a graph where the x-axis represents time until expiration and the y-axis represents the option’s time value. The curve would start relatively flat, indicating a slow rate of decay when the option has a considerable amount of time remaining. However, as the expiration date nears, the curve becomes much steeper, showing a rapid decline in time value. This accelerated decay is due to the diminishing probability of a significant price change in the underlying asset before expiration. The closer to expiration, the less opportunity there is for the option to move into the money. What is time value of an option affected by? Time decay is often represented by “theta,” a Greek letter that quantifies the expected decrease in an option’s value for each day that passes. As expiration looms, the absolute value of theta increases, reflecting the faster rate of decay.
This non-linear decay has significant implications for different option strategies. For example, sellers of options, such as in a covered call strategy or short put strategy, benefit from this accelerated time decay, especially close to expiration. Their goal is often for the option to expire worthless, allowing them to keep the premium received. Conversely, buyers of options face the challenge of time decay eroding their investment, necessitating a substantial and timely move in the underlying asset’s price to offset this decay. Choosing between longer-dated versus shorter-dated options requires a careful consideration of the effects of time decay. Longer-dated options have a higher initial time value but decay more slowly at first, while shorter-dated options have less time value but decay much faster as expiration approaches. Understanding the expiration curve and its impact on time value is essential for making informed decisions in option trading strategies. What is time value of an option and its curve are important concepts to learn to master options trading.
Real-World Examples: Applying Time Value in Option Trading
Time value profoundly impacts various option trading strategies. Consider a covered call writer, an investor who owns shares of a stock and sells call options on those shares. This strategy benefits directly from the decay of the option’s time value. As time passes and the option nears expiration, its time value decreases, allowing the covered call writer to keep the premium received from selling the option, provided the stock price remains below the option’s strike price. The gradual erosion of the option’s time value is the source of profit in this scenario. This showcases how understanding what is time value of an option is key for selecting profitable strategies.
Conversely, option buyers face the challenge of time decay. For a call or put option buyer to profit, the underlying asset’s price must move significantly and swiftly in the anticipated direction to offset the diminishing time value. If the price movement is insufficient or occurs too slowly, the option’s time value will erode to the point where the option becomes worthless at expiration. It’s crucial for option buyers to assess the potential for rapid price appreciation or depreciation and choose options with expiration dates that provide adequate time for the anticipated move to materialize, keeping in mind what is time value of an option.
The choice between longer-dated and shorter-dated options also hinges on an understanding of time value. Longer-dated options possess higher time value due to the extended period during which the underlying asset price can fluctuate. These options are more expensive but offer greater potential for profit if the anticipated price movement occurs. Shorter-dated options are cheaper but experience more rapid time decay. While the initial outlay is lower, the underlying asset must move quickly and decisively to generate a profit before the time value diminishes substantially. Evaluating what is time value of an option, its rate of decay, and the underlying asset’s volatility is a key to choosing the most suitable option contract. For instance, options on SPY, AAPL, and TSLA show different time value changes due to the different nature of the underlying assets.
Beyond Black-Scholes: The Nuances of Time Value Pricing Models
While understanding what is time value of an option, it’s crucial to acknowledge the models used for valuation. The Black-Scholes model is a popular tool. However, numerous other models exist that can offer greater precision. These alternative models incorporate various factors. They may include interest rates, dividend yields, and volatility skews. Using these models can refine the estimation of what is time value of an option represents in different market conditions.
The key to accuracy lies in the parameters used. Models such as Black-Scholes require accurate inputs. Interest rates, asset prices, and volatility expectations are vital. Furthermore, certain models have unique, model-specific parameters. The accuracy of these parameters directly impacts the calculated time value. Inaccurate inputs will lead to a skewed representation of what is time value of an option. Therefore, carefully selecting and validating the inputs is essential when using pricing models.
It’s also important to remember that models provide an *estimation*, not a precise calculation. Market dynamics are complex and ever-changing. No model can perfectly predict future price movements. The theoretical what is time value of an option can be calculated with these models but is often different than the real price. Factors like supply and demand can influence the options price. Understanding the limitations of models is crucial. It helps traders make informed decisions about what is time value of an option and its influence on their trading strategies.
Managing Time Value in Popular Options Contracts: SPY, AAPL, and TSLA
Understanding what is time value of an option is crucial when trading options on popular assets like SPY (S&P 500 ETF), AAPL (Apple), and TSLA (Tesla). The characteristics of time value can differ significantly based on the underlying asset’s volatility, trading volume, and market sentiment. Each of these factors impacts the option’s premium and, consequently, its decay rate as expiration approaches. Therefore, traders need to analyze these differences to make informed trading decisions.
For example, options on a volatile stock such as TSLA typically exhibit higher time value compared to options on a more stable index like SPY. This is because TSLA’s price can swing dramatically, increasing the potential for the option to move in the money before expiration. This increased potential directly translates into a higher premium paid for the option, reflecting the uncertainty and opportunity. Options on AAPL, while generally less volatile than TSLA, also possess a substantial time value component, driven by the company’s significant market capitalization and regular news events. Investors should carefully consider what is time value of an option when trading these assets.
Furthermore, the trading volume of an option also influences its time value. Options with higher trading volume tend to have tighter bid-ask spreads, making it easier to enter and exit positions. However, high volume can also lead to faster time decay, especially as expiration nears. The time value is influenced by investor sentiments on what is time value of an option, which also impacts the implied volatility. Options traders must consider what is time value of an option and balance the potential for profit with the risk of time decay, adjusting their strategies based on the specific characteristics of each underlying asset. Examining the implied volatility of SPY, AAPL and TSLA can shed light on what is time value of an option.