Understanding the Basics of Government Debt Instruments
Government securities, including treasury bonds, bills, and notes, are debt instruments issued by governments to finance their operations and raise capital. These securities play a crucial role in the economy, providing a low-risk investment option for individuals and institutions. The U.S. Department of the Treasury is responsible for issuing these securities, which are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. Treasury bonds, bills, and notes are traded on the secondary market, allowing investors to buy and sell them easily. With a wide range of maturity periods and returns, government securities cater to diverse investment goals and risk tolerance. In the United States, treasury bonds, bills, and notes are popular investment instruments, offering a safe haven for investors seeking stable returns. By understanding the basics of government debt instruments, investors can make informed decisions about incorporating treasury bonds, bills, and notes into their investment portfolios.
How to Diversify Your Portfolio with Treasury Securities
Diversifying a portfolio with treasury securities can be an effective way to reduce risk and increase returns. By incorporating treasury bonds, bills, and notes into an investment strategy, investors can benefit from the low-risk nature of these securities. Treasury securities offer a stable source of income, which can help to offset the volatility of other investments. Additionally, they provide a high degree of liquidity, making it easy to buy and sell them on the secondary market. To diversify a portfolio with treasury securities, investors can consider allocating a portion of their assets to treasury bonds, bills, and notes. This can be done by purchasing individual securities or through a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund (ETF) that tracks a treasury securities index. By spreading investments across different types of treasury securities, investors can reduce their exposure to any one particular security and increase the overall stability of their portfolio. Furthermore, treasury securities can be used to hedge against inflation, as their returns are often tied to inflation rates. By incorporating treasury bonds, bills, and notes into a diversified portfolio, investors can create a robust investment strategy that balances risk and return.
Treasury Bills: A Low-Risk Investment Option
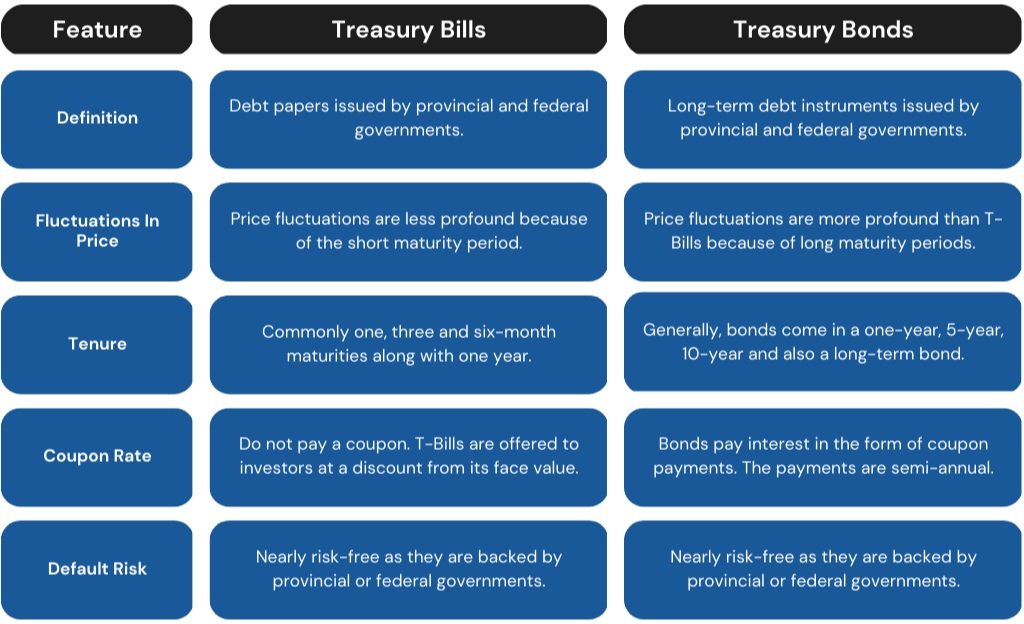
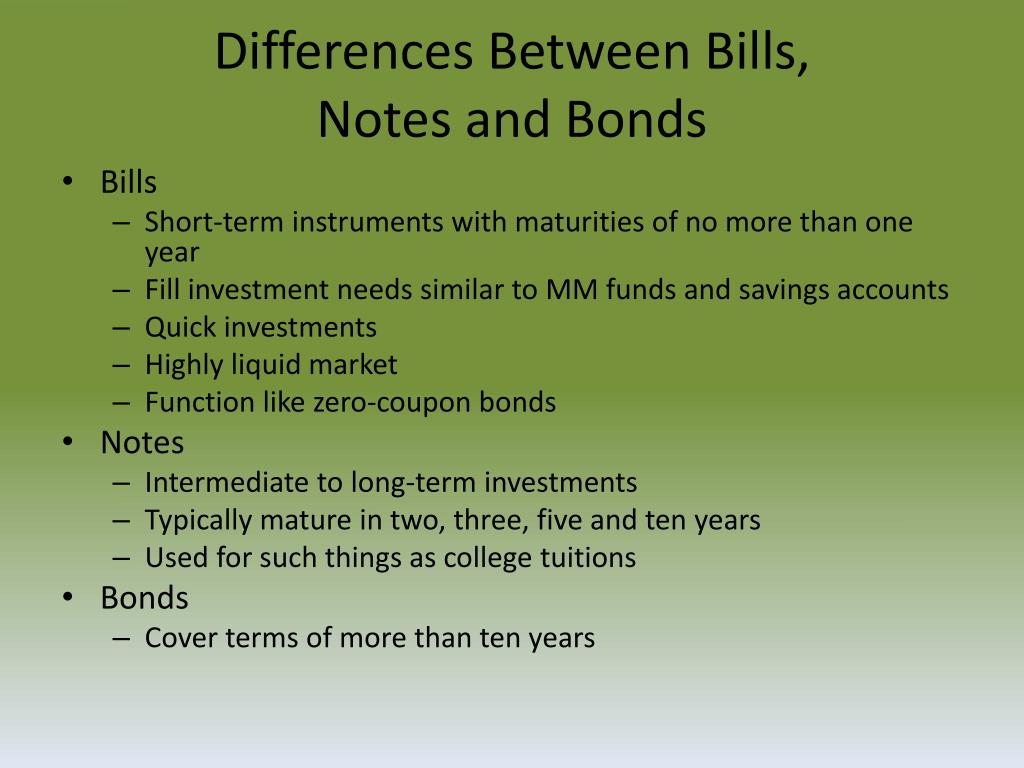
Treasury bills, also known as T-bills, are a type of short-term government debt instrument issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. They are considered a low-risk investment option, offering a high degree of liquidity and a low return. Treasury bills have a maturity period ranging from a few weeks to a year, making them an attractive option for investors seeking a short-term investment solution. There are four main types of treasury bills: 4-week, 13-week, 26-week, and 52-week bills. Each type of bill has a different maturity period, with the 4-week bill being the shortest and the 52-week bill being the longest. Treasury bills are sold at a discount to their face value and do not pay interest before maturity. Instead, the return on investment is the difference between the purchase price and the face value. For example, if an investor purchases a 4-week treasury bill with a face value of $1,000 for $990, the return on investment would be $10. Treasury bills are an attractive option for investors seeking a low-risk investment with a short-term time horizon. They can be used to park excess cash, manage cash flow, or reduce overall portfolio risk.
Treasury Notes: A Mid-Term Investment Solution
Treasury notes are a type of government debt instrument that offers a mid-term investment solution for investors. They are issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury with maturities ranging from 2 to 10 years. Treasury notes are considered a low-risk investment option, providing a fixed return in the form of interest payments, known as coupon payments, every six months until maturity. At maturity, the investor receives the face value of the note. Treasury notes are auctioned off by the Treasury Department on a regular schedule, with new issues available every week. They can be purchased directly through the Treasury Department’s website or through a broker. There are several types of treasury notes, including 2-year, 3-year, 5-year, and 7-year notes. Each type of note has a different maturity period, with the 2-year note being the shortest and the 10-year note being the longest. Treasury notes offer a higher return than treasury bills, but a lower return than treasury bonds, making them an attractive option for investors seeking a mid-term investment solution. They can be used to diversify a portfolio, manage cash flow, or generate regular income. When investing in treasury notes, it is essential to consider the interest rate environment, as changes in interest rates can affect the value of the notes.
Treasury Bonds: A Long-Term Investment Opportunity
Treasury bonds are a type of long-term government debt instrument issued by the U.S. Department of the Treasury. They offer a fixed return in the form of interest payments, known as coupon payments, every six months until maturity. At maturity, the investor receives the face value of the bond. Treasury bonds are considered a low-risk investment option, providing a stable source of income over a long period. They are auctioned off by the Treasury Department on a regular schedule, with new issues available every month. Treasury bonds can be purchased directly through the Treasury Department’s website or through a broker. There are several types of treasury bonds, including 10-year and 30-year bonds. Each type of bond has a different maturity period, with the 10-year bond being the shortest and the 30-year bond being the longest. Treasury bonds offer a higher return than treasury bills and notes, making them an attractive option for investors seeking a long-term investment solution. They can be used to generate regular income, diversify a portfolio, or achieve long-term financial goals. When investing in treasury bonds, it is essential to consider the interest rate environment, as changes in interest rates can affect the value of the bonds. Additionally, investors should be aware of the risk of inflation, which can erode the purchasing power of the bond’s interest payments and principal.
Comparing Treasury Bonds, Bills, and Notes: Which is Right for You?
When it comes to investing in treasury securities, it’s essential to understand the differences between treasury bonds, bills, and notes. Each type of security has its unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks, making it crucial to choose the right investment instrument based on individual financial goals and risk tolerance. Treasury bills, for instance, offer a short-term investment solution with maturities ranging from a few weeks to a year. They provide a low-risk return, but the returns are generally lower compared to treasury notes and bonds. Treasury notes, on the other hand, offer a mid-term investment solution with maturities ranging from 2 to 10 years. They provide a higher return than treasury bills but lower than treasury bonds. Treasury bonds, with maturities ranging from 10 to 30 years, offer a long-term investment solution with a higher return than both treasury bills and notes. However, they also come with a higher level of risk due to their longer maturity period. When comparing treasury bonds, bills, and notes, it’s essential to consider factors such as maturity, risk, and return. Investors seeking a low-risk, short-term investment solution may find treasury bills suitable, while those seeking a higher return over a longer period may prefer treasury bonds. Treasury notes, with their mid-term maturity, can provide a balance between risk and return. By understanding the differences between treasury bonds, bills, and notes, investors can make informed decisions and create a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial goals and risk tolerance. Ultimately, the right investment instrument depends on individual circumstances, and it’s crucial to evaluate personal financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before making a decision.
Investing in Treasury Securities: A Step-by-Step Guide
Investing in treasury bonds, bills, and notes can be a straightforward process, and this step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of purchasing and managing these securities. To start, investors can purchase treasury securities directly through the U.S. Department of the Treasury’s website, TreasuryDirect, or through a broker. When buying through TreasuryDirect, investors can create an account, fund it, and then bid on auctions for treasury securities. The process is similar when working with a broker, although they may charge a fee for their services. Once purchased, treasury securities can be held until maturity or sold on the secondary market. When selling, investors can use TreasuryDirect or a broker to facilitate the transaction. It’s essential to understand the process of buying and selling treasury securities to make informed investment decisions. Additionally, investors should be aware of the fees associated with purchasing and selling treasury securities, as well as any tax implications. By following these steps, investors can easily incorporate treasury bonds, bills, and notes into their investment portfolio, taking advantage of the low-risk returns they offer. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, investing in treasury securities can be a valuable addition to your investment strategy.
Maximizing Returns with Treasury Securities: Tips and Strategies
To maximize returns with treasury bonds, bills, and notes, investors can employ various strategies to optimize their portfolio. One effective approach is laddering, which involves investing in a series of treasury securities with staggered maturities. This technique helps to reduce risk and increase returns by spreading investments across different time horizons. Diversification is another key strategy, as it involves allocating investments across different types of treasury securities, such as treasury bonds, bills, and notes. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can reduce risk and increase potential returns. Tax implications are also an essential consideration when investing in treasury securities. For instance, interest earned on treasury securities is exempt from state and local taxes, making them an attractive option for tax-conscious investors. To monitor and adjust a treasury securities portfolio over time, investors should regularly review their investments and rebalance their portfolio as needed. This involves selling securities that have matured or underperformed and reinvesting the proceeds in new securities that align with their investment goals. By incorporating these tips and strategies into an investment approach, investors can maximize returns with treasury bonds, bills, and notes, while minimizing risk and achieving their long-term financial objectives. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, incorporating treasury securities into your investment strategy can provide a low-risk path to achieving your financial goals.