Unlocking the Secrets of the S&P 500’s Sector Weighting
Investors seeking to maximize returns in the S&P 500 must understand the intricacies of sector weighting, a crucial component of portfolio management. The sector weighting of S&P 500, which refers to the proportion of each sector’s market capitalization within the index, has a profound impact on investment decisions and portfolio performance. A deep understanding of sector weighting enables investors to make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and optimize their portfolios for maximum returns. In fact, research has shown that sector allocation can account for up to 90% of a portfolio’s performance, highlighting the importance of getting it right. By grasping the concepts of sector weighting, investors can gain a competitive edge in the market and achieve their long-term investment goals.
How to Analyze Sector Weighting for Informed Investment Choices
Accurate analysis of sector weighting is crucial for making informed investment decisions in the S&P 500. To access sector data, investors can utilize various resources, including financial news websites, stock exchanges, and financial databases. Interpreting sector data requires a deep understanding of market trends, economic indicators, and the sector’s performance relative to the broader market. By analyzing sector weighting, investors can identify opportunities for growth, detect potential risks, and adjust their portfolios accordingly. For instance, a sector with a high weighting in the S&P 500 may indicate strong performance and potential for future growth, while a sector with a low weighting may suggest underperformance and potential for decline. By considering these factors, investors can make data-driven decisions and optimize their portfolios for maximum returns.
The Current State of the S&P 500: A Sector-by-Sector Breakdown
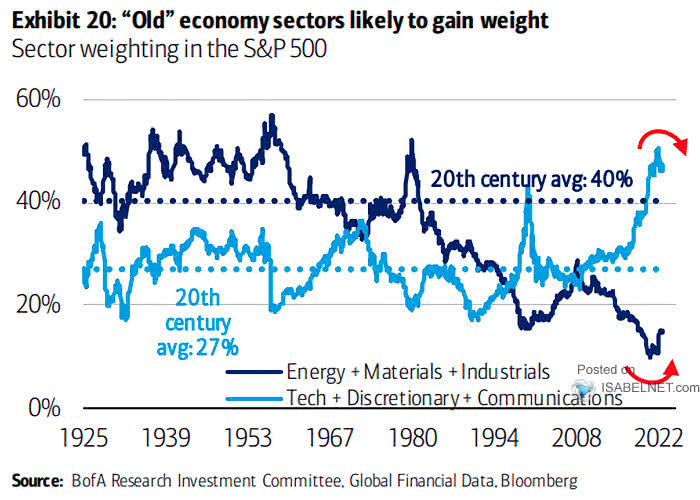
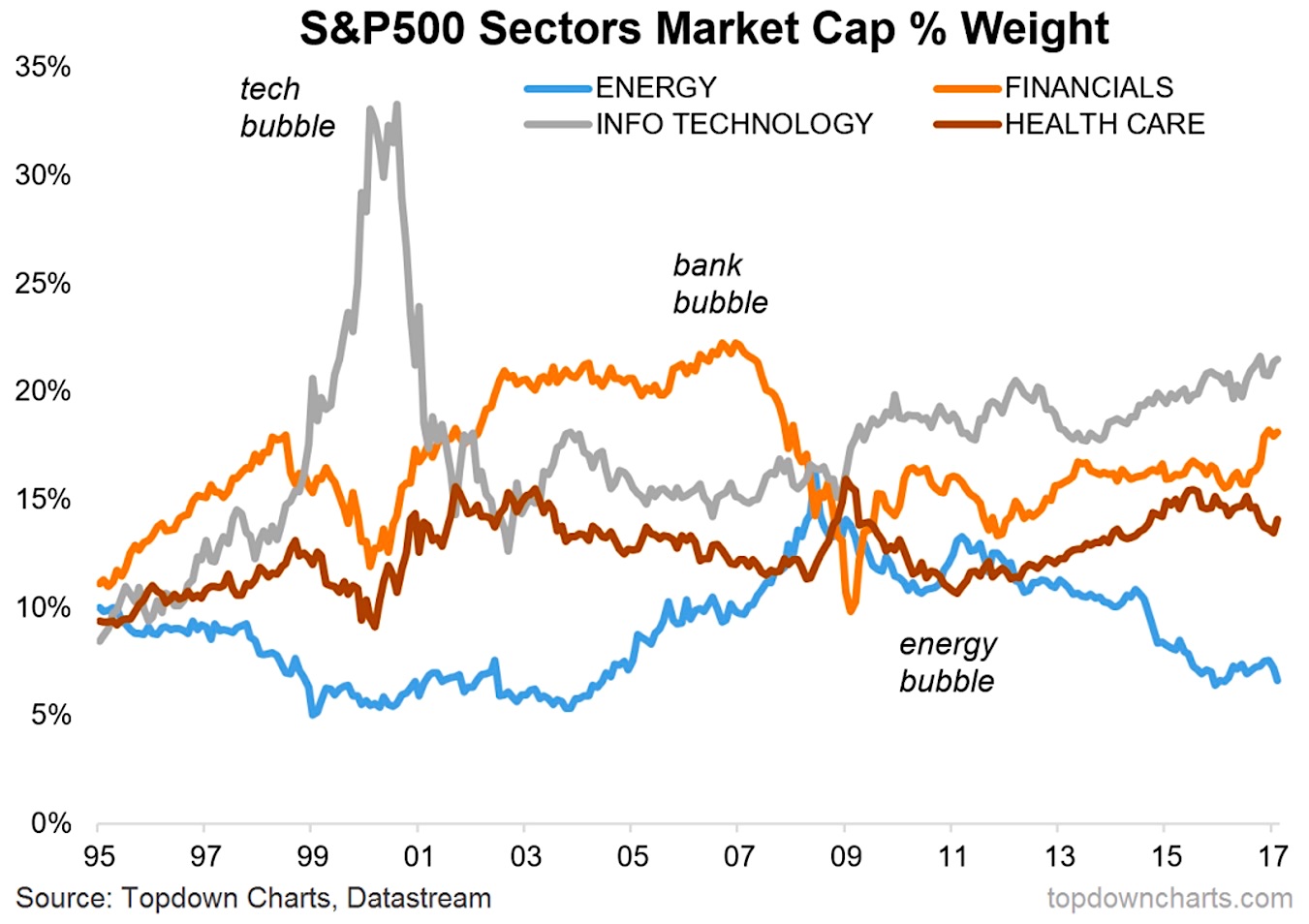
The sector weighting of S&P 500 is constantly evolving, and understanding the current landscape is crucial for making informed investment decisions. As of now, the technology sector dominates the S&P 500, accounting for approximately 27% of the index’s total market capitalization. This is followed closely by the healthcare sector, which makes up around 14% of the index. On the other hand, the energy and materials sectors have been underperforming, with weightings of around 5% and 3%, respectively. These figures are subject to change, and investors must stay up-to-date with the latest sector weighting data to optimize their portfolios. By analyzing the current sector weighting of the S&P 500, investors can identify opportunities for growth, detect potential risks, and adjust their portfolios accordingly. For instance, investors may consider overweighting their portfolios in top-performing sectors, such as technology, while underweighting or avoiding underperforming sectors, such as energy. By doing so, investors can maximize returns and minimize potential losses.
Understanding the Impact of Sector Rotation on Your Portfolio
Sector rotation is a crucial concept for investors to grasp, as it can significantly impact the performance of their portfolios. Sector rotation refers to the phenomenon of money flowing from one sector to another, driven by changes in market conditions, economic trends, and investor sentiment. This rotation can lead to significant shifts in the sector weighting of the S&P 500, with some sectors experiencing increased demand and others facing declining interest. For instance, during times of economic growth, investors may rotate into cyclical sectors such as consumer discretionary and industrials, while during times of economic uncertainty, investors may seek safe-haven sectors such as healthcare and utilities. To adapt to sector rotation, investors must stay vigilant and adjust their portfolios accordingly. This may involve rebalancing their portfolios to maintain an optimal sector weighting, overweighting top-performing sectors, and underweighting or avoiding underperforming sectors. By doing so, investors can maximize returns and minimize potential losses. The sector weighting of the S&P 500 is constantly evolving, and understanding sector rotation is essential for making informed investment decisions and achieving long-term portfolio success.
Strategies for Optimizing Sector Allocation in Your Portfolio
To optimize sector allocation in a portfolio, investors must adopt a strategic approach that balances risk and potential returns. One key strategy is diversification, which involves spreading investments across various sectors to minimize exposure to any one sector. This can be achieved by allocating a percentage of the portfolio to each sector, based on the sector weighting of the S&P 500. For example, if the technology sector accounts for 27% of the S&P 500, an investor may consider allocating a similar percentage of their portfolio to technology stocks. Another strategy is risk management, which involves identifying potential risks and adjusting sector allocation accordingly. This may involve overweighting defensive sectors, such as healthcare and utilities, during times of economic uncertainty, and underweighting cyclical sectors, such as consumer discretionary and industrials. Rebalancing is also crucial, as it involves periodically reviewing and adjusting sector allocation to ensure that it remains aligned with the investor’s goals and risk tolerance. By adopting these strategies, investors can optimize their sector allocation and maximize returns while minimizing potential losses. The sector weighting of the S&P 500 serves as a valuable benchmark for investors, providing insights into the performance of different sectors and guiding informed investment decisions.
The Role of Sector Weighting in Risk Management and Diversification
Sector weighting plays a crucial role in managing risk and achieving diversification in a portfolio. By allocating assets across different sectors, investors can reduce their exposure to any one sector and minimize potential losses. The sector weighting of the S&P 500 serves as a valuable benchmark for investors, providing insights into the performance of different sectors and guiding informed investment decisions. For instance, during times of economic uncertainty, investors may overweight defensive sectors, such as healthcare and utilities, which tend to be less volatile and more resilient to market downturns. Conversely, during times of economic growth, investors may overweight cyclical sectors, such as consumer discretionary and industrials, which tend to be more sensitive to changes in the economy. By adopting a sector-based approach to risk management, investors can create a more balanced portfolio that is better equipped to navigate changing market conditions. Furthermore, sector weighting can also help investors achieve diversification, which is critical for reducing risk and increasing potential returns. By spreading investments across multiple sectors, investors can reduce their reliance on any one sector and increase their exposure to a broader range of investment opportunities. By understanding the sector weighting of the S&P 500 and incorporating it into their investment strategy, investors can create a more robust and resilient portfolio that is better positioned for long-term success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Sector Weighting and Allocation
When it comes to sector weighting and allocation, investors often make mistakes that can have a significant impact on their portfolio’s performance. One common mistake is failing to regularly review and adjust sector allocation, leading to a mismatch between the portfolio’s sector weighting and the sector weighting of the S&P 500. This can result in overexposure to underperforming sectors and underexposure to top-performing sectors. Another mistake is relying too heavily on past performance, rather than considering current market trends and economic indicators. This can lead to a failure to adapt to changes in sector performance and a lack of diversification in the portfolio. Additionally, investors may overlook the importance of sector rotation, failing to recognize when a sector is experiencing a downturn and when it’s time to rebalance the portfolio. By understanding these common mistakes, investors can avoid costly errors and optimize their sector allocation to achieve better returns. It’s essential to stay informed about the sector weighting of the S&P 500 and to continuously monitor and adjust sector allocation to ensure that it remains aligned with investment goals and risk tolerance.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Monitoring and Adjusting Sector Weighting
To achieve optimal sector allocation, it’s essential to stay ahead of the curve by continuously monitoring and adjusting sector weighting in response to changing market conditions and economic trends. This involves regularly reviewing the sector weighting of the S&P 500 and rebalancing the portfolio to ensure that it remains aligned with investment goals and risk tolerance. By doing so, investors can capitalize on emerging trends and opportunities, while minimizing exposure to underperforming sectors. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and adjustment of sector weighting can help investors adapt to shifts in the market environment, such as changes in interest rates, inflation, or geopolitical events. By staying informed about the sector weighting of the S&P 500 and making adjustments as needed, investors can optimize their sector allocation and achieve better returns over the long term. This proactive approach to sector weighting can help investors stay ahead of the curve and achieve their investment objectives in an ever-changing market landscape.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/weighting-of-SP-64bd20169a194e8f91a0499a1ecd4705.jpg)