Understanding Treasury Bills and Their Appeal
Treasury Bills, or T-bills, are short-term debt securities issued by the U.S. government. They are considered one of the safest investments available. The U.S. government backs them, minimizing the risk of default. This makes them ideal for risk-averse investors and those seeking short-term stability. T-bills offer a risk-free rate of return, a benchmark against which other investments are often measured. The current t bill current interest rate reflects prevailing market conditions and government policy. Understanding the t bill current interest rate is crucial for informed investment decisions. Investors can use T-bills to preserve capital while earning a modest return, making them a cornerstone of many diversified portfolios. The appeal of T-bills lies in their predictable returns and low risk, making them a valuable component of any investment strategy. The simplicity and security of T-bills make them accessible to a wide range of investors, regardless of experience level.
T-bills are sold at a discount to their face value. At maturity, the investor receives the full face value. The difference between the purchase price and the face value represents the investor’s return. This return is often expressed as an annualized yield, which helps investors compare the returns of different T-bills and other investments. The t bill current interest rate, therefore, is a key factor influencing an investor’s decision to purchase T-bills. Factors influencing the t bill current interest rate include economic conditions and government policy. Understanding these factors helps investors predict potential returns on their investments. Investors often use T-bills as a safe haven during periods of market uncertainty, further solidifying their position as a low-risk investment option. The low risk and readily available information on the t bill current interest rate make them attractive to a broad spectrum of investors.
The t bill current interest rate is a reflection of several economic factors. These include the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, inflation, and overall economic growth. The Federal Reserve’s actions directly influence interest rates. High inflation typically leads to higher interest rates on T-bills, as investors demand a higher return to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Strong economic growth can also push interest rates up, as investors are more willing to take on risk in a booming economy. Conversely, weak economic growth might lead to lower interest rates. This is because investors seek safer options, like T-bills, increasing demand and potentially lowering yields. Keeping abreast of these factors allows investors to make better decisions regarding their T-bill investments, maximizing returns while mitigating potential risks. The t bill current interest rate thus provides a valuable indicator of broader economic trends.
Factors Influencing Current T-Bill Interest Rates
Several key economic factors influence the t bill current interest rate. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a crucial role. Interest rate hikes generally increase T-bill yields, making them more attractive to investors. Conversely, interest rate cuts tend to lower T-bill rates. This is because the Fed’s actions directly impact the overall cost of borrowing and influence investor expectations for future returns. Understanding the Fed’s policy decisions is vital to predicting t bill current interest rate movements.
Inflation significantly impacts the t bill current interest rate. When inflation rises, investors demand higher returns on their investments to compensate for the decreased purchasing power of their money. This increased demand pushes up T-bill rates. Conversely, lower inflation allows for lower T-bill rates. The relationship between inflation and T-bill yields is often inverse, meaning that as inflation goes up, the t bill current interest rate tends to increase, and vice-versa. Government reports on inflation, like the Consumer Price Index (CPI), are important indicators to watch.
Economic growth and investor demand also affect the t bill current interest rate. Strong economic growth can lead to increased investor confidence, potentially driving up demand for T-bills. This increased demand, in turn, can raise T-bill rates. Conversely, weak economic growth can reduce investor demand, lowering rates. Investor sentiment plays a considerable part in determining the t bill current interest rate. News about economic indicators, such as GDP growth and unemployment figures, influence investor expectations and their subsequent actions, thereby impacting the T-bill market. A healthy economy generally leads to higher T-bill rates compared to periods of economic uncertainty. The t bill current interest rate is therefore influenced by the interplay of these economic factors.
Where to Find the Most Up-to-Date T-Bill Rates
Finding the current t bill interest rate requires reliable sources. The official U.S. Treasury website provides direct access to the most accurate data. This is the primary source for t bill current interest rate information. Investors should always prioritize this site. It offers detailed information on various Treasury securities, including T-bills. The site is regularly updated, ensuring the accuracy of the t bill current interest rate figures. Navigating the site is straightforward, even for first-time users. Understanding where to locate this data is crucial for informed decision-making.
Reputable financial news organizations also publish regularly updated t bill current interest rate data. These sources typically aggregate information from the Treasury Department and other reliable sources. Major financial news outlets provide analysis and commentary alongside the rate data. This contextual information helps investors understand the broader economic factors influencing the t bill current interest rate. However, it’s crucial to select established and respected news sources. Avoid less credible sources, as they may present inaccurate or misleading information regarding the t bill current interest rate. Always cross-reference information from multiple sources to ensure accuracy.
Dedicated financial data providers offer comprehensive market data, including real-time t bill current interest rate updates. These services usually come with a subscription fee. They often provide advanced analytical tools and charting capabilities. These tools are invaluable for experienced investors seeking detailed market insights. However, for casual investors, the free information available from the U.S. Treasury website and reputable news organizations may suffice. The cost-benefit ratio should be carefully considered when deciding on a data provider. The choice depends largely on your investment needs and experience level. Remember to always verify t bill current interest rate information from multiple sources for accuracy before making investment decisions.
How to Interpret T-Bill Rate Data: Understanding the Current T-Bill Interest Rate
Treasury bills, or T-bills, offer a secure investment option. Understanding how their rates are presented is crucial. The most common way to express a T-bill’s return is through its annualized yield. This represents the return an investor would receive if they held the bill until maturity. The annualized yield considers the bill’s discount rate and its term to maturity. For example, a T-bill with a discount rate of 5% and a 90-day maturity might have an annualized yield slightly higher than 5%, reflecting the compounding effect over the year. This t bill current interest rate is key information. Investors should focus on the annualized yield when comparing T-bill rates to other short-term investments. It provides a standardized measure of return across different maturities.
Another way to see the t bill current interest rate is through the discount rate. This rate is applied to the face value of the T-bill to determine its purchase price. It shows the difference between the bill’s purchase price and its face value. For instance, a $10,000 T-bill with a 5% discount rate for a 90-day period will sell for approximately $9,876.71. The discount rate might seem lower than the annualized yield at first glance, especially for shorter-term bills. However, both methods convey the same underlying information: the investor’s return. Understanding both representations is vital for accurately comparing current T-bill interest rates, especially when comparing T-bills with differing maturities. The t bill current interest rate, expressed as a discount rate, is often shown on TreasuryDirect and other financial websites.
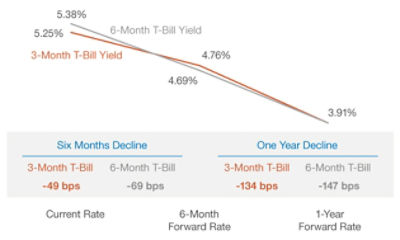
It’s also important to note that the t bill current interest rate fluctuates. Factors like inflation and Federal Reserve policy significantly impact these rates. Investors should regularly check reputable sources for the most current information. Paying close attention to the annualized yield allows for easier comparisons among different T-bill maturities and other short-term investments, providing a clearer understanding of potential returns and helping investors make informed decisions about their investments. Remember, always use reliable sources to obtain accurate t bill current interest rate data and avoid potential misinformation.
How to Invest in Treasury Bills
Investing in Treasury bills (T-bills) offers a straightforward path to accessing the current t bill current interest rate. Individuals can purchase T-bills directly through TreasuryDirect, the U.S. Treasury’s online system. This method allows for direct interaction with the government, eliminating intermediary fees. TreasuryDirect provides a user-friendly interface, facilitating the purchase and management of T-bills. Minimum investment amounts vary depending on the T-bill’s maturity date; however, it’s important to note that the current t bill current interest rate is not fixed and fluctuates based on market conditions. The platform guides investors through the process and provides information regarding t bill current interest rate updates.
Alternatively, investors can acquire T-bills through brokerage accounts. Many brokerage firms offer access to the Treasury market. This option provides a convenient single point of access for managing various investments, including T-bills. However, brokerage firms typically charge fees for their services, which can slightly reduce the net returns compared to purchasing directly through TreasuryDirect. Choosing between these methods depends on individual preferences, the size of the investment, and the importance of minimizing transaction costs. Regardless of the chosen method, understanding the current t bill current interest rate remains crucial for making informed investment decisions.
T-bills are sold at a discount to their face value. At maturity, the investor receives the face value of the bill. The difference between the purchase price and the face value represents the interest earned. Maturity durations for T-bills typically range from a few weeks to a year. Before investing, potential investors should carefully consider the current t bill current interest rate and weigh the investment’s duration against their financial goals. Shorter-term T-bills offer less potential for interest rate appreciation but carry a lower risk of capital loss if interest rates rise. Investors should always assess their risk tolerance before investing in any financial instrument, including T-bills. Staying informed on the current t bill current interest rate and market conditions is paramount.
Comparing T-Bill Rates to Other Short-Term Investments
Treasury bills offer a compelling alternative to other short-term investment options. Understanding the nuances of each can help investors make informed decisions. High-yield savings accounts, for instance, provide easy access to funds and typically offer competitive interest rates. However, these rates are often variable and may not match the current t bill interest rate, especially during periods of economic uncertainty. The t bill current interest rate tends to be more stable, reflecting the perceived safety of US government debt. Certificates of deposit (CDs) provide fixed interest rates for a specific term. While offering a degree of certainty, the returns may lag behind a rising t bill current interest rate if held to maturity. CDs also typically restrict early withdrawals, impacting liquidity. Money market accounts (MMAs) combine checking account features with interest-bearing capabilities. While convenient, MMA interest rates are often lower than the current t bill interest rate, particularly for larger investment amounts. The t bill current interest rate, therefore, represents a benchmark for short-term yields, reflecting the risk-free rate of return.
Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and financial goals when comparing these options. The relative stability of the t bill current interest rate makes it appealing to risk-averse investors seeking capital preservation. Those with a higher risk tolerance might find higher potential returns in other short-term investments, but should carefully assess the associated risks of fluctuating interest rates or limited liquidity. The choice ultimately depends on individual circumstances. Understanding the current t bill interest rate in relation to other options is crucial for effective portfolio management. For example, if the t bill current interest rate surpasses the yield on a high-yield savings account, a shift in allocations might be considered. Conversely, if the t bill current interest rate is low, investors might consider options offering potentially higher returns, keeping in mind the potential trade-off with increased risk.
Analyzing the t bill current interest rate alongside the yields of other short-term instruments provides a comprehensive view of the investment landscape. Regular monitoring of these rates enables investors to adapt their strategies proactively. For example, investors might strategically allocate funds across different options to balance risk and return. Diversifying across T-Bills, high-yield savings accounts, and potentially CDs allows for a mix of stability and potential for higher yields depending on the current economic climate and the prevailing t bill current interest rate. The decision to invest in one over the other will depend on each investor’s individual risk profile and financial objectives.
Strategies for Maximizing Returns on T-Bills
Maximizing returns on T-bill investments requires a strategic approach. One strategy involves carefully timing purchases. Investors might try to buy T-bills when the t bill current interest rate is anticipated to rise. However, accurately predicting interest rate movements is challenging. Market timing carries inherent risks. A more reliable approach focuses on consistent investment and diversification. Regular purchases help average out fluctuations in the t bill current interest rate. Diversifying across different maturities mitigates risk. Investing in a mix of short-term and longer-term T-bills can offer a balanced approach. Remember, even small increases in the t bill current interest rate can add up over time.
Reinvesting matured T-bills is another key strategy. When a T-bill matures, reinvesting the proceeds into new T-bills allows investors to take advantage of potentially higher yields. This compounding effect gradually increases returns. Tracking the t bill current interest rate helps identify opportune moments to reinvest. Regularly reviewing available rates provides an overview of the market. This enables informed decisions and helps investors capitalize on potentially favorable rates. This is particularly important when considering the impact of inflation on purchasing power.
Beyond timing and reinvestment, understanding your investment goals plays a crucial role. T-bills are low-risk investments, ideal for preserving capital and providing a stable return. Therefore, a conservative approach is often best. Focusing on long-term growth, rather than trying to rapidly increase profits, maximizes the benefits of the low risk. Investors should analyze their risk tolerance and investment timeline. This will help them develop a T-bill investment strategy that aligns with their needs and objectives. Monitoring the t bill current interest rate remains vital in order to maintain an effective investment strategy. By following these strategies, investors can improve their returns from their T-bill investments.
Understanding the Risks of Investing in T-Bills
While Treasury bills are generally considered a low-risk investment, it’s crucial to understand potential drawbacks. Inflation, the gradual increase in the price of goods and services, can erode the purchasing power of your returns. If the t bill current interest rate is lower than the inflation rate, the real return on your investment may be negative. This is especially true for longer-term investments. Investors should carefully consider their investment horizon and the current inflation rate when assessing the potential impact on their returns. Understanding the relationship between the t bill current interest rate and inflation is crucial for informed decision-making.
Another factor to consider is liquidity. Although T-bills are generally considered highly liquid, meaning they can be easily converted to cash, there might be minor delays depending on the method of investment and market conditions. For instance, selling a T-bill before maturity might not always fetch the intended value. If an investor needs immediate access to a substantial portion of their invested funds, there is a slight risk of facing a potential liquidity issue. While this risk is minimal for most investors, it is a point to keep in mind, particularly for larger investments or those anticipating immediate access to capital. The t bill current interest rate shouldn’t overshadow the importance of considering liquidity needs.
Despite these potential downsides, the relative safety and stability of T-bills remain significant advantages. Compared to other short-term investments with higher yields, the risk associated with T-bills remains comparatively low. The US government backs these securities, making default virtually impossible. Therefore, investors prioritize the low-risk nature of T-bills, often accepting a slightly lower t bill current interest rate for the peace of mind associated with this security. Careful consideration of your individual risk tolerance and financial goals remains crucial before investing in any financial instrument, including T-bills. Monitoring the t bill current interest rate alongside broader economic indicators will allow for more informed investment strategies.