What are Prepaid Assets and Why Do They Matter?
In the world of finance, prepaid assets on the balance sheet play a crucial role in a company’s financial health and decision-making processes. A prepaid asset is a payment made by a business for goods or services that will be received in the future. These assets are recorded on the balance sheet as a current asset, typically under the category of “prepaid expenses” or “prepaid assets.” The significance of prepaid assets lies in their ability to provide a clear picture of a company’s financial position and performance. By accurately recording and managing prepaid assets on the balance sheet, businesses can make informed decisions about their cash flow, investments, and resource allocation. In essence, prepaid assets on the balance sheet serve as a critical component of a company’s financial foundation, enabling businesses to navigate the complexities of financial management with confidence.
How to Identify and Record Prepaid Assets on Your Balance Sheet
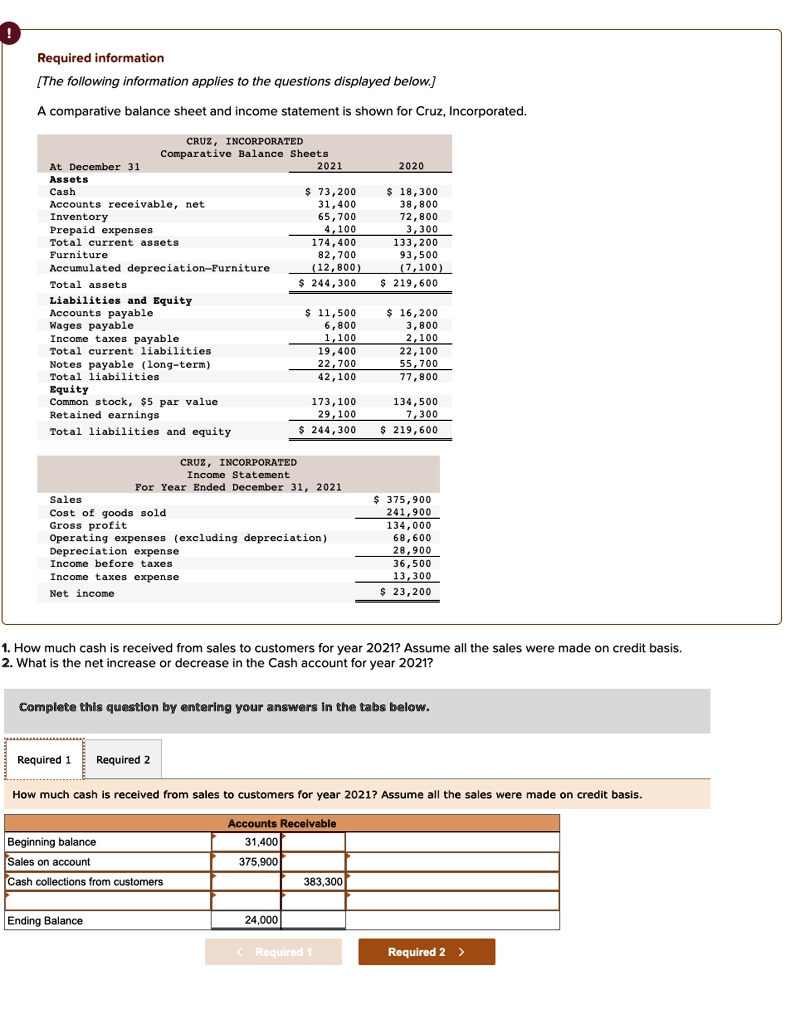
Identifying and recording prepaid assets on the balance sheet is a crucial step in maintaining accurate financial records. To identify prepaid assets, businesses should review their financial transactions and identify payments made for goods or services that will be received in the future. These payments can include prepaid rent, insurance premiums, software subscriptions, and other expenses. Once identified, prepaid assets should be recorded on the balance sheet as a current asset, typically under the category of “prepaid expenses” or “prepaid assets.”
The accounting treatment of prepaid assets involves initially recording the payment as a prepaid asset, and then gradually expensing it over the period of benefit. For example, if a company pays $12,000 for a one-year insurance policy, the initial entry would be to debit prepaid insurance and credit cash for $12,000. Each month, the company would then expense $1,000 (1/12 of the total payment) by debiting insurance expense and crediting prepaid insurance. This ensures that the expense is matched with the period of benefit, providing a more accurate picture of the company’s financial performance.
Accurate recording and management of prepaid assets on the balance sheet is essential for businesses to make informed decisions about their financial health and performance. By following these steps, companies can ensure that their prepaid assets are properly accounted for and reflected on their balance sheet, providing a clear picture of their financial position and enabling them to make strategic decisions for future growth.
The Difference Between Prepaid Assets and Other Current Assets
In the realm of current assets, prepaid assets on the balance sheet occupy a unique position, distinct from other current assets such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventory. While all these assets are expected to be converted into cash or consumed within a year, prepaid assets are characterized by their prepayment for goods or services that will be received in the future. This fundamental difference is crucial for accurate financial reporting and decision-making.
Cash, for instance, is a liquid asset that can be readily used to meet financial obligations. Accounts receivable, on the other hand, represent amounts owed to the company for goods or services already delivered. Inventory, meanwhile, consists of goods or materials held for sale, production, or distribution. In contrast, prepaid assets on the balance sheet represent payments made in advance for goods or services that will be received in the future, such as prepaid rent, insurance premiums, or software subscriptions.
The distinction between prepaid assets and other current assets is vital because it affects how these assets are valued, reported, and utilized in financial analysis. By recognizing the unique characteristics of prepaid assets, businesses can ensure that they are accurately reflected on the balance sheet, providing a more comprehensive picture of the company’s financial position and performance. This, in turn, enables informed decision-making and strategic planning for future growth and success.
Common Examples of Prepaid Assets in Business Operations
In various industries, prepaid assets on the balance sheet play a vital role in facilitating business operations. These assets can take many forms, and understanding their applications is essential for effective financial management. Here are some common examples of prepaid assets:
Prepaid rent is a common prepaid asset in the real estate and property management industries. By paying rent in advance, companies can secure a location for their operations and avoid last-minute scrambles to find alternative spaces. Similarly, prepaid insurance premiums are a type of prepaid asset that provides protection against unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or accidents.
In the technology sector, prepaid software subscriptions are a popular example of prepaid assets. These subscriptions provide access to essential software tools and services, enabling companies to streamline their operations and improve productivity. Other examples of prepaid assets include prepaid utility deposits, prepaid maintenance contracts, and prepaid advertising expenses.
These prepaid assets are used in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, and retail. For instance, a hospital may prepay for medical equipment or supplies, while a manufacturer may prepay for raw materials or machinery. In the retail sector, companies may prepay for inventory or advertising expenses.
By recognizing and understanding these common examples of prepaid assets, businesses can better manage their finances, optimize their cash flow, and make informed decisions about their operations. Effective management of prepaid assets on the balance sheet is crucial for achieving long-term financial success and sustainability.
The Impact of Prepaid Assets on Cash Flow and Financial Ratios
Prepaid assets on the balance sheet have a significant impact on a company’s cash flow, financial ratios, and overall financial performance. By understanding how prepaid assets affect these key financial metrics, businesses can make informed decisions about their financial management and strategic planning.
Prepaid assets can improve cash flow by reducing the amount of cash required for future expenses. For instance, prepaid rent or insurance premiums can reduce the need for large cash outlays in the future, freeing up cash for other business needs. This can be particularly beneficial for companies with limited liquidity or those operating in industries with fluctuating cash flows.
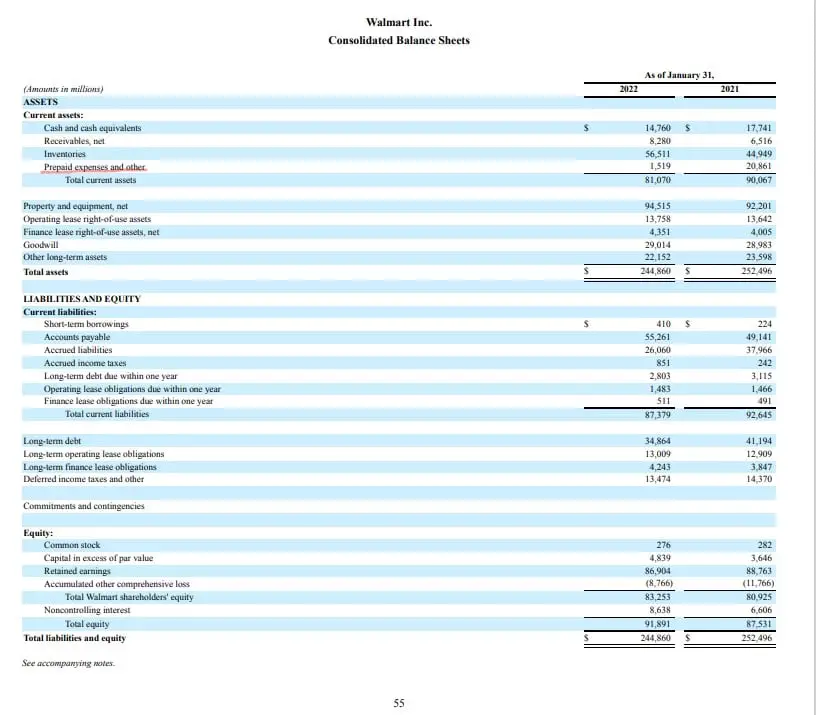
Prepaid assets also influence financial ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio. These ratios measure a company’s ability to pay its short-term debts and are critical for assessing liquidity and financial health. By including prepaid assets in these ratios, businesses can gain a more accurate picture of their financial position and make adjustments to optimize their liquidity.
In addition, prepaid assets can affect a company’s financial performance metrics, such as return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE). By properly valuing and accounting for prepaid assets, businesses can ensure that these metrics accurately reflect their financial performance and make informed decisions about investments and resource allocation.
For example, a company that prepays for software subscriptions may recognize the expense over the subscription period, rather than upfront. This can improve the company’s ROA and ROE by spreading the expense over time, rather than recognizing it all at once. Similarly, a company that prepays for insurance premiums may reduce its cash outlays in the future, freeing up cash for other business needs and improving its financial performance.
By understanding the impact of prepaid assets on cash flow, financial ratios, and financial performance, businesses can optimize their financial management and make informed decisions about their operations. Effective management of prepaid assets on the balance sheet is crucial for achieving long-term financial success and sustainability.
Managing Prepaid Assets for Optimal Financial Performance
Effective management of prepaid assets on the balance sheet is crucial for achieving optimal financial performance. By implementing best practices and strategies, businesses can minimize waste, optimize cash flow, and improve financial forecasting. Here are some tips for managing prepaid assets effectively:
First, it’s essential to regularly review and update prepaid asset accounts to ensure accuracy and relevance. This includes monitoring prepaid asset balances, identifying potential errors or discrepancies, and making adjustments as needed. By doing so, businesses can avoid misclassification or incorrect valuation of prepaid assets, which can lead to inaccurate financial reporting.
Second, companies should establish clear policies and procedures for prepaid asset management. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, setting thresholds for prepaid asset expenditures, and establishing approval processes for prepaid asset transactions. By having a structured approach to prepaid asset management, businesses can ensure consistency and transparency in their financial reporting.
Third, businesses should consider implementing a prepaid asset tracking system to monitor and analyze prepaid asset activity. This can include using specialized software or spreadsheets to track prepaid asset balances, identify trends and patterns, and generate reports and analytics. By having a comprehensive view of prepaid asset activity, businesses can make informed decisions about their financial management and strategic planning.
Fourth, companies should prioritize cash flow optimization when managing prepaid assets. This includes identifying opportunities to reduce prepaid asset expenditures, negotiating with suppliers or vendors to secure better terms, and exploring alternative financing options. By optimizing cash flow, businesses can improve their liquidity, reduce debt, and increase their financial flexibility.
Finally, businesses should consider the impact of prepaid assets on their financial forecasting and planning. This includes incorporating prepaid asset data into financial models and forecasts, identifying potential risks and opportunities, and developing strategies to mitigate or capitalize on these factors. By doing so, businesses can improve their financial forecasting, reduce uncertainty, and make more informed decisions about their operations.
By implementing these strategies and best practices, businesses can unlock the full potential of prepaid assets on their balance sheet and achieve optimal financial performance. Effective management of prepaid assets is critical for long-term financial success and sustainability.
Avoiding Common Mistakes in Prepaid Asset Accounting
When it comes to prepaid assets on the balance sheet, accuracy and attention to detail are crucial. However, common mistakes and pitfalls can occur, leading to inaccurate financial reporting and poor decision-making. Here are some common errors to avoid in prepaid asset accounting:
Misclassification of prepaid assets is a common mistake. This occurs when prepaid assets are incorrectly classified as other current assets, such as cash or accounts receivable. To avoid this mistake, it’s essential to understand the definition and characteristics of prepaid assets and to ensure that they are properly classified on the balance sheet.
Incorrect valuation of prepaid assets is another common error. This can occur when the value of prepaid assets is not accurately determined or when the asset is not properly amortized over its useful life. To avoid this mistake, businesses should ensure that they have a clear understanding of the valuation methodology and that they regularly review and update their prepaid asset valuations.
Failing to properly account for prepaid asset amortization is another common mistake. This can occur when the expense is not properly recognized over the useful life of the asset or when the asset is not properly depreciated. To avoid this mistake, businesses should ensure that they have a clear understanding of the amortization schedule and that they regularly review and update their prepaid asset amortization.
Not regularly reviewing and updating prepaid asset accounts is another common mistake. This can occur when businesses fail to regularly review their prepaid asset accounts, leading to inaccuracies and errors. To avoid this mistake, businesses should ensure that they regularly review and update their prepaid asset accounts to ensure accuracy and relevance.
By avoiding these common mistakes and pitfalls, businesses can ensure that their prepaid assets on the balance sheet are accurately accounted for and that they are making informed decisions about their financial management and strategic planning. Effective prepaid asset management is critical for long-term financial success and sustainability.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Prepaid Assets on Your Balance Sheet
In conclusion, prepaid assets on the balance sheet play a critical role in a company’s financial health and decision-making processes. By understanding the significance of prepaid assets, identifying and recording them accurately, and managing them effectively, businesses can unlock their full potential and achieve optimal financial performance.
Throughout this article, we have explored the importance of prepaid assets on the balance sheet, including their definition, accounting treatment, and impact on cash flow and financial ratios. We have also discussed common examples of prepaid assets, strategies for managing them effectively, and common mistakes to avoid in prepaid asset accounting.
The key takeaways from this article are clear: prepaid assets on the balance sheet are a vital component of a company’s financial management and strategic planning. By implementing effective prepaid asset management strategies, businesses can minimize waste, optimize cash flow, and improve financial forecasting. Moreover, by avoiding common mistakes and pitfalls in prepaid asset accounting, businesses can ensure accurate financial reporting and informed decision-making.
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business environment, effective management of prepaid assets on the balance sheet is crucial for long-term financial success and sustainability. By unlocking the full potential of prepaid assets, businesses can gain a competitive edge, improve their financial performance, and achieve their strategic objectives.
By implementing the strategies and best practices outlined in this article, businesses can ensure that their prepaid assets on the balance sheet are accurately accounted for, effectively managed, and optimized for optimal financial performance. Remember, prepaid assets on the balance sheet are a valuable resource that can be leveraged to drive business success – unlock their full potential today!



/dotdash_Final_Other_Current_Assets_OCA_Dec_2020-01-1ef8bd75eff345e7ac48ba70fb718619.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/prepaid-expense-4191042-recirc-blue-1d8d154bf0c94ba6858fe12907d2b694.jpg)