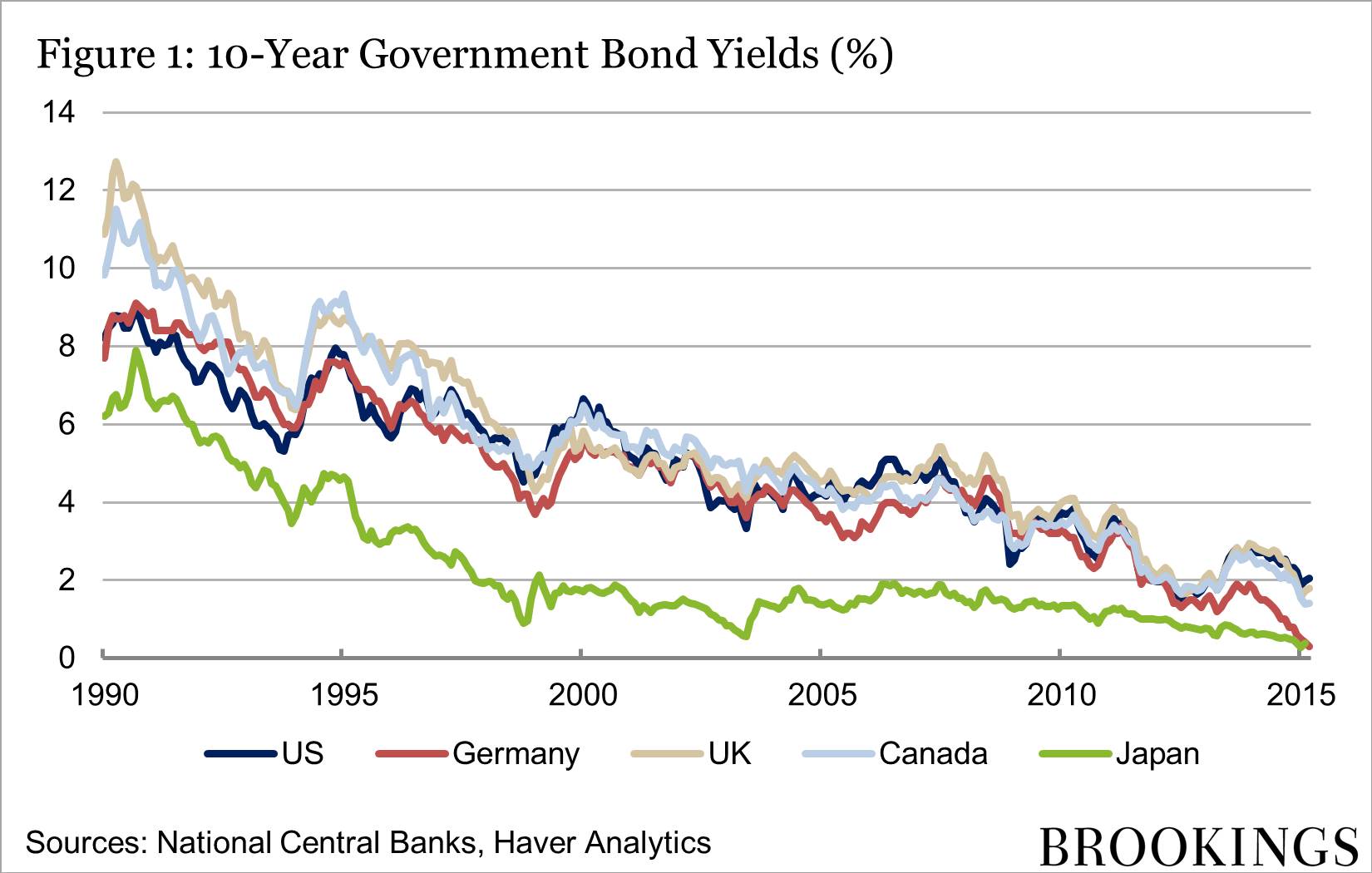
Understanding the Concept of Term Premiums
In the insurance industry, term premiums play a crucial role in determining the cost of coverage. A term premium is the amount of money paid to an insurance company in exchange for a specific period of coverage. This premium is typically calculated based on a variety of factors, including the policyholder’s age, health, and lifestyle. When asking “what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium,” it’s essential to understand that this specific term premium refers to a unique type of coverage that spans 10 years, with a 3-month premium payment period. Term premiums are an essential component of insurance policies, as they help policyholders manage risk and ensure financial protection in the event of unforeseen circumstances.
Deciphering the 10-Year to 3-Month Term Premium Puzzle
The 10-year to 3-month term premium is a unique type of coverage that offers policyholders a specific period of protection. But what makes this term premium so special? To answer the question “what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium,” it’s essential to delve into its characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. One of the primary advantages of this term premium is its flexibility, allowing policyholders to adjust their premium payments to suit their financial situation. For instance, the 3-month premium payment period provides a shorter commitment period, making it an attractive option for those who want to test the waters before committing to a longer term.
However, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons of this term premium. One of the significant drawbacks is the potential for higher premiums compared to shorter-term policies. Additionally, the 10-year term may not be suitable for everyone, particularly those with changing financial circumstances or uncertain futures. Despite these limitations, the 10-year to 3-month term premium remains a popular choice for many policyholders, offering a balance between flexibility and long-term protection.
How to Calculate Term Premiums: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating term premiums can seem like a daunting task, but with a clear understanding of the factors involved, it’s a manageable process. To determine the cost of a term premium, insurance providers consider several key factors, including the policyholder’s age, health, and lifestyle. Additionally, the term length and premium payment period, such as the 10-year to 3-month term premium, also play a significant role in determining the premium rate.
When calculating term premiums, it’s essential to consider the following steps:
1. Determine the term length: The longer the term, the higher the premium rate. For instance, a 10-year term premium will typically be more expensive than a 5-year term premium.
2. Assess the premium payment period: The frequency and duration of premium payments can impact the overall cost of the policy. In the case of the 10-year to 3-month term premium, the shorter premium payment period can result in lower premiums.
3. Evaluate the policyholder’s risk profile: Insurance providers assess the policyholder’s risk profile, including their age, health, and lifestyle, to determine the likelihood of a claim being made.
4. Use online calculators: Many insurance providers offer online calculators that can help policyholders estimate their term premium rates. These calculators take into account the factors mentioned above and provide a personalized quote.
By following these steps, policyholders can gain a better understanding of how term premiums are calculated and make informed decisions when selecting an insurance policy. Remember, understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how it’s calculated can help you navigate the complex world of term premiums.
The Impact of Term Length on Premium Rates
When it comes to term premiums, one of the most significant factors influencing premium rates is the term length. The length of the term can have a profound impact on the cost of the policy, and understanding this relationship is crucial for making informed insurance decisions. In general, longer terms result in higher premiums, while shorter terms lead to lower premiums.
For instance, a 10-year term premium will typically be more expensive than a 5-year term premium. This is because the insurance provider is committing to provide coverage for a longer period, which increases the risk of a claim being made. Conversely, a shorter term premium, such as the 10-year to 3-month term premium, may offer lower premiums due to the shorter commitment period.
However, it’s essential to consider the trade-offs between term length and premium rates. While a shorter term may offer lower premiums, it may also provide less comprehensive coverage or require more frequent premium payments. On the other hand, a longer term may offer more extensive coverage, but at a higher cost.
When evaluating term premiums, it’s crucial to weigh the pros and cons of different term lengths and premium rates. By understanding the impact of term length on premium rates, policyholders can make informed decisions about their insurance coverage and ensure they’re getting the best value for their money. Remember, understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how term length affects premium rates can help you navigate the complex world of term premiums.
Comparing Term Premiums: What to Look for in an Insurance Policy
When comparing term premiums from different insurance providers, it’s essential to evaluate the coverage options and policy features to ensure you’re getting the best value for your money. Understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how it compares to other term premiums can help you make an informed decision.
Here are some key factors to consider when comparing term premiums:
1. Premium rates: Compare the premium rates offered by different insurance providers to ensure you’re getting the best deal. Keep in mind that lower premiums may not always be the best option, as they may come with reduced coverage or more restrictive policy terms.
2. Coverage options: Evaluate the coverage options offered by each insurance provider, including the term length, premium payment period, and death benefit. Consider your specific needs and ensure the policy provides adequate coverage.
3. Policy features: Look for policies that offer additional features, such as convertibility, renewability, or riders, which can enhance the overall value of the policy.
4. Insurer reputation: Research the insurance provider’s reputation, financial stability, and customer service to ensure you’re working with a reliable and trustworthy partner.
5. Policy flexibility: Consider policies that offer flexibility in terms of premium payments, term length, or coverage options, which can be beneficial in case your circumstances change.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can compare term premiums from different insurance providers and make an informed decision about your insurance coverage. Remember, understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how to compare term premiums can help you navigate the complex world of term premiums and make the best choice for your needs.
The Role of Interest Rates in Term Premiums
Interest rates play a significant role in determining term premiums, and understanding their impact is crucial for making informed insurance decisions. When interest rates rise, the cost of borrowing increases, which can affect the premium rates offered by insurance providers. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the cost of borrowing decreases, leading to potentially lower premium rates.
In the context of term premiums, changes in interest rates can have a ripple effect on policyholders. For instance, if interest rates rise, insurance providers may increase premium rates to maintain their profit margins. This can result in higher premiums for policyholders, particularly those with longer term lengths. On the other hand, if interest rates fall, insurance providers may lower premium rates, making term premiums more affordable for policyholders.
It’s essential to consider the impact of interest rates when evaluating term premiums, particularly when comparing policies from different insurance providers. Understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how interest rates affect premium rates can help policyholders make informed decisions about their insurance coverage.
For example, if interest rates are rising, a policyholder may want to consider a shorter term length to avoid higher premium rates. Conversely, if interest rates are falling, a policyholder may want to consider a longer term length to take advantage of potentially lower premium rates.
In conclusion, interest rates play a critical role in determining term premiums, and understanding their impact is vital for making informed insurance decisions. By considering the role of interest rates in term premiums, policyholders can navigate the complex world of term premiums and make the best choices for their needs.
Real-World Examples of Term Premiums in Action
Term premiums are not just theoretical concepts; they have real-world applications that can benefit individuals and businesses alike. Here are some examples of term premiums in action, highlighting their benefits and uses:
Example 1: Family Protection
A 35-year-old married couple with two young children wants to ensure their family’s financial security in the event of their death. They purchase a 10-year term life insurance policy with a 3-month term premium, which provides a death benefit of $500,000. The policy’s term premium is $50 per month, which is affordable and fits their budget. In the event of their death, the policy’s death benefit will help their family maintain their lifestyle and cover funeral expenses.
Example 2: Business Protection
A business owner wants to protect their business from financial loss in the event of their death. They purchase a key person insurance policy with a 10-year term premium, which provides a death benefit of $1 million. The policy’s term premium is $100 per month, which is a small price to pay for the financial security it provides. In the event of their death, the policy’s death benefit will help the business cover the costs of finding and training a replacement, ensuring business continuity.
Example 3: Mortgage Protection
A homeowner wants to ensure their mortgage is paid off in the event of their death. They purchase a mortgage life insurance policy with a 10-year term premium, which provides a death benefit equal to the outstanding mortgage balance. The policy’s term premium is $30 per month, which is a small price to pay for the peace of mind it provides. In the event of their death, the policy’s death benefit will help their family pay off the mortgage, ensuring they can keep their home.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and benefits of term premiums in different scenarios. Understanding what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium and how it can be used in real-world situations can help individuals and businesses make informed insurance decisions.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of Term Premiums
In conclusion, understanding term premiums is crucial for making informed insurance decisions. By grasping the concept of term premiums, including what is the 10 year to 3 month term premium, individuals and businesses can navigate the complex world of insurance with confidence.
This comprehensive guide has provided a detailed overview of term premiums, including their unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks. From calculating term premiums to understanding the impact of interest rates, this article has covered it all.
By applying the knowledge gained from this article, readers can make informed decisions about their insurance coverage, ensuring they get the best possible rates and coverage options. Whether it’s protecting loved ones, businesses, or mortgages, term premiums offer a flexible and affordable solution.
Remember, understanding term premiums is key to unlocking the secrets of the insurance industry. By staying informed and educated, individuals and businesses can make the most of their insurance investments and secure their financial futures.
In the world of insurance, knowledge is power. By grasping the intricacies of term premiums, readers can take control of their insurance decisions and make informed choices that benefit them in the long run.