Understanding the Concept of Cross Currency Swaps
In the realm of international finance, companies often grapple with the complexities of foreign exchange risk. This is where cross currency swaps come into play, providing a powerful tool for managing risk and optimizing funding costs. But what are cross currency swaps? In essence, they are financial derivatives that enable companies to swap principal and interest payments in different currencies, thereby hedging against exchange rate fluctuations and reducing uncertainty. By leveraging cross currency swaps, companies can access cheaper funding in international markets, improve cash flow management, and increase financial flexibility. In this article, we will delve into the world of cross currency swaps, exploring their mechanics, benefits, and applications, and providing insights into how they can be used to optimize funding costs and manage risk.
How to Hedge Currency Risk with Cross Currency Swaps
Cross currency swaps offer a powerful tool for companies to hedge against currency risk, providing a means to fix exchange rates and reduce exposure to market volatility. By entering into a cross currency swap agreement, companies can effectively lock in a fixed exchange rate for a specific period, eliminating the uncertainty associated with fluctuating currency values. This can be particularly beneficial for companies with international operations, as it enables them to better manage cash flows and reduce the impact of currency fluctuations on their bottom line. Furthermore, cross currency swaps can also be used to hedge against potential losses arising from currency fluctuations, providing an added layer of protection for companies operating in international markets.
The Mechanics of a Cross Currency Swap Agreement
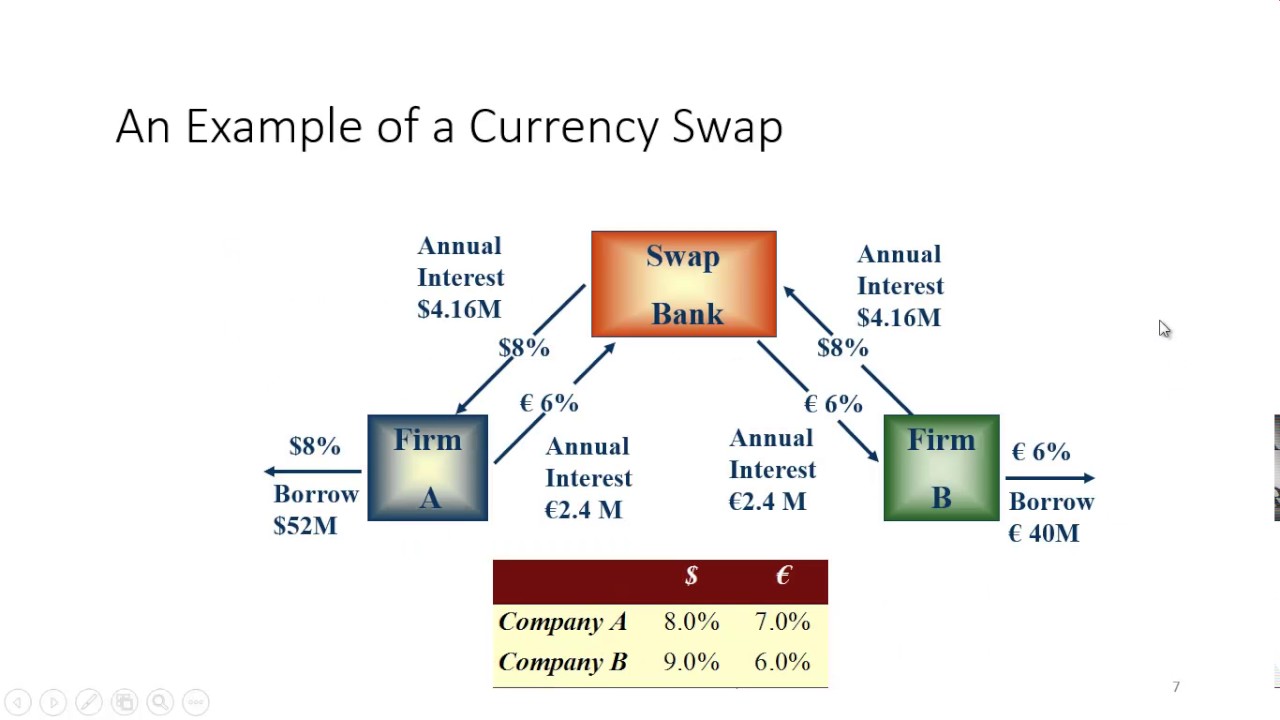
A cross currency swap agreement is a contractual arrangement between two parties, typically a borrower and a lender, where they agree to exchange principal and interest payments in different currencies. The agreement involves a series of cash flows, with each party making payments to the other in their respective currencies. The borrower, typically a company seeking to manage foreign exchange risk, enters into a swap agreement with a lender, often a bank or financial institution. The swap counterparty, usually a bank or swap dealer, facilitates the transaction by providing the necessary liquidity and hedging expertise. In a cross currency swap, the borrower receives a loan in one currency and simultaneously swaps it for a loan in another currency, thereby managing foreign exchange risk and accessing cheaper funding in international markets. By understanding the mechanics of a cross currency swap agreement, companies can better navigate the complexities of international financing and optimize their funding costs.
Types of Cross Currency Swaps: Fixed vs. Floating Rate
Cross currency swaps come in two primary forms: fixed rate and floating rate. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for companies seeking to manage foreign exchange risk and optimize funding costs. Fixed rate cross currency swaps involve the exchange of fixed interest payments in different currencies, providing a high degree of certainty and predictability. This type of swap is particularly useful for companies with long-term funding needs, as it allows them to lock in a fixed interest rate for an extended period. On the other hand, floating rate cross currency swaps involve the exchange of floating interest payments, typically tied to a benchmark rate such as LIBOR. This type of swap is more suitable for companies with short-term funding needs or those seeking to take advantage of fluctuations in interest rates. While fixed rate swaps offer greater predictability, floating rate swaps provide more flexibility and potential for cost savings. By understanding the characteristics of each type of cross currency swap, companies can make informed decisions about which type best suits their financing needs.
Real-World Applications of Cross Currency Swaps
Cross currency swaps have become an essential tool for companies operating in international markets. Multinational corporations, banks, and hedge funds alike use cross currency swaps to manage foreign exchange risk, optimize funding costs, and improve cash flow management. For instance, a multinational corporation with operations in the United States and Europe may use a cross currency swap to convert a euro-denominated loan into a US dollar-denominated loan, thereby managing its foreign exchange risk. Similarly, a bank may use a cross currency swap to hedge its exposure to currency fluctuations in its lending portfolio. Hedge funds, on the other hand, may use cross currency swaps to speculate on currency movements and generate returns. The versatility of cross currency swaps has made them an indispensable component of international finance, enabling companies to navigate complex currency markets with confidence. By understanding how companies in various industries use cross currency swaps, businesses can better appreciate the benefits of this powerful financial tool.
Benefits and Risks of Cross Currency Swaps
Cross currency swaps offer a range of benefits that make them an attractive option for companies seeking to manage foreign exchange risk and optimize funding costs. One of the primary advantages of cross currency swaps is the ability to reduce currency risk, providing companies with greater certainty and predictability in their financial planning. Additionally, cross currency swaps can improve cash flow management by allowing companies to convert foreign currency-denominated debt into their domestic currency, thereby reducing the impact of exchange rate fluctuations. Furthermore, cross currency swaps can increase financial flexibility, enabling companies to access cheaper funding in international markets and take advantage of arbitrage opportunities. However, like any financial instrument, cross currency swaps are not without risk. Counterparty risk, or the risk that the swap counterparty defaults on its obligations, is a significant concern. Market volatility can also impact the value of the swap, leading to potential losses. By understanding the benefits and risks of cross currency swaps, companies can make informed decisions about whether to use these instruments and how to manage their associated risks. What are cross currency swaps? They are a powerful tool for managing foreign exchange risk, but they require careful consideration and management to maximize their benefits.
Key Players in the Cross Currency Swap Market
The cross currency swap market is comprised of a range of key players, each playing a critical role in facilitating cross border financing. Banks are among the most prominent players, offering cross currency swaps to their corporate clients as a means of managing foreign exchange risk. Financial institutions, such as investment banks and asset managers, also participate in the cross currency swap market, providing liquidity and hedging services to their clients. Swap dealers, specialized financial institutions that facilitate cross currency swaps, play a crucial role in matching buyers and sellers and providing pricing and execution services. Additionally, multinational corporations, hedge funds, and other financial institutions may also participate in the cross currency swap market, using these instruments to manage their foreign exchange risk and optimize their funding costs. Understanding the roles and motivations of these key players is essential for companies seeking to navigate the cross currency swap market and unlock its benefits. What are cross currency swaps? They are a powerful tool for managing foreign exchange risk, and understanding the key players in the market is critical for their effective use.
Best Practices for Executing a Cross Currency Swap
When executing a cross currency swap, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure that the transaction is successful and that the company’s risk management objectives are met. One of the most critical steps is to conduct a thorough risk assessment, identifying the potential risks associated with the swap and developing strategies to mitigate them. Careful counterparty selection is also crucial, as the creditworthiness and reliability of the swap counterparty can have a significant impact on the success of the transaction. Effective documentation is also vital, as it helps to clarify the terms of the swap and reduce the risk of disputes or misunderstandings. Additionally, companies should ensure that they have a clear understanding of the swap’s terms and conditions, including the exchange rates, payment schedules, and termination provisions. By following these best practices, companies can ensure that their cross currency swaps are executed effectively and that they achieve their risk management and funding objectives. What are cross currency swaps? They are a powerful tool for managing foreign exchange risk, and executing them effectively requires careful planning and attention to detail.