What is an Overnight Index Swap?
In the realm of financial markets, an overnight index swap (OIS) is a type of financial derivative that plays a crucial role in managing risk and hedging against interest rate fluctuations. Essentially, an OIS is a contract between two parties that involves the exchange of fixed and floating interest payments based on a notional amount. The floating leg of the swap is typically tied to a benchmark rate, such as the federal funds effective rate or the euro overnight index average (EONIA), which reflects the overnight lending rate between banks.
The primary purpose of an OIS is to enable financial institutions to hedge against potential losses or gains arising from changes in interest rates. By entering into an OIS contract, parties can effectively lock in a fixed interest rate, thereby mitigating the risks associated with floating interest rates. This is particularly useful for banks, corporations, and other financial entities that need to manage their exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
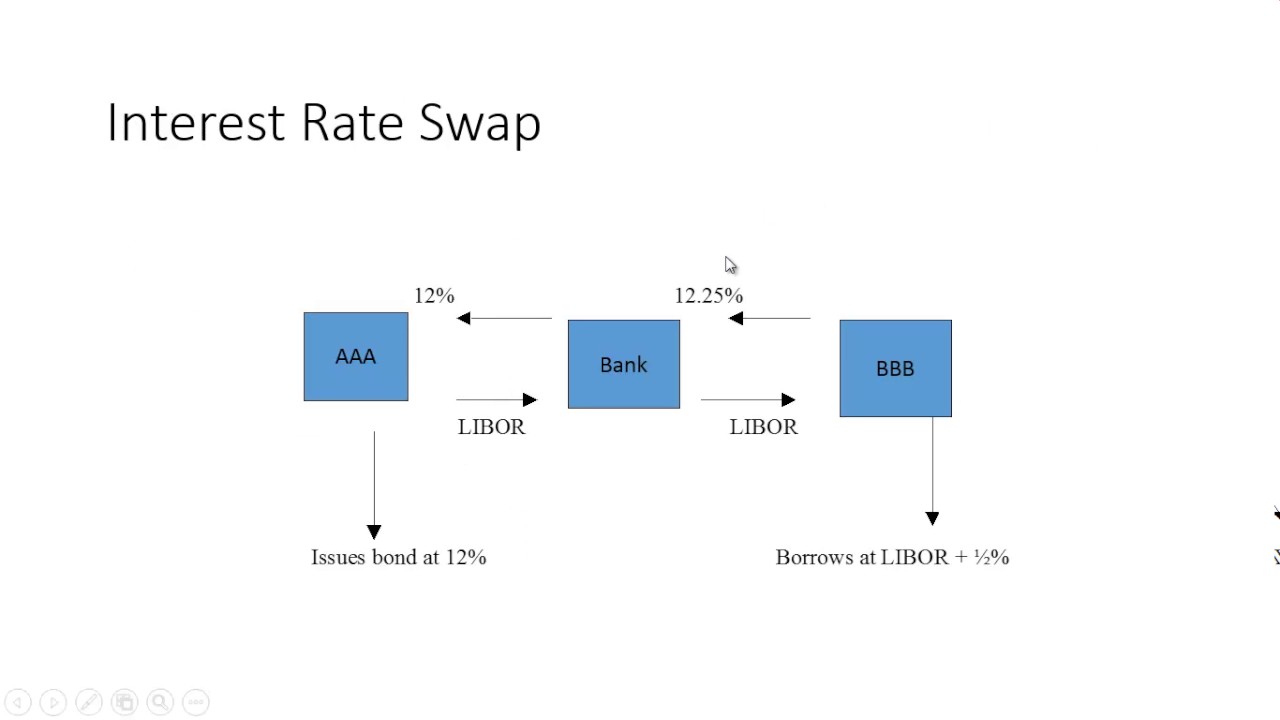
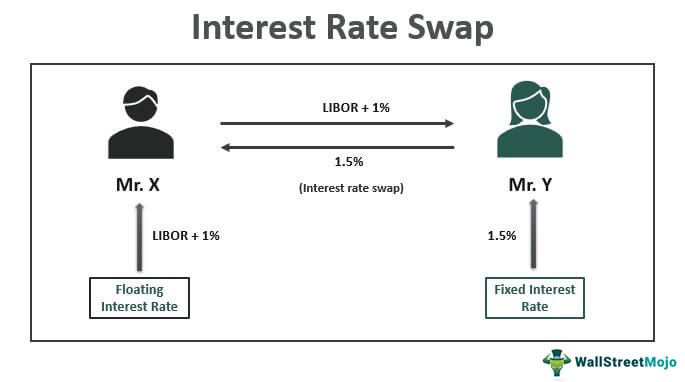
It’s essential to distinguish OIS from other financial instruments, such as forward rate agreements (FRAs) and interest rate swaps (IRS). While these instruments share some similarities with OIS, they differ in terms of their underlying mechanisms and applications. For instance, FRAs are used to hedge against specific interest rate risks, whereas OIS provides a more comprehensive hedging solution.
In the context of financial markets, understanding what is the overnight index swap rate is vital for making informed investment decisions. The OIS rate serves as a benchmark for pricing and valuing various financial instruments, including bonds, derivatives, and other securities. As such, it has a profound impact on the overall functioning of financial markets and the economy as a whole.
How to Calculate Overnight Index Swap Rates
Calculating overnight index swap (OIS) rates is a crucial step in understanding the intricacies of financial markets. The OIS rate is a benchmark rate that reflects the average interest rate at which banks lend and borrow money from each other overnight. To calculate the OIS rate, market participants use a combination of mathematical formulas and variables.
The most common method for calculating OIS rates involves the use of a weighted average of the interest rates offered by a panel of banks. This panel typically consists of a group of major banks that provide quotes for overnight lending rates. The weighted average is calculated by multiplying each bank’s quote by its corresponding weight, which is usually based on the bank’s market share or creditworthiness.
The formula for calculating the OIS rate can be expressed as follows:
OIS Rate = (Σ [Bank Quote x Weight]) / Σ Weight
Where:
Bank Quote = the interest rate quoted by each bank on the panel
Weight = the weight assigned to each bank based on its market share or creditworthiness
Σ = the summation symbol, indicating the sum of the products
The accuracy of OIS rate calculations is
The Role of Central Banks in Shaping Overnight Index Swap Rates
Central banks play a pivotal role in shaping overnight index swap (OIS) rates, which have a profound impact on the overall economy. The monetary policy decisions made by central banks have a direct influence on OIS rates, which in turn affect the interest rates offered by banks to their customers. As a result, understanding the relationship between central banks and OIS rates is crucial for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers.
Central banks use various tools to implement their monetary policy, including setting interest rates, buying or selling government securities, and regulating the money supply. These actions have a ripple effect on the entire economy, influencing the borrowing costs, inflation rates, and employment levels. In the context of OIS rates, central banks’ decisions have a direct impact on the overnight lending rates between banks, which in turn affect the OIS rate.
The OIS rate reflects market expectations of future interest rates, which are heavily influenced by central banks’ monetary policy decisions. When central banks raise interest rates to combat inflation or curb economic growth, the OIS rate also increases, indicating higher borrowing costs for banks and their customers. Conversely, when central banks lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, the OIS rate decreases, making borrowing cheaper and more accessible.
The influence of central banks on OIS rates is not limited to their monetary policy decisions. Central banks also play a crucial role in maintaining financial stability, regulating the banking system, and providing liquidity to the market. These actions have a direct impact on the OIS rate, which is sensitive to changes in market conditions and liquidity.
In recent years, central banks have become more proactive in shaping OIS rates, using unconventional monetary policies such as quantitative easing and forward guidance to influence market expectations. These policies have had a significant impact on OIS rates, which have become increasingly important for investors and financial institutions seeking to hedge against interest rate risks.
In conclusion, central banks play a vital role in shaping OIS rates, which are a critical component of the financial system. Understanding the relationship between central banks and OIS rates is essential for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
Overnight Index Swap Rates vs. LIBOR: What’s the Difference?
In the realm of financial markets, two benchmark rates have garnered significant attention: Overnight Index Swap (OIS) rates and LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate). While both rates are used to gauge the cost of borrowing, they differ in their underlying mechanisms, applications, and characteristics. Understanding the distinctions between OIS rates and LIBOR is crucial for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
LIBOR, established in 1986, is a benchmark rate that reflects the average interest rate at which major banks lend to each other in the London interbank market. LIBOR is calculated based on submissions from a panel of banks, which provide their estimated borrowing costs. In contrast, OIS rates are based on the overnight lending rates between banks, which are influenced by central banks’ monetary policy decisions.
One key difference between OIS rates and LIBOR lies in their tenor structure. LIBOR is available in various maturities, ranging from overnight to 12 months, whereas OIS rates are typically overnight rates. This distinction has significant implications for risk management and hedging strategies, as OIS rates are more sensitive to short-term interest rate fluctuations.
OIS rates have gained popularity in recent years due to their perceived accuracy and reliability. Unlike LIBOR, which has been plagued by manipulation scandals and liquidity concerns, OIS rates are considered more robust and less susceptible to manipulation. Additionally, OIS rates are more closely tied to central banks’ monetary policy decisions, making them a more effective tool for gauging market expectations of future interest rates.
Despite these differences, both OIS rates and LIBOR play important roles in financial markets. LIBOR remains a widely used benchmark rate, particularly in the context of floating-rate loans and derivatives. OIS rates, on the other hand, are increasingly used in risk management and hedging strategies, as well as in the pricing of overnight index swaps and other financial instruments.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between OIS rates and LIBOR is essential for navigating the complexities of financial markets. While both rates have their advantages and limitations, OIS rates are gaining popularity due to their perceived accuracy and reliability. As financial markets continue to evolve, the role of OIS rates and LIBOR will likely continue to shift, with OIS rates becoming an increasingly important benchmark rate for investors and financial institutions.
The Impact of Overnight Index Swap Rates on Financial Markets
The Overnight Index Swap (OIS) rate has a profound impact on various financial markets, influencing investment decisions, portfolio management, and risk assessment. As a benchmark rate, OIS rates reflect market expectations of future interest rates, making them a crucial component of financial markets.
In the bond market, OIS rates affect the pricing and valuation of fixed-income securities. When OIS rates rise, bond yields increase, making borrowing more expensive and reducing the attractiveness of bonds. Conversely, when OIS rates fall, bond yields decrease, making borrowing cheaper and increasing the appeal of bonds. This, in turn, affects the overall demand and supply of bonds, influencing their prices and yields.
In the derivatives market, OIS rates play a critical role in the pricing and valuation of interest rate swaps, options, and futures. As OIS rates change, the value of these derivatives instruments also changes, affecting the profitability of hedging strategies and speculation. This, in turn, influences the overall demand and supply of derivatives, impacting their prices and volatility.
In the currency market, OIS rates influence exchange rates and currency valuations. When OIS rates rise in a particular country, its currency tends to appreciate, making exports more expensive and imports cheaper. Conversely, when OIS rates fall, the currency tends to depreciate, making exports cheaper and imports more expensive. This, in turn, affects the overall trade balance and economic growth of a country.
Changes in OIS rates also impact investment decisions and portfolio management. When OIS rates rise, investors may shift their investments from fixed-income securities to equities or other asset classes, seeking higher returns. Conversely, when OIS rates fall, investors may shift their investments from equities to fixed-income securities, seeking safer returns. This, in turn, affects the overall asset allocation and risk profile of investment portfolios.
In conclusion, OIS rates have a far-reaching impact on various financial markets, influencing investment decisions, portfolio management, and risk assessment. As a benchmark rate, OIS rates reflect market expectations of future interest rates, making them a crucial component of financial markets. Understanding the impact of OIS rates on financial markets is essential for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
Real-World Applications of Overnight Index Swap Rates
Overnight Index Swap (OIS) rates have numerous real-world applications in various financial markets, including hedging, speculation, and risk management. Understanding how OIS rates are used in practice is essential for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
In hedging strategies, OIS rates are used to mitigate interest rate risks associated with floating-rate loans, bonds, and derivatives. For instance, a company with a floating-rate loan can enter into an OIS to fix its interest rate costs, thereby reducing its exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Similarly, investors can use OIS rates to hedge against potential losses in their bond portfolios.
In speculation, OIS rates are used to bet on future interest rate movements. For example, a trader who expects interest rates to rise may enter into an OIS to benefit from the expected increase in rates. Conversely, a trader who expects interest rates to fall may enter into an OIS to benefit from the expected decrease in rates.
In risk management, OIS rates are used to assess and manage interest rate risks associated with financial instruments. For instance, a bank can use OIS rates to estimate the potential losses or gains associated with its loan portfolio, thereby enabling it to manage its risk exposure more effectively.
The benefits of incorporating OIS rates into investment strategies are numerous. OIS rates provide a more accurate reflection of market expectations of future interest rates, enabling investors to make more informed investment decisions. Additionally, OIS rates offer a more robust and reliable benchmark rate compared to LIBOR, which has been plagued by manipulation scandals and liquidity concerns.
Incorporating OIS rates into investment strategies can also enhance portfolio performance and reduce risk. By using OIS rates to hedge against interest rate risks, investors can reduce their exposure to potential losses and increase their returns. Furthermore, OIS rates can be used to identify potential investment opportunities, such as arbitrage opportunities between different financial markets.
In conclusion, OIS rates have numerous real-world applications in various financial markets, including hedging, speculation, and risk management. Understanding how OIS rates are used in practice is essential for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets. By incorporating OIS rates into investment strategies, investors can enhance portfolio performance, reduce risk, and make more informed investment decisions.
Challenges and Limitations of Overnight Index Swap Rates
While Overnight Index Swap (OIS) rates have become a widely accepted benchmark rate, they are not without their challenges and limitations. Understanding these drawbacks is essential for investors, financial institutions, and policymakers seeking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.
One of the primary challenges facing OIS rates is market volatility. During times of high market stress, OIS rates can become volatile, making it difficult to accurately price and value financial instruments. This volatility can lead to liquidity issues, where market participants are unable to buy or sell financial instruments at fair prices.
Another limitation of OIS rates is the potential for regulatory challenges. As OIS rates become increasingly popular, regulatory bodies may impose stricter regulations on their use, potentially limiting their availability and increasing their costs. This could lead to a decrease in their adoption and a shift towards alternative benchmark rates.
Liquidity issues are also a significant challenge facing OIS rates. During times of low market liquidity, OIS rates may not accurately reflect market expectations of future interest rates, leading to potential mispricing and misvaluation of financial instruments. This can have significant implications for investors and financial institutions, potentially leading to losses and decreased profitability.
Furthermore, OIS rates are not immune to manipulation and gaming. As with any financial instrument, there is a risk that market participants may attempt to manipulate OIS rates for their own benefit, potentially leading to inaccurate and unreliable rates.
Despite these challenges and limitations, OIS rates remain a widely accepted and widely used benchmark rate. By understanding these drawbacks, investors, financial institutions, and policymakers can better navigate the complexities of financial markets and make more informed investment decisions.
In addition, addressing these challenges and limitations can help to improve the accuracy and reliability of OIS rates, potentially leading to more efficient and effective financial markets. This, in turn, can have positive implications for economic growth and stability.
Ultimately, the challenges and limitations of OIS rates highlight the need for continued innovation and development in the field of financial benchmark rates. By addressing these challenges and limitations, we can create more robust and reliable benchmark rates, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective financial markets.
The Future of Overnight Index Swap Rates: Trends and Predictions
The Overnight Index Swap (OIS) rate has become a widely accepted benchmark rate in financial markets, and its future looks promising. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, OIS rates are likely to play an increasingly important role in shaping investment decisions and portfolio management.
One emerging trend in the future of OIS rates is the increasing adoption of alternative benchmark rates. With the decline of LIBOR, OIS rates are becoming the go-to benchmark rate for many financial institutions. This trend is likely to continue, with OIS rates becoming even more widely used in the coming years.
Another trend that is likely to shape the future of OIS rates is the increasing use of technology in financial markets. The rise of fintech and digital platforms is likely to lead to more efficient and accurate calculations of OIS rates, making them even more reliable and trustworthy.
In terms of regulatory frameworks, there are likely to be changes in the coming years that will impact the use of OIS rates. For example, the introduction of new benchmark rates, such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), may lead to a shift away from OIS rates. However, it is likely that OIS rates will continue to play an important role in financial markets, even as new benchmark rates emerge.
Despite these trends and predictions, there are still challenges that need to be addressed in the future of OIS rates. For example, the potential for market volatility and liquidity issues remains a concern, and regulatory challenges may impact the accuracy and reliability of OIS rates.
However, by understanding these trends and predictions, investors, financial institutions, and policymakers can better prepare for the future of OIS rates. By staying ahead of the curve, they can make more informed investment decisions and navigate the complexities of financial markets with confidence.
In the end, the future of OIS rates looks bright, with increasing adoption, technological advancements, and regulatory changes all contributing to their continued importance in financial markets. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, OIS rates are likely to remain a key benchmark rate, shaping investment decisions and portfolio management for years to come.
What is the overnight index swap rate? It is a benchmark rate that is likely to continue playing a vital role in financial markets, and understanding its future trends and predictions is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of financial markets.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_final_Currency_Swap_vs_Interest_Rate_Swap_Whats_the_Difference_Jan_2021-01-d0d9bf99a16c467daeab2fd073b67051.jpg)


/122574802-5bfc2b8d46e0fb0026016ef5.jpg)