What are Prepaid Expenses and Why Do They Matter?
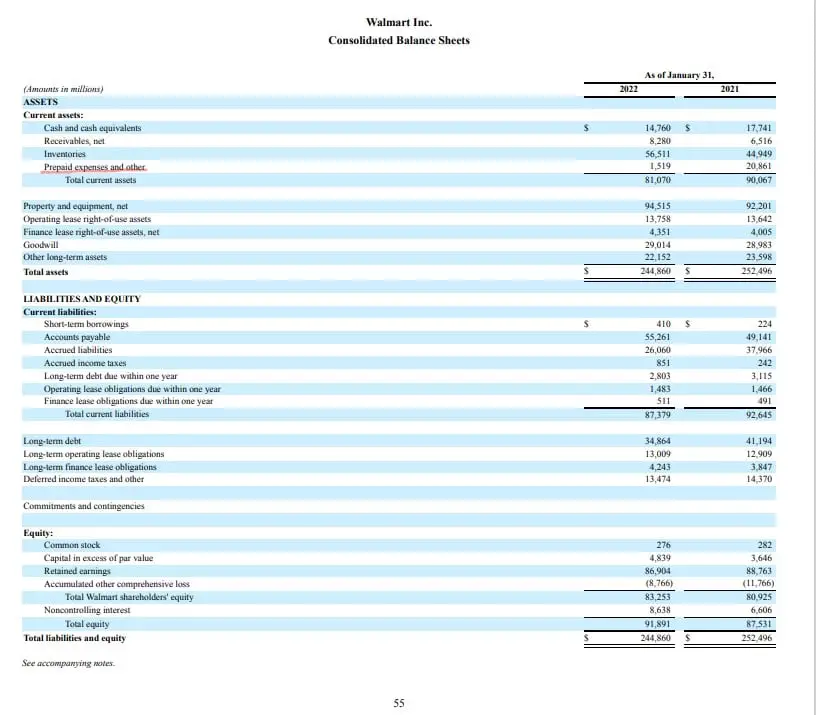
In the realm of financial reporting, prepaid expenses play a vital role in accurately reflecting a company’s financial position. Prepaid expenses in balance sheet refer to payments made by a business for goods or services that have not yet been received or consumed. These expenses are essential to a company’s financial health, as they impact both the balance sheet and cash flow.
By understanding prepaid expenses, businesses can better manage their finances, make informed decisions, and ensure compliance with accounting standards. Prepaid expenses in balance sheet are a type of asset, as they represent a future benefit to the business. When a company prepays for a service or product, it is essentially paying for something that will be received or used in the future.
This prepaid amount is initially recorded as an asset on the balance sheet, and then gradually expensed over time as the benefit is received. For instance, if a company prepays for a year’s worth of insurance, the initial payment is recorded as an asset, and then expensed monthly as the insurance coverage is used. The significance of prepaid expenses lies in their ability to provide a more accurate picture of a company’s financial situation.
How to Account for Prepaid Expenses in Your Balance Sheet
Accurate accounting for prepaid expenses in balance sheet is crucial for a company’s financial reporting. To ensure compliance with accounting standards and maintain a healthy financial position, businesses must properly record and manage prepaid expenses. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to account for prepaid expenses in your balance sheet:
Step 1: Identify Prepaid Expenses – The first step is to identify the prepaid expenses in your business. This includes payments made for goods or services that have not yet been received or consumed, such as rent, insurance, and subscriptions.
Step 2: Record the Initial Payment – When a prepaid expense is incurred, record the initial payment as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet. This is typically done by debiting the prepaid asset account and crediting the cash account.
Step 3: Expense the Prepaid Asset – As the benefit of the prepaid expense is received, expense the prepaid asset over time. This is typically done by debiting the expense account and crediting the prepaid asset account.
Example: Suppose a company prepays $12,000 for a year’s worth of insurance coverage. The initial payment would be recorded as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet. Each month, $1,000 would be expensed as the insurance coverage is used.
By following these steps, businesses can ensure accurate accounting for prepaid expenses in balance sheet and maintain a healthy financial position. Proper management of prepaid expenses can also help optimize cash flow, reduce costs, and improve financial performance.
The Difference Between Prepaid Expenses and Accrued Expenses
In financial reporting, it’s essential to distinguish between prepaid expenses and accrued expenses, as they have distinct characteristics and accounting treatments. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial for accurate financial reporting and informed business decisions.
Prepaid expenses, as discussed earlier, refer to payments made by a business for goods or services that have not yet been received or consumed. These expenses are initially recorded as assets on the balance sheet and then gradually expensed over time as the benefit is received.
Accrued expenses, on the other hand, represent expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid. These expenses are typically recorded as liabilities on the balance sheet and are expensed when payment is made. Examples of accrued expenses include salaries owed to employees, taxes owed to the government, and utilities used but not yet billed.
The key differences between prepaid expenses and accrued expenses lie in their timing and accounting treatment. Prepaid expenses are paid before they are used, while accrued expenses are used before they are paid. Prepaid expenses are initially recorded as assets, while accrued expenses are recorded as liabilities.
For instance, suppose a company prepays $10,000 for a year’s worth of insurance coverage. This would be recorded as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet. In contrast, if the company incurs $5,000 in salaries owed to employees but has not yet paid them, this would be recorded as an accrued expense liability on the balance sheet.
By understanding the distinction between prepaid expenses and accrued expenses, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting, optimize cash flow, and make informed decisions about their financial resources.
Common Examples of Prepaid Expenses in Business
Prepaid expenses are a common phenomenon in business, and they can take many forms. Understanding these examples can help businesses identify and account for prepaid expenses in their financial reporting. Here are some common examples of prepaid expenses in business:
Rent: Many businesses pay rent in advance for their offices, warehouses, or retail spaces. This prepaid rent is initially recorded as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet and then expensed over the rental period.
Insurance: Companies often pay insurance premiums in advance to cover their assets, employees, or business operations. These prepaid insurance premiums are recorded as prepaid assets and expensed over the insurance coverage period.
Subscriptions: Businesses may pay for software, cloud services, or membership subscriptions in advance. These prepaid subscriptions are recorded as prepaid assets and expensed over the subscription period.
Utilities: Companies may pay for utilities such as electricity, gas, or water in advance. These prepaid utilities are recorded as prepaid assets and expensed over the utility period.
Travel and Training: Businesses may pay for employee travel or training expenses in advance. These prepaid expenses are recorded as prepaid assets and expensed over the travel or training period.
Advertising: Companies may pay for advertising services in advance, such as print or online ads. These prepaid advertising expenses are recorded as prepaid assets and expensed over the advertising period.
By recognizing and accounting for these common examples of prepaid expenses, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting, optimize cash flow, and make informed decisions about their financial resources. Prepaid expenses in balance sheet play a critical role in financial management, and understanding these examples can help businesses master asset management.
The Impact of Prepaid Expenses on Financial Ratios and Analysis
Prepaid expenses have a significant impact on a company’s financial ratios and analysis, which are crucial for investors, analysts, and other stakeholders to evaluate a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions. Understanding how prepaid expenses affect these metrics is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis.
The current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts, is significantly influenced by prepaid expenses. When a company prepays for goods or services, it initially records the payment as a prepaid asset on the balance sheet. As the benefit is received, the prepaid asset is gradually expensed, reducing the current ratio. Therefore, analysts and investors must consider prepaid expenses when evaluating a company’s liquidity and ability to meet its short-term obligations.
Cash flow statements are also affected by prepaid expenses. When a company prepays for goods or services, it reduces its cash outflow, which can improve its cash flow from operations. However, as the prepaid asset is expensed, it reduces the cash flow from operations, making it essential to consider prepaid expenses when analyzing a company’s cash flow.
Return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE) are also impacted by prepaid expenses. As prepaid expenses are initially recorded as assets, they can inflate a company’s asset base, reducing its ROA and ROE. However, as the prepaid asset is expensed, it reduces the asset base, increasing ROA and ROE.
Analysts and investors must carefully consider prepaid expenses when evaluating a company’s financial performance. By understanding the impact of prepaid expenses on financial ratios and analysis, they can make more informed decisions about investments, credit, and other business opportunities. Accurate accounting and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet are critical for reliable financial analysis and decision-making.
In conclusion, prepaid expenses have a significant impact on a company’s financial ratios and analysis. By understanding how prepaid expenses affect these metrics, analysts and investors can make more informed decisions and evaluate a company’s financial performance more accurately.
Managing Prepaid Expenses for Better Cash Flow Management
Effective management of prepaid expenses is crucial for businesses to optimize cash flow, reduce costs, and improve financial performance. By understanding how to manage prepaid expenses, companies can make informed decisions about their financial resources and achieve their goals.
One key strategy for managing prepaid expenses is to identify and prioritize essential expenses. Businesses should categorize their prepaid expenses into essential and non-essential expenses, focusing on the most critical expenses that impact their operations. This approach enables companies to allocate their financial resources more efficiently and make better decisions about their prepaid expenses.
Another important strategy is to negotiate with suppliers and vendors. Businesses can negotiate with their suppliers and vendors to obtain better payment terms, discounts, or other benefits that can help reduce their prepaid expenses. By building strong relationships with their suppliers and vendors, companies can optimize their prepaid expenses and improve their cash flow.
Implementing a prepaid expense management system is also essential for effective management. This system should be able to track and record prepaid expenses, provide real-time updates, and offer insights into expense trends and patterns. By using a prepaid expense management system, businesses can streamline their expense management process, reduce errors, and make more informed decisions.
Additionally, businesses should regularly review and analyze their prepaid expenses to identify areas for improvement. This review should include an analysis of expense trends, vendor performance, and cash flow impact. By regularly reviewing and analyzing their prepaid expenses, companies can identify opportunities to reduce costs, optimize cash flow, and improve their financial performance.
Finally, businesses should ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately recorded and reported in their balance sheet. Accurate accounting and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet are critical for reliable financial analysis and decision-making. By ensuring that their prepaid expenses are accurately recorded and reported, companies can make more informed decisions about their financial resources and achieve their goals.
By implementing these strategies, businesses can effectively manage their prepaid expenses, optimize cash flow, reduce costs, and improve their financial performance. Effective prepaid expense management is critical for businesses to achieve their goals and succeed in today’s competitive market.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Prepaid Expense Accounting
Accurate accounting and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet are critical for reliable financial analysis and decision-making. However, common mistakes and misconceptions in prepaid expense accounting can lead to errors, misstatements, and inaccurate financial reporting. To avoid these mistakes, it is essential to understand the common pitfalls and take steps to prevent them.
One common mistake is misclassifying prepaid expenses as assets or liabilities. Prepaid expenses should be recorded as assets on the balance sheet, but they are often mistakenly recorded as liabilities or expenses. This error can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and misstatements.
Another mistake is failing to amortize prepaid expenses over the correct period. Prepaid expenses should be amortized over the period they relate to, but businesses often fail to do so, leading to inaccurate financial reporting and misstatements.
Not accounting for prepaid expenses in the correct accounting period is another common mistake. Prepaid expenses should be recorded in the period they are paid, not when they are incurred. This error can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and misstatements.
Additionally, businesses often fail to consider the impact of prepaid expenses on their cash flow statements. Prepaid expenses can significantly impact a company’s cash flow, and failing to consider this impact can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and misstatements.
To avoid these common mistakes, businesses should ensure that they have a clear understanding of prepaid expenses and their accounting treatment. They should also implement robust accounting processes and controls to ensure accurate recording and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet.
Regular review and analysis of prepaid expenses can also help identify and correct errors and misconceptions. By regularly reviewing and analyzing their prepaid expenses, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting and decision-making.
Finally, businesses should ensure that their accounting staff and personnel are trained and knowledgeable about prepaid expense accounting. This can help prevent errors and misconceptions and ensure accurate financial reporting and decision-making.
By avoiding common mistakes in prepaid expense accounting, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting, reliable financial analysis, and informed decision-making. Accurate accounting and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet are critical for business success, and avoiding common mistakes is essential for achieving this goal.
Best Practices for Prepaid Expense Management in Different Industries
Effective prepaid expense management is crucial for businesses across various industries. However, each industry has its unique challenges and opportunities when it comes to managing prepaid expenses. In this section, we will discuss industry-specific best practices for prepaid expense management, highlighting the key considerations and strategies for different sectors.
In the retail industry, prepaid expenses such as rent, utilities, and inventory are common. To manage these expenses effectively, retailers should implement a robust inventory management system to track and optimize their prepaid expenses. They should also negotiate with suppliers to obtain better payment terms and discounts.
In the technology industry, prepaid expenses such as software licenses, subscriptions, and research and development costs are prevalent. To manage these expenses effectively, tech companies should implement a centralized expense management system to track and record their prepaid expenses. They should also consider outsourcing certain functions to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
In the healthcare industry, prepaid expenses such as medical equipment, supplies, and insurance are common. To manage these expenses effectively, healthcare providers should implement a robust asset management system to track and optimize their prepaid expenses. They should also negotiate with suppliers to obtain better payment terms and discounts.
In the manufacturing industry, prepaid expenses such as raw materials, equipment, and labor are prevalent. To manage these expenses effectively, manufacturers should implement a robust production planning system to track and optimize their prepaid expenses. They should also consider implementing just-in-time inventory management to reduce costs and improve efficiency.
Regardless of the industry, businesses should ensure that they have a clear understanding of their prepaid expenses and their accounting treatment. They should also implement robust accounting processes and controls to ensure accurate recording and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet.
By following these industry-specific best practices, businesses can effectively manage their prepaid expenses, optimize cash flow, reduce costs, and improve financial performance. Accurate accounting and reporting of prepaid expenses in balance sheet are critical for business success, and understanding the unique challenges and opportunities of each industry is essential for achieving this goal.