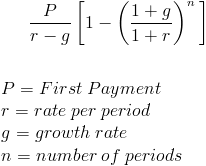Gauging the Worth of Increasing Income: An Introduction
Understanding the present value of growing annuity is crucial for making informed financial decisions. It enables investors and businesses to accurately gauge the worth of future income streams that are expected to increase over time. This calculation is particularly useful in various scenarios, such as evaluating investment opportunities, planning for retirement, and assessing the overall value of companies. The present value of growing annuity helps to understand how much an investment is worth today, taking into account its projected growth. This insight facilitates better resource allocation and strategic planning.
A growing annuity is a series of payments that increase at a constant rate over a specified period. Each payment is higher than the previous one, reflecting the predetermined growth rate. This is different from a regular annuity, where payments remain constant throughout the payment period. A regular annuity involves a fixed payment amount at regular intervals, whereas the payments in a growing annuity increase consistently. This distinction is significant when evaluating investments or liabilities with escalating cash flows. For example, projecting revenue growth or dividend payouts, a growing annuity more accurately reflects the anticipated income stream than a regular annuity would. Therefore, grasping the concept of the present value of growing annuity provides a more precise valuation in situations involving variable income.
To fully appreciate the concept of the present value of growing annuity, its practical applications must be considered. It’s used in evaluating dividend-paying stocks with an anticipated yearly increase in dividend payouts, evaluating the potential of real estate investments with increasing rental yields and assessing business prospects with projected revenue growth. It’s essential to be able to work out the present value of growing annuity, as it provides a more realistic financial assessment of future returns. This calculation enables informed decisions that align with long-term financial objectives and risk tolerance. By considering the growth rate, the investor gains a clearer understanding of the investment’s overall value, leading to better financial outcomes. Understanding the present value of growing annuity is an essential component of financial literacy.
How to Calculate Present Value of Growing Annuity: A Step-by-Step Approach
Calculating the present value of growing annuity involves a straightforward process. This section provides a clear, step-by-step guide. Understanding this calculation is crucial for anyone evaluating investments or planning for the future. The present value of growing annuity helps determine the current worth of a series of payments that increase at a constant rate. The formula for calculating the present value of a growing annuity is: PV = Pmt / (r – g) * [1 – (1 + g)^n / (1 + r)^n]. Let’s break down each component of this formula.
PV represents the present value, which is what we aim to find. Pmt is the payment amount received at the end of the first period. The variable ‘r’ signifies the discount rate, reflecting the rate of return that could be earned on an alternative investment with similar risk. ‘g’ denotes the growth rate, which is the constant percentage increase in payments each period. Finally, ‘n’ represents the number of periods over which the payments will be received. To use the formula, assign values to each variable. Then, perform the calculation by following the order of operations. Start by calculating (1 + g) and (1 + r), raise them to the power of ‘n’, and proceed with the rest of the equation. This step-by-step approach makes it easier to understand and apply the formula effectively to determine the present value of growing annuity.
For example, imagine an annuity with an initial payment (Pmt) of $1,000. It has a discount rate (r) of 8%, a growth rate (g) of 4%, and spans 10 years (n). Input these values into the formula: PV = 1000 / (0.08 – 0.04) * [1 – (1 + 0.04)^10 / (1 + 0.08)^10]. This simplifies to PV = 1000 / 0.04 * [1 – (1.04)^10 / (1.08)^10]. Calculating further, PV = 25000 * [1 – 1.4802 / 2.1589]. Therefore, PV = 25000 * [1 – 0.6856], which results in PV = 25000 * 0.3144. Thus, the present value of this growing annuity is $7,860. This illustrates how the formula is applied in practice to find the present value of growing annuity, providing a tangible understanding of its application.
Essential Factors Influencing Present Value Calculations
The present value of growing annuity calculation is influenced by several key factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate valuation and informed financial decisions. The primary elements affecting the present value of a growing annuity are the discount rate, the growth rate, and the initial payment amount. Each of these components plays a significant role in determining the overall present value.
The discount rate, often reflecting prevailing interest rates or the required rate of return, has an inverse relationship with the present value of growing annuity. A higher discount rate implies a greater opportunity cost or risk, thereby reducing the present value. Conversely, a lower discount rate increases the present value, as future cash flows are discounted at a lower rate. When evaluating investment opportunities, it is crucial to select a discount rate that accurately reflects the risk profile of the investment. Small changes in the discount rate can have a substantial impact on the present value calculation. For instance, if the discount rate used is lower than the actual return, the present value of growing annuity will be overvalued. Conversely, a higher rate reduces the present value and impacts financial assessment.
The growth rate of the annuity payments also significantly affects the present value of growing annuity. A higher growth rate leads to a greater present value, assuming all other factors remain constant. This is because the increasing payments in the future are worth more in today’s terms. However, it is important to note that the growth rate cannot exceed the discount rate; otherwise, the present value calculation becomes mathematically invalid, resulting in a negative or undefined present value. Conservative growth rate estimates are advisable to avoid overstating the present value. The initial payment amount naturally influences the present value, with larger initial payments resulting in a higher present value. It’s also worth noting that the number of periods affects the present value of growing annuity, with longer periods generally increasing present value, provided the growth rate is positive and less than the discount rate. Sensitivity analysis, where different values for these factors are tested, can provide a range of potential present values, aiding in more robust decision-making. The present value of growing annuity is closely linked to these elements, and a detailed analysis of each is essential for precise valuation.
Illustrative Examples: Real-World Applications in Finance
The present value of growing annuity concept finds numerous applications in finance. Consider a dividend-paying stock. Imagine a company currently pays an annual dividend of $2 per share. Analysts project this dividend to grow at a rate of 5% per year. An investor wants to determine the present value of this growing stream of dividends over the next 10 years. The investor’s required rate of return (discount rate) is 10%. Using the present value of growing annuity formula, the calculation would be: PV = $2 / (0.10 – 0.05) * [1 – (1 + 0.05)^10 / (1 + 0.10)^10]. This evaluates to PV = $2 / 0.05 * [1 – (1.05)^10 / (1.10)^10], which results in a present value of approximately $15.44. This suggests the investor should be willing to pay up to $15.44 for each share of this stock, assuming the growth and discount rate assumptions are accurate.
Another practical application is in real estate investment. Suppose an investor is evaluating a rental property. The property currently generates $12,000 in annual rental income. The income is expected to grow at a rate of 3% per year. The investor plans to hold the property for 15 years. Their required rate of return is 8%. To calculate the present value of this growing annuity of rental income, the formula is: PV = $12,000 / (0.08 – 0.03) * [1 – (1 + 0.03)^15 / (1 + 0.08)^15]. Simplifying, PV = $12,000 / 0.05 * [1 – (1.03)^15 / (1.08)^15]. This results in a present value of approximately $119,372. This indicates the investor should consider purchasing the property if the price is below this present value, given their expected return and growth assumptions. The present value of growing annuity helps in informed decision-making.
Businesses also use the present value of growing annuity to assess potential opportunities. A company is considering launching a new product line. They project the product will generate $50,000 in revenue in the first year, with an expected growth rate of 7% annually for the next 5 years. The company’s discount rate is 12%. The present value of this growing stream of revenue is calculated as: PV = $50,000 / (0.12 – 0.07) * [1 – (1 + 0.07)^5 / (1 + 0.12)^5]. This simplifies to PV = $50,000 / 0.05 * [1 – (1.07)^5 / (1.12)^5], giving a present value of approximately $201,473. This represents the present value of the projected revenues. Businesses leverage the present value of growing annuity for strategic financial planning.
Leveraging Tools and Resources: Online Calculators and Software
Calculating the present value of a growing annuity can be simplified significantly using various tools and resources. Numerous online calculators are readily available. These calculators often require users to input the payment amount, discount rate, growth rate, and number of periods. The calculator then performs the complex calculation, providing the present value of the growing annuity quickly and efficiently. This eliminates the need for manual calculations, reducing the risk of errors and saving valuable time. Many offer additional features, such as sensitivity analysis, allowing users to explore how changes in input variables affect the present value.
Spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, also provides powerful tools for calculating the present value of a growing annuity. Excel’s built-in financial functions, like PV, can be used to perform this calculation. This offers greater flexibility than online calculators. Users can create customized spreadsheets to perform the calculation repeatedly with different inputs. They can also incorporate other financial formulas to conduct more comprehensive financial analysis. This allows for a more detailed and adaptable approach to present value calculations.
Specialized financial software packages offer even more advanced features. These often include sophisticated modeling capabilities. These programs provide users with comprehensive tools for financial planning and analysis. They allow for more complex scenarios involving the present value of a growing annuity. While these advanced tools are beneficial, it’s crucial to remember that the accuracy of any calculation depends on the accuracy of the input data. Users should always understand the underlying assumptions and limitations of any tool they employ when calculating the present value of a growing annuity. A thorough understanding of the underlying principles remains paramount.
Distinguishing Growing Annuities From Other Financial Instruments
Understanding the present value of a growing annuity requires differentiating it from other financial instruments. A regular annuity involves a fixed payment stream over a set period. Unlike a growing annuity, the payments do not increase over time. The present value calculation for a regular annuity is simpler, omitting the growth rate component. This simpler calculation is useful when evaluating investments with consistent cash flows, such as a bond paying fixed coupon payments.
Perpetuities represent a stream of payments that continues indefinitely. The present value of a perpetuity uses a slightly modified formula that does not involve the number of periods (n), as the payments never end. A growing perpetuity extends this concept to include a constant growth rate in the payments. The present value of a growing perpetuity is useful for valuing assets with expected perpetual income streams, though realistically, such streams often face eventual termination. While both growing annuities and perpetuities account for growth, the finite timeframe of a growing annuity is a crucial difference impacting its present value. The present value of a growing annuity reflects the value of a series of increasing payments over a defined period.
Lump-sum payments, in contrast, represent a single payment received at a future date. The present value calculation for a lump sum simply discounts the future amount back to its current equivalent value using the discount rate. This is a simpler calculation than that for a growing annuity, which deals with multiple payments and the added complexity of the growth rate. Investors need to consider these differences to assess the suitability of each financial instrument for their particular goals. The choice between a lump-sum payment, a regular annuity, a perpetuity, or a present value of a growing annuity depends greatly on the specific characteristics of the cash flow and the investor’s time horizon.
Potential Pitfalls and Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating the Present Value of a Growing Annuity
Calculating the present value of a growing annuity requires precision. Inaccurate estimations can stem from using an inappropriate discount rate. The discount rate reflects the opportunity cost of capital and prevailing market interest rates. An incorrect discount rate significantly impacts the present value calculation. Overestimating the discount rate lowers the present value, while underestimating it inflates the value. Accurate forecasting of future interest rates is crucial but challenging, impacting the reliability of the present value of a growing annuity.
Another common mistake involves neglecting the growth rate. The growth rate represents the anticipated increase in future payments. Failing to incorporate a realistic growth rate leads to miscalculations. If the growth rate is underestimated, the present value will be too low. Conversely, overestimating the growth rate results in an overvalued present value of a growing annuity. Sensitivity analysis, exploring various growth rate scenarios, helps mitigate this risk. The present value calculation is highly sensitive to both the discount rate and the growth rate, so care must be taken when inputting these variables.
Furthermore, misinterpreting the results is a frequent error. The present value of a growing annuity provides a snapshot of the future cash flows’ current worth. It does not represent the future value or the final amount received. Investors should understand this crucial distinction. The calculation assumes constant growth, which is rarely perfectly accurate in real-world scenarios. Unexpected economic shifts or changes in the underlying asset can disrupt this assumption, affecting the accuracy of the present value of a growing annuity. Therefore, it is essential to use this calculation as one component of a broader investment analysis, not as the sole decision-making factor.
Mastering Growing Annuity Valuation: A Summary and Conclusion
Understanding the present value of a growing annuity is crucial for sound financial decision-making. This guide has provided a step-by-step approach to calculating the present value of a growing annuity, explaining the formula and its key variables. The impact of discount rates, growth rates, and payment amounts on the present value calculation has been explored. Various real-world applications, from valuing dividend-paying stocks to assessing business opportunities, have been illustrated. Utilizing online calculators and spreadsheet software can streamline the process, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Remember to always understand the underlying assumptions and limitations of the model.
Accurate calculation of the present value of a growing annuity requires careful consideration of several factors. Failing to account for growth rates or using incorrect discount rates can lead to significant errors. The model’s assumption of constant growth should be carefully considered. The present value of a growing annuity differs significantly from other financial instruments like regular annuities, perpetuities, and lump-sum payments. Recognizing these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate financial instrument for specific investment scenarios. Mastering the concepts presented here empowers informed financial decisions. The ability to accurately assess the present value of future income streams offers a significant advantage in various investment and business contexts.
This comprehensive overview of the present value of a growing annuity equips readers with the knowledge to make informed financial decisions. By understanding the factors affecting the calculation, leveraging available tools, and avoiding common pitfalls, individuals and businesses can accurately assess the value of future income streams. The present value of a growing annuity calculation is a valuable skill, applicable across numerous financial scenarios. Continued learning about related financial topics will further enhance this valuable skill set. This knowledge empowers more strategic and effective financial planning.