What is an Overnight Index Swap and How Does it Work?
When it comes to managing interest rate risks, overnight index swaps (OIS) are a crucial tool in the financial markets. But what is an overnight index swap? In essence, an OIS is a type of derivative instrument that enables parties to exchange fixed and floating interest payments based on a notional amount. This financial tool is designed to hedge against potential losses or gains resulting from changes in interest rates. By understanding how overnight index swaps work, investors and financial institutions can better navigate the complexities of interest rate risk management.
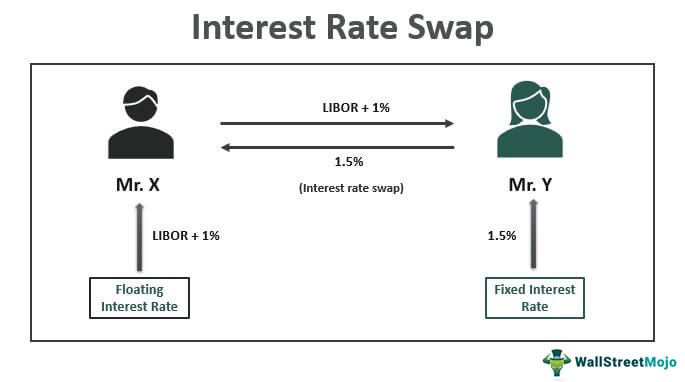
In an OIS, two parties agree to exchange the difference between a fixed rate and a floating rate, usually based on a benchmark rate such as the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) or the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). This allows them to manage their exposure to interest rate fluctuations and mitigate potential losses. With the ability to customize the terms of the swap, including the notional amount, tenor, and fixed rate, overnight index swaps offer a flexible solution for managing interest rate risk.
The Role of Overnight Index Swaps in Modern Finance
In today’s complex financial markets, overnight index swaps (OIS) play a vital role in managing interest rate risks, facilitating investment strategies, and maintaining market stability. As a widely used derivative instrument, OIS have become an essential tool for financial institutions, corporations, and investors seeking to navigate the intricacies of interest rate fluctuations.
The importance of overnight index swaps lies in their ability to provide a flexible and efficient means of managing interest rate risk. By allowing parties to exchange fixed and floating interest payments, OIS enable market participants to hedge against potential losses or gains resulting from changes in interest rates. This, in turn, helps to reduce uncertainty, increase confidence, and promote stability in the financial markets.
In addition to their role in risk management, overnight index swaps are also used in various investment strategies, such as asset liability management, portfolio optimization, and yield enhancement. By providing a means to customize the terms of the swap, including the notional amount, tenor, and fixed rate, OIS offer a high degree of flexibility, allowing investors to tailor their investments to suit their specific needs and objectives.
How to Use Overnight Index Swaps for Risk Management
When it comes to managing interest rate risks, overnight index swaps (OIS) can be a powerful tool in a financial institution’s or investor’s arsenal. To effectively utilize OIS for risk management, follow these steps:
Step 1: Identify Interest Rate Risk Exposure – Determine the extent of interest rate risk exposure in your portfolio or balance sheet. This will help you understand the potential impact of interest rate changes on your investments or liabilities.
Step 2: Determine the Appropriate OIS Strategy – Based on your risk exposure, decide on the most suitable OIS strategy. This could involve receiving fixed and paying floating, or vice versa, depending on your risk management objectives.
Step 3: Choose the Right Benchmark Rate – Select a suitable benchmark rate for the OIS, such as LIBOR or SOFR, which aligns with your risk management goals and market conditions.
Step 4: Set the Notional Amount and Tenor – Determine the notional amount and tenor of the OIS, taking into account your risk exposure, market conditions, and investment horizon.
Step 5: Monitor and Adjust – Continuously monitor the OIS position and adjust as necessary to ensure that it remains aligned with your risk management objectives.
Examples of scenarios where OIS can be effectively employed for risk management include:
– Hedging against potential losses from changes in interest rates on floating-rate loans or investments.
– Managing interest rate risk in asset liability management, such as matching floating-rate assets with floating-rate liabilities.
– Enhancing returns on investments by taking advantage of interest rate differentials between markets.
The Benefits of Overnight Index Swaps: A Deep Dive
Overnight index swaps (OIS) offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive tool for financial institutions, corporations, and investors seeking to manage interest rate risks and optimize their investments. Some of the key advantages of using OIS include:
Flexibility – OIS provide a high degree of flexibility, allowing parties to customize the terms of the swap, including the notional amount, tenor, and fixed rate. This enables users to tailor their OIS to suit their specific risk management objectives and investment strategies.
Cost Savings – By using OIS, parties can reduce their costs associated with managing interest rate risks. OIS can help to minimize the impact of interest rate changes on investments or liabilities, resulting in cost savings and improved profitability.
Enhanced Returns – OIS can also be used to enhance returns on investments. By taking advantage of interest rate differentials between markets, investors can use OIS to generate additional revenue and improve their overall investment performance.
Risk Management – One of the primary benefits of OIS is their ability to provide effective risk management. By hedging against potential losses from changes in interest rates, OIS can help to reduce uncertainty and increase confidence in investment decisions.
Market Efficiency – OIS can also contribute to market efficiency by providing a means for market participants to express their views on interest rates. This helps to promote price discovery and improve the overall functioning of financial markets.
In addition to these benefits, OIS are also widely used in a variety of applications, including asset liability management, portfolio optimization, and yield enhancement. As a result, they have become an essential tool for financial institutions, corporations, and investors seeking to navigate the complexities of interest rate markets.
Understanding the Risks Associated with Overnight Index Swaps
While overnight index swaps (OIS) offer a range of benefits, they are not without risks. It is essential for market participants to understand the potential risks and challenges associated with OIS to use them effectively and minimize potential losses.
Market Volatility – One of the primary risks associated with OIS is market volatility. Changes in interest rates can result in significant losses if not properly hedged. Market participants must carefully monitor market conditions and adjust their OIS positions accordingly to mitigate potential losses.
Counterparty Risk – OIS, like other derivatives, are subject to counterparty risk. This refers to the risk that the counterparty may default on their obligations, resulting in losses for the other party. Market participants must carefully assess the creditworthiness of their counterparties and implement risk management strategies to mitigate this risk.
Regulatory Requirements – OIS are subject to various regulatory requirements, including capital adequacy requirements, margining, and reporting. Market participants must ensure compliance with these regulations to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Liquidity Risk – OIS markets can be subject to liquidity risk, particularly during times of market stress. Market participants must ensure that they have sufficient liquidity to meet their obligations and adjust their positions accordingly.
Operational Risk – OIS transactions involve operational risks, including the risk of errors, failures, and fraud. Market participants must implement robust operational processes and controls to mitigate these risks.
It is essential for market participants to carefully consider these risks and implement effective risk management strategies to minimize potential losses. By doing so, they can harness the benefits of OIS while mitigating the associated risks.
A Comparison of Overnight Index Swaps with Other Derivatives
Overnight index swaps (OIS) are a type of derivative instrument that is often compared to other derivatives, such as futures, options, and forwards. While these instruments share some similarities, they also have distinct characteristics that set them apart. Understanding the differences between OIS and other derivatives is essential for market participants seeking to optimize their risk management and investment strategies.
Futures – Futures contracts are standardized agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific date. Unlike OIS, futures are traded on exchanges and are subject to margining requirements. Futures are often used for hedging and speculation, but they can be less flexible than OIS, which can be customized to meet specific risk management objectives.
Options – Options are derivatives that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price. Options are often used for hedging and speculation, but they can be more complex and expensive than OIS. Unlike OIS, options have an expiration date, and their value can be affected by factors such as volatility and time decay.
Forwards – Forwards are customized agreements to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific date. Like OIS, forwards are over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives, but they are often used for hedging and speculation, rather than risk management. Forwards can be less flexible than OIS, which can be tailored to meet specific risk management objectives.
In contrast to these derivatives, OIS are specifically designed to hedge against interest rate risks, providing a unique solution for market participants seeking to manage their exposure to changes in interest rates. OIS are also highly flexible, allowing parties to customize the terms of the swap to meet their specific risk management objectives. Additionally, OIS are often less complex and expensive than options, making them a more attractive solution for many market participants.
By understanding the differences between OIS and other derivatives, market participants can make informed decisions about which instruments to use in their risk management and investment strategies. Whether seeking to hedge against interest rate risks, speculate on market movements, or optimize investment returns, OIS and other derivatives offer a range of solutions that can help market participants achieve their objectives.
Real-World Applications of Overnight Index Swaps
Overnight index swaps (OIS) are widely used in various industries, including banking, investment, and corporate finance. Their flexibility and ability to hedge against interest rate risks make them an attractive solution for many organizations. Here are some real-world examples of how OIS are used in practice:
Case Study 1: Bank Risk Management – A commercial bank uses OIS to hedge against interest rate risks associated with its loan portfolio. By entering into an OIS, the bank can fix its borrowing costs and reduce its exposure to changes in interest rates, ensuring a stable income stream.
Case Study 2: Corporate Finance – A multinational corporation uses OIS to manage its foreign exchange risk. By swapping its foreign currency-denominated debt into its domestic currency, the corporation can reduce its exposure to exchange rate fluctuations and ensure a stable cash flow.
Case Study 3: Investment Management – An investment firm uses OIS to enhance the returns of its fixed-income portfolio. By entering into an OIS, the firm can take advantage of differences in interest rates between two currencies, generating additional revenue and improving its overall performance.
Case Study 4: Asset Liability Management – A pension fund uses OIS to manage its asset liability mismatch. By swapping its long-term liabilities into shorter-term obligations, the fund can reduce its exposure to interest rate risks and ensure a stable funding position.
These case studies demonstrate the versatility and effectiveness of OIS in managing interest rate risks and enhancing returns. By understanding how OIS are used in real-world scenarios, market participants can better appreciate their potential benefits and applications.
In addition to these examples, OIS are also used in other areas, such as mortgage-backed securities, credit default swaps, and inflation-indexed instruments. Their widespread adoption is a testament to their value as a risk management tool and their ability to provide flexibility and stability in an increasingly complex financial market.
The Future of Overnight Index Swaps: Trends and Opportunities
The overnight index swap (OIS) market has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for risk management solutions and the need for more efficient hedging strategies. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, OIS are likely to play an even more critical role in modern finance. Here are some emerging trends and opportunities that are shaping the future of OIS:
Digitalization and Automation – The OIS market is expected to become more digitalized, with the adoption of automation and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. This will enable faster and more efficient trade execution, as well as improved risk management and monitoring.
Increased Adoption by Non-Bank Financial Institutions – Non-bank financial institutions, such as pension funds and insurance companies, are increasingly using OIS to manage their interest rate risks. This trend is expected to continue, driven by the need for more effective risk management strategies.
Growing Importance of ESG Considerations – Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations are becoming more important in the OIS market, as investors seek to align their investments with their values. OIS providers are responding by developing ESG-compliant products and solutions.
Expansion into New Markets – The OIS market is expected to expand into new markets, such as emerging economies and alternative asset classes. This will provide new opportunities for investors and risk managers, as well as challenges for OIS providers.
Regulatory Evolution – Regulatory requirements, such as the uncleared margin rules, are expected to continue to evolve, shaping the OIS market and influencing the way OIS are traded and cleared.
In conclusion, the future of OIS looks promising, with emerging trends and opportunities driving growth and innovation in the market. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, OIS are likely to play an increasingly important role in modern finance, providing risk management solutions and investment opportunities for a wide range of market participants.
What is an overnight index swap? It is a powerful tool for managing interest rate risks and enhancing returns. As the OIS market continues to evolve, it is essential for market participants to stay informed about the latest trends and opportunities, and to understand how OIS can be used to achieve their risk management and investment objectives.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overnightindexswap.asp-final-216af61ba0f84575815b62a83457d7b9.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/overnightindexswap.asp-final-216af61ba0f84575815b62a83457d7b9.jpg)