Understanding the Yield Curve: A Key to Investment Success
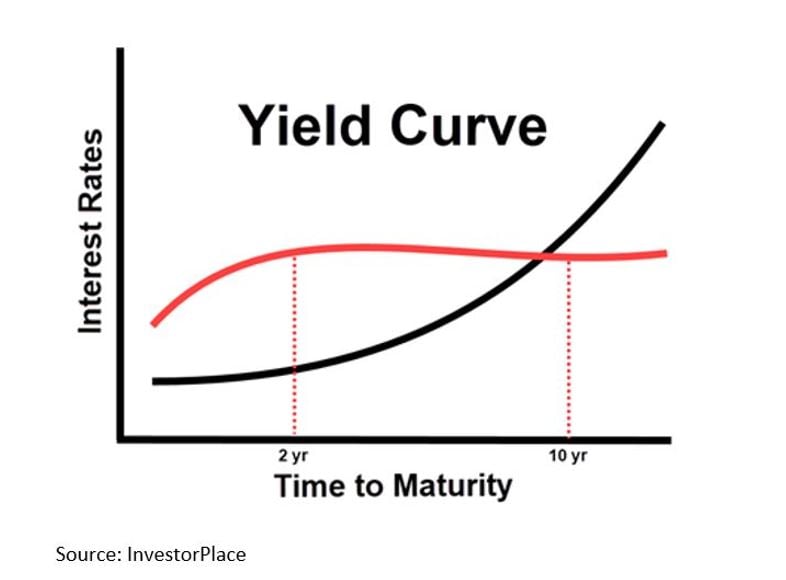
The yield curve is a fundamental concept in bond investing, serving as a graphical representation of the relationship between bond yields and their corresponding maturities. It plays a crucial role in investment decisions, as it helps investors understand the returns they can expect from their investments and make informed decisions. The yield curve can take on various shapes, including upward sloping, downward sloping, and flat, each with its own implications for investment strategies.
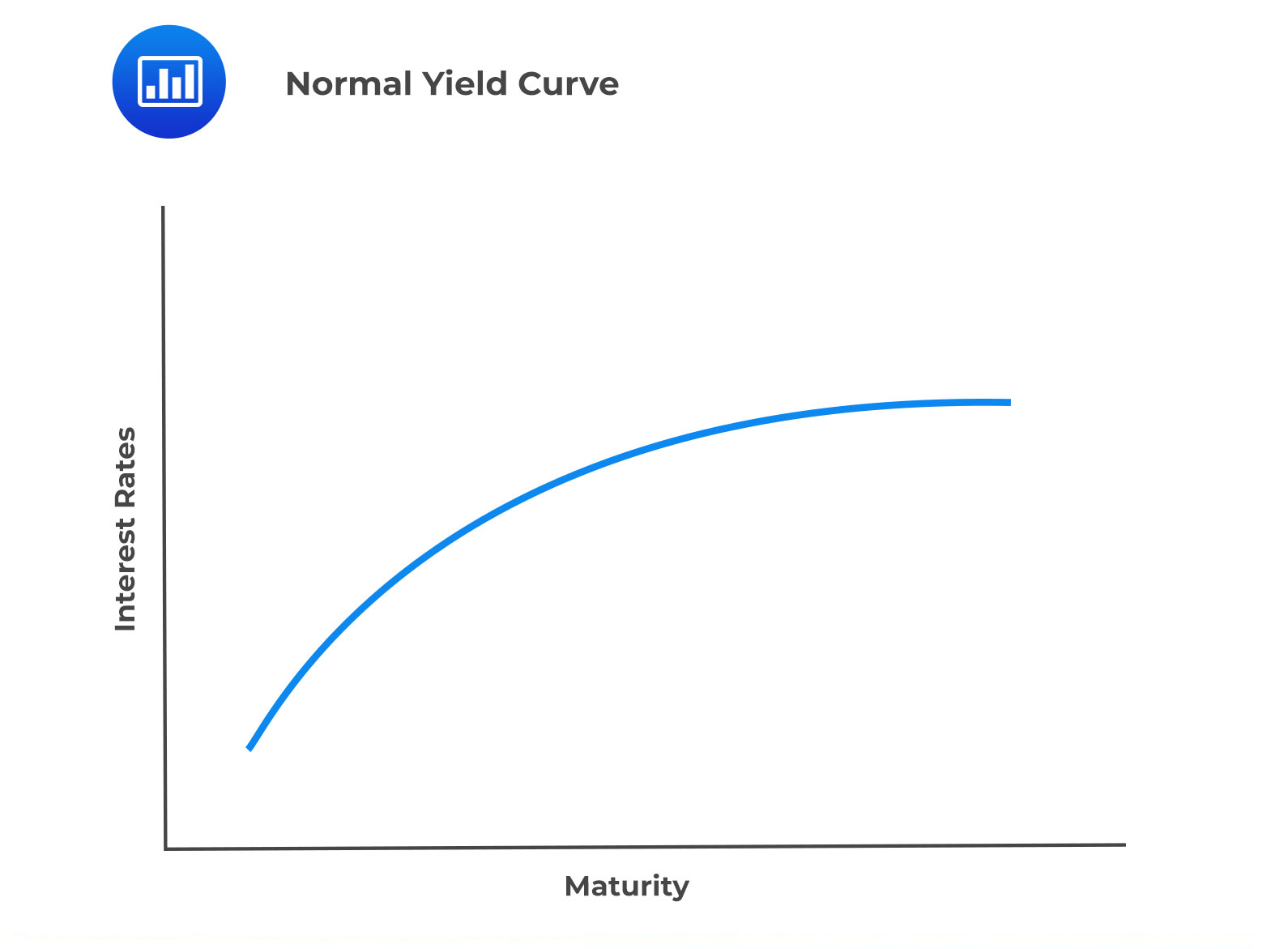
An upward sloping yield curve, for instance, indicates that longer-term bonds offer higher yields to compensate for the increased risk of investing over a longer period. This type of curve is often seen in a growing economy, where investors demand higher returns for tying up their money for longer periods. On the other hand, a downward sloping yield curve suggests that shorter-term bonds offer higher yields, making them more attractive to investors. This type of curve may occur in a declining economy, where investors become risk-averse and seek shorter-term investments.
A flat yield curve, also known as a humped yield curve, indicates that the yields of bonds with different maturities are similar. This type of curve may occur when the market expects short-term interest rates to rise, causing investors to demand higher returns for shorter-term bonds. Understanding the different types of yield curves and their implications is essential for investors seeking to optimize their returns and manage their risk exposure.
What is Rolling Down the Yield Curve?
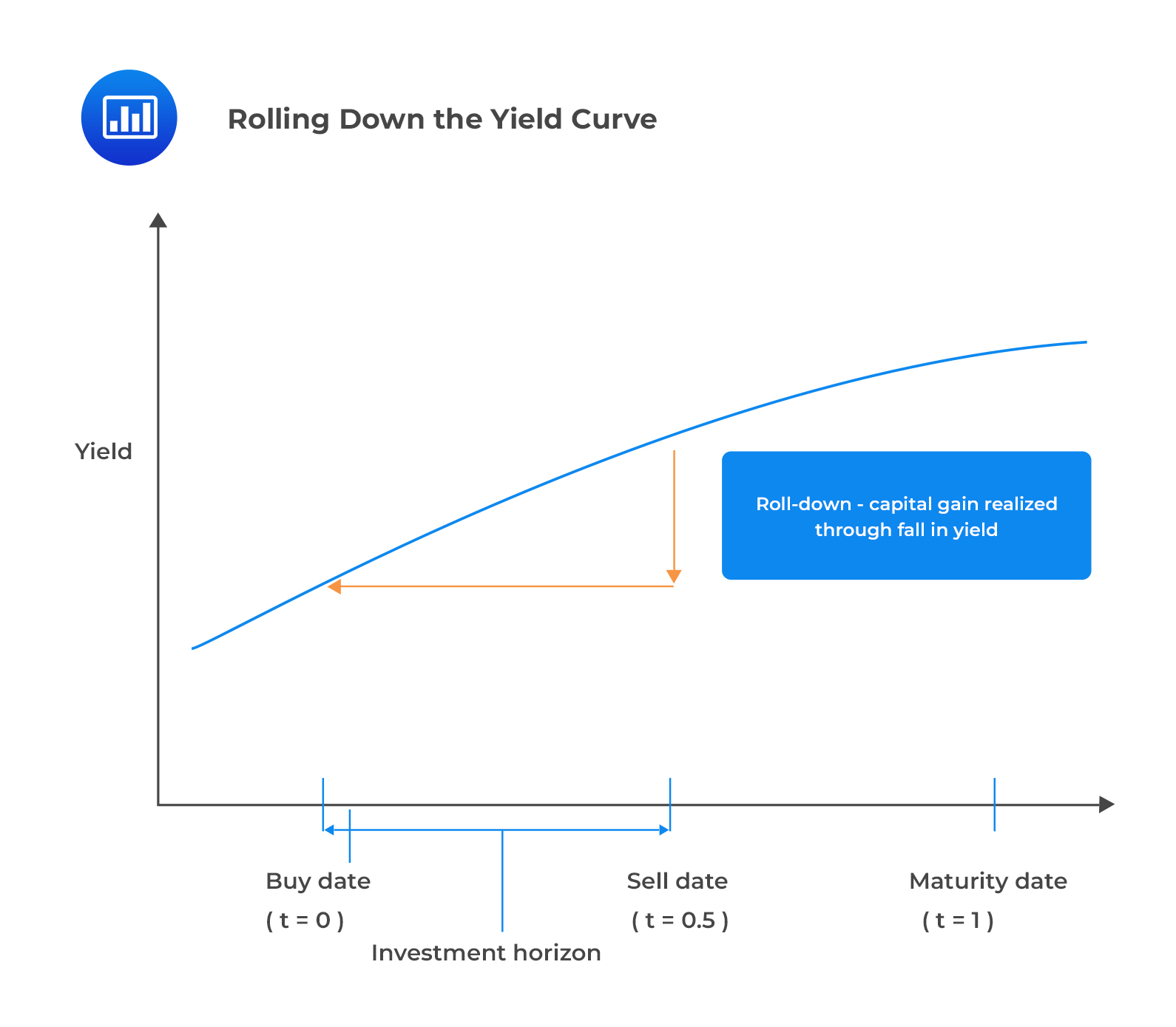
Rolling down the yield curve is a popular investment strategy that involves selling existing bonds and reinvesting the proceeds in new bonds with shorter maturities and higher yields. This approach takes advantage of the natural slope of the yield curve, where shorter-term bonds typically offer lower yields than longer-term bonds. By rolling down the yield curve, investors can optimize their returns by capturing the higher yields offered by shorter-term bonds, while minimizing their exposure to interest rate risk.
The benefits of rolling down the yield curve are numerous. For instance, it allows investors to take advantage of the higher yields offered by shorter-term bonds, which can result in higher returns over time. Additionally, this strategy can help investors manage their interest rate risk by reducing their exposure to longer-term bonds, which are more sensitive to changes in interest rates. Furthermore, rolling down the yield curve can provide investors with a regular stream of income, as they can reinvest the proceeds from maturing bonds in new bonds with shorter maturities.
This strategy can be applied in different market conditions. For example, in a rising interest rate environment, rolling down the yield curve can help investors minimize their losses by reducing their exposure to longer-term bonds. In a declining interest rate environment, this strategy can help investors maximize their returns by capturing the higher yields offered by shorter-term bonds. By understanding the yield curve and implementing a rolling down the yield curve strategy, investors can optimize their returns and achieve investment success.
How to Maximize Returns by Rolling Down the Yield Curve
To maximize returns by rolling down the yield curve, investors should focus on identifying opportunities to capture higher yields while managing risk. Here are some practical tips and strategies to consider:
First, investors should regularly review their bond portfolios to identify opportunities to roll down the yield curve. This involves selling existing bonds and reinvesting the proceeds in new bonds with shorter maturities and higher yields. By doing so, investors can take advantage of the natural slope of the yield curve and capture higher returns.
Second, investors should consider the credit quality of the bonds they invest in. Higher-quality bonds with shorter maturities may offer lower yields, but they also come with lower credit risk. Investors should balance their desire for higher returns with their risk tolerance and adjust their strategy accordingly.
Third, investors should be prepared to adjust their strategy based on market changes. In a rising interest rate environment, for example, investors may need to adjust their strategy to minimize losses and maximize returns. This may involve rolling down the yield curve more quickly or investing in shorter-term bonds to reduce interest rate risk.
Fourth, investors should consider diversifying their bond portfolios to minimize risk. This can be achieved by investing in bonds with different maturities, credit qualities, and issuers. By diversifying their portfolios, investors can reduce their exposure to any one particular bond or issuer and maximize their returns over time.
Finally, investors should consider working with a financial advisor or investment manager to implement a rolling down the yield curve strategy. A professional can help investors identify opportunities, manage risk, and adjust their strategy based on market changes. By working with a professional, investors can maximize their returns and achieve investment success.
By following these tips and strategies, investors can maximize their returns by rolling down the yield curve and achieve investment success. Whether investing in corporate bonds, government bonds, or municipal bonds, a rolling down the yield curve strategy can help investors optimize their returns and achieve their investment goals.
The Risks and Challenges of Rolling Down the Yield Curve
While rolling down the yield curve can be an effective strategy for optimizing investment returns, it is not without its risks and challenges. Investors should be aware of the potential pitfalls associated with this approach and take steps to mitigate them.
One of the primary risks of rolling down the yield curve is interest rate risk. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds with longer maturities decreases, which can result in losses for investors. To mitigate this risk, investors can adjust their strategy by rolling down the yield curve more quickly or investing in shorter-term bonds.
Another risk associated with rolling down the yield curve is credit risk. When investors sell existing bonds and reinvest in new bonds with shorter maturities, they may be exposed to credit risk if the issuer of the new bond defaults. To mitigate this risk, investors should focus on investing in high-quality bonds with strong credit ratings.
Liquidity risk is another challenge associated with rolling down the yield curve. When investors sell existing bonds, they may not be able to find suitable replacement bonds with the desired characteristics, which can result in liquidity risk. To mitigate this risk, investors should maintain a diversified bond portfolio and consider working with a financial advisor or investment manager.
In addition to these risks, investors should also be aware of the potential challenges associated with rolling down the yield curve. For example, this strategy requires frequent buying and selling of bonds, which can result in higher transaction costs. Additionally, investors may need to adjust their strategy based on market changes, which can be time-consuming and require significant expertise.
Despite these risks and challenges, rolling down the yield curve can be a highly effective strategy for optimizing investment returns. By understanding the potential risks and challenges and taking steps to mitigate them, investors can maximize their returns and achieve investment success. By incorporating this strategy into their overall investment approach, investors can navigate the bond market with confidence and achieve their long-term investment goals.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Rolling Down the Yield Curve
To illustrate the effectiveness of rolling down the yield curve, let’s examine several real-world examples of how this strategy has been successfully implemented in different investment scenarios.
Case Study 1: Corporate Bonds
In 2018, a large corporation issued a 10-year bond with a 4% coupon rate. An investor purchased the bond and held it for two years, earning a total return of 8%. However, as interest rates began to rise, the investor decided to roll down the yield curve by selling the bond and reinvesting in a 5-year bond with a 3.5% coupon rate. By doing so, the investor was able to capture a higher yield while reducing their exposure to interest rate risk.
Case Study 2: Government Bonds
In 2020, a government agency issued a 30-year bond with a 3.25% coupon rate. An investor purchased the bond and held it for three years, earning a total return of 9.75%. However, as interest rates began to rise, the investor decided to roll down the yield curve by selling the bond and reinvesting in a 10-year bond with a 2.75% coupon rate. By doing so, the investor was able to reduce their exposure to interest rate risk while still earning a competitive return.
Case Study 3: Municipal Bonds
In 2019, a municipal government issued a 20-year bond with a 3.5% coupon rate. An investor purchased the bond and held it for two years, earning a total return of 7%. However, as interest rates began to rise, the investor decided to roll down the yield curve by selling the bond and reinvesting in a 5-year bond with a 2.5% coupon rate. By doing so, the investor was able to capture a higher yield while reducing their exposure to interest rate risk.
These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of rolling down the yield curve in different investment scenarios. By regularly reviewing their bond portfolios and adjusting their strategy based on market changes, investors can optimize their returns and achieve investment success.
Comparing Rolling Down the Yield Curve to Other Investment Strategies
Rolling down the yield curve is just one of several investment strategies that bond investors can use to optimize their returns. Two other popular strategies are laddering and barbelling. In this section, we’ll compare and contrast these approaches to help investors determine which strategy is best suited to their investment goals and risk tolerance.
Laddering involves dividing a bond portfolio into equal segments with staggered maturity dates. This approach provides a steady stream of income as bonds mature and are replaced with new bonds at prevailing market rates. While laddering can provide a predictable income stream, it may not be as effective in a rising rate environment, as investors may be locked into lower yields on their existing bonds.
Barbelling, on the other hand, involves investing in a combination of short-term and long-term bonds. This approach can provide a balance between income generation and capital appreciation, as short-term bonds provide liquidity and long-term bonds offer higher yields. However, barbelling may not be as effective in a falling rate environment, as investors may be exposed to higher interest rate risk on their long-term bonds.
In contrast, rolling down the yield curve offers a more dynamic approach to bond investing. By regularly reviewing their bond portfolios and adjusting their strategy based on market changes, investors can optimize their returns and minimize their exposure to interest rate risk. This approach requires more active management, but can provide higher returns and greater flexibility in response to changing market conditions.
Ultimately, the choice between rolling down the yield curve, laddering, and barbelling will depend on an investor’s individual goals, risk tolerance, and market expectations. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each approach, investors can make informed decisions and develop a bond investment strategy that meets their needs.
Rolling down the yield curve offers a number of benefits, including the ability to capture higher yields, minimize interest rate risk, and adjust to changing market conditions. By incorporating this strategy into their overall investment approach, bond investors can optimize their returns and achieve investment success.
Rolling Down the Yield Curve in a Rising Rate Environment
In a rising interest rate environment, bond investors face the challenge of managing their portfolios to minimize losses and maximize returns. Rolling down the yield curve can be an effective strategy in such conditions, but it requires careful consideration and adjustments to the approach.
When interest rates rise, existing bonds with lower yields become less attractive, and investors may face losses if they sell their bonds before maturity. Rolling down the yield curve can help mitigate these losses by selling existing bonds and reinvesting in new bonds with higher yields. This approach can also help investors take advantage of the rising rate environment by capturing higher yields on their new bond investments.
However, rolling down the yield curve in a rising rate environment also presents some challenges. For example, investors may face higher interest rate risk, as rising rates can lead to higher yields on new bonds, but also increase the risk of losses on existing bonds. Additionally, investors may need to consider the impact of rising rates on the creditworthiness of bond issuers, as higher rates can increase the cost of borrowing and lead to credit downgrades.
To adjust the rolling down the yield curve strategy in a rising rate environment, investors can consider the following tactics:
– Shortening the duration of their bond portfolios to reduce interest rate risk
– Focusing on high-quality bond issuers with strong creditworthiness
– Considering alternative bond investments, such as floating-rate notes or inflation-linked bonds
– Regularly reviewing and rebalancing their bond portfolios to ensure they remain aligned with their investment goals and risk tolerance
By understanding the implications of rolling down the yield curve in a rising rate environment and making adjustments to their strategy, bond investors can navigate this challenging market condition and achieve their investment objectives.
Rolling down the yield curve is a dynamic strategy that requires ongoing monitoring and adjustments to respond to changing market conditions. By incorporating this approach into their overall investment strategy, bond investors can optimize their returns and achieve investment success, even in a rising rate environment.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Yield Curve Management
In conclusion, navigating the bond market requires a deep understanding of the yield curve and its implications on investment decisions. Rolling down the yield curve is a powerful strategy that can help bond investors optimize their returns and manage risk in various market conditions.
By implementing a rolling down the yield curve approach, investors can take advantage of the yield curve’s shape and slope to maximize their returns. This strategy involves regularly reviewing and adjusting the bond portfolio to capture higher yields, minimize interest rate risk, and respond to changing market conditions.
Throughout this article, we have explored the concept of the yield curve, the benefits and risks of rolling down the yield curve, and how to apply this strategy in different market scenarios. We have also examined the implications of rolling down the yield curve in a rising rate environment and compared it to other investment strategies.
The key takeaways from this article are clear: understanding the yield curve is crucial to investment success, and rolling down the yield curve can be a highly effective strategy for bond investors. By mastering the art of yield curve management, investors can optimize their returns, manage risk, and achieve their investment objectives.
Whether you are a seasoned bond investor or just starting to explore the world of fixed-income investing, rolling down the yield curve is a strategy worth considering. With its flexibility, adaptability, and potential for high returns, this approach can help you navigate the complexities of the bond market and achieve investment success.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Par_Yield_Curve_Apr_2020-01-3d27bef7ca0c4320ae2a5699fb798f47.jpg)