What Are Prepaid Expenses and Why Do They Matter?
In financial reporting, prepaid expenses play a vital role in ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. A prepaid expense is a payment made by a business for goods or services that have not yet been received. These expenses are essential for businesses to operate efficiently, as they provide a means to allocate costs to future periods. Common examples of prepaid expenses include rent, insurance premiums, and subscription services. For instance, a company may pay for a year’s worth of insurance coverage upfront, which would be recorded as a prepaid expense on the balance sheet. By understanding prepaid expenses and their significance in financial reporting, businesses can ensure accurate financial statements, including the balance sheet, and make informed decisions about their financial resources.
How to Record Prepaid Expenses on Your Balance Sheet
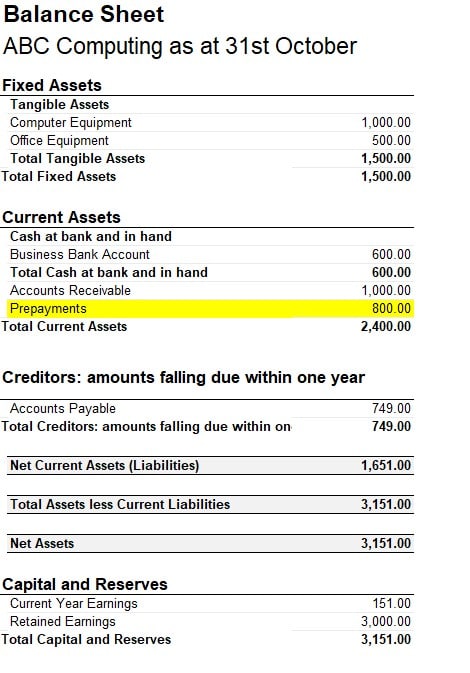
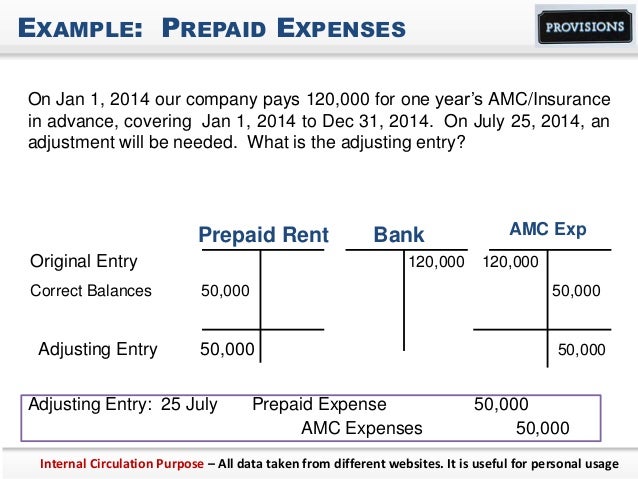
Recording prepaid expenses on a balance sheet is a crucial step in accurate financial reporting. To ensure compliance with accounting standards, businesses must follow a specific process for recording prepaid expenses. The correct accounting treatment for prepaid expenses involves initially recording the payment as a prepaid expense asset on the balance sheet. This is typically done using the following journal entry: Debit Prepaid Expense Asset (asset account) and Credit Cash (asset account). For example, if a company pays $12,000 for a year’s worth of insurance coverage upfront, the initial journal entry would be: Debit Prepaid Insurance Expense ($12,000) and Credit Cash ($12,000). As the insurance coverage is used up over time, the prepaid expense asset is gradually expensed and matched with the revenue it relates to. This process is known as amortization, and it ensures that the expense is recognized in the correct period. By following this step-by-step process, businesses can accurately record prepaid expenses on their balance sheet, providing a clear picture of their financial position.
The Difference Between Prepaid Expenses and Assets
In financial reporting, it is essential to distinguish between prepaid expenses and assets, as they are often confused or misclassified. A prepaid expense is a payment made for goods or services that have not yet been received, whereas an asset is a resource controlled by the business that is expected to generate future economic benefits. To illustrate the difference, consider a company that pays $10,000 for a year’s worth of software subscription. This payment would be classified as a prepaid expense, as the software has not yet been used. In contrast, if the company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000, this would be classified as an asset, as it is expected to generate future economic benefits. To determine whether a payment should be classified as a prepaid expense or an asset, businesses should consider the following factors: the nature of the payment, the timing of the payment, and the expected benefits. By understanding the key characteristics of prepaid expenses and assets, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting and avoid misclassification errors. This, in turn, can have a significant impact on the accuracy of the balance sheet, particularly when it comes to prepaid expenses on balance sheet.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Accounting for Prepaid Expenses
When accounting for prepaid expenses, businesses often make mistakes that can have a significant impact on the accuracy of their financial reports. One common error is misclassifying prepaid expenses as assets. This can occur when a business pays for a service or good that has not yet been received, but mistakenly records it as an asset on the balance sheet. For example, if a company pays for a year’s worth of insurance coverage upfront, it should be recorded as a prepaid expense, not an asset. Another common mistake is failing to amortize prepaid expenses correctly. This can lead to inaccurate financial reporting, as the expense is not matched with the revenue it relates to. To avoid these mistakes, businesses should ensure that they have a clear understanding of the accounting treatment for prepaid expenses and implement a systematic approach to recording and amortizing them. This includes setting up a prepaid expense account, tracking payments, and performing regular reconciliations. By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses can ensure that their financial reports accurately reflect their financial position, including prepaid expenses on balance sheet.
The Impact of Prepaid Expenses on Financial Ratios and Analysis
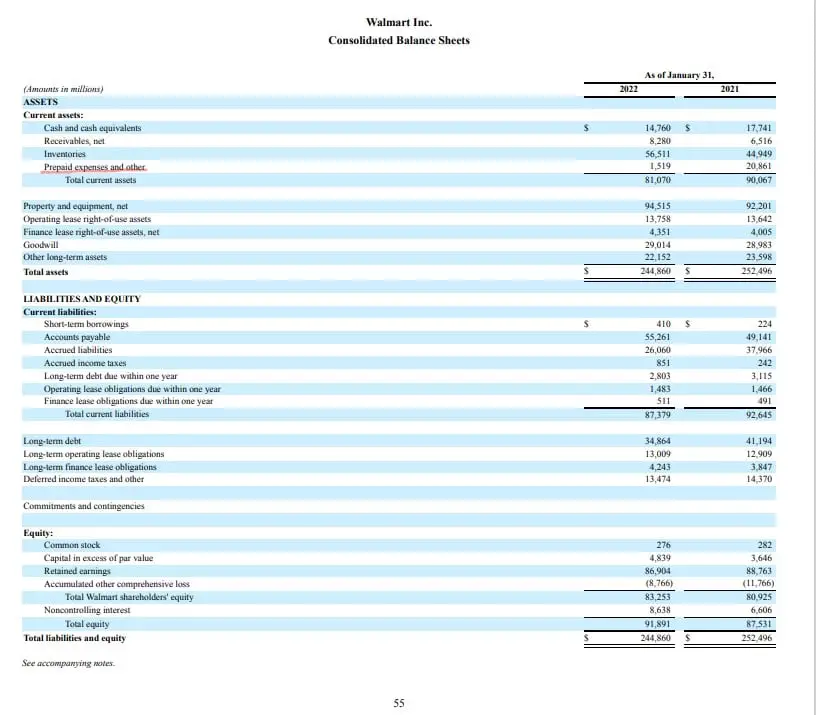
Prepaid expenses can have a significant impact on financial ratios and analysis, making it essential to accurately account for them on the balance sheet. One of the key ratios affected by prepaid expenses is the current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts. If prepaid expenses are not properly accounted for, the current ratio may be overstated, leading to inaccurate conclusions about a company’s liquidity. Similarly, the quick ratio, which excludes inventory and other current assets, can also be affected by prepaid expenses. Additionally, prepaid expenses can impact cash flow statements, as they represent a cash outlay that has not yet been matched with revenue. To adjust for prepaid expenses when analyzing financial performance, businesses should consider the following: first, identify the prepaid expenses on the balance sheet; second, determine the period over which the expense will be amortized; and third, adjust the financial ratios and analysis accordingly. By taking these steps, businesses can ensure that their financial analysis accurately reflects their financial position, including prepaid expenses on balance sheet. This, in turn, can inform better decision-making and drive business success.
Prepaid Expenses in Different Industries: Unique Considerations
While prepaid expenses are a common feature of financial reporting across various industries, there are unique considerations and best practices that apply to specific sectors. In the real estate industry, for example, prepaid expenses may include rent, property taxes, and insurance premiums. To accurately account for these expenses, real estate companies should ensure that they are properly amortized over the relevant period. In the healthcare industry, prepaid expenses may include medical equipment leases, insurance premiums, and subscription services. Healthcare providers should be mindful of the specific accounting rules and regulations that apply to their industry, such as those related to Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement. In the retail industry, prepaid expenses may include inventory purchases, rent, and marketing expenses. Retailers should ensure that they are accurately tracking and amortizing these expenses to reflect their financial performance accurately. By understanding the unique considerations and best practices for prepaid expenses in their industry, businesses can ensure that they are accurately accounting for these expenses on their balance sheet, including prepaid expenses on balance sheet, and making informed decisions about their financial performance.
Best Practices for Managing Prepaid Expenses in Your Business
To ensure accurate and effective management of prepaid expenses, businesses should implement the following best practices. First, set up a prepaid expense account to track and record all prepaid expenses. This will enable easy identification and amortization of these expenses over the relevant period. Second, establish a system for tracking payments and receipts related to prepaid expenses, including invoices, receipts, and bank statements. This will help to ensure that all prepaid expenses are properly accounted for and amortized. Third, perform regular reconciliations of the prepaid expense account to ensure that it is accurate and up-to-date. This will help to identify any errors or discrepancies and enable prompt correction. Additionally, businesses should establish a clear policy for prepaid expenses, including guidelines for when to capitalize and amortize prepaid expenses, and how to account for them on the balance sheet, including prepaid expenses on balance sheet. By following these best practices, businesses can ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for, and that their financial reporting is reliable and informative.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Prepaid Expense Accounting
In conclusion, prepaid expenses play a critical role in accurate financial reporting and decision-making. By understanding what prepaid expenses are, how to record them on the balance sheet, and how to manage them effectively, businesses can ensure that their financial statements are reliable and informative. Accurate prepaid expense accounting is essential for making informed decisions about investments, funding, and resource allocation. It also enables businesses to comply with accounting standards and regulations, and to avoid costly errors and penalties. By following the best practices outlined in this article, businesses can ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for, and that their financial performance is accurately reflected on their balance sheet, including prepaid expenses on balance sheet. Ultimately, accurate prepaid expense accounting is crucial for business success, and is an essential component of effective financial management.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prepaid-expense-4191042-recirc-blue-1d8d154bf0c94ba6858fe12907d2b694.jpg)