Why Historical Data Matters in Investment Decisions
In the world of finance, making informed investment decisions is crucial for success. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is by leveraging historical data. Nasdaq 100 index historical data, in particular, offers a wealth of information that can help investors navigate the complexities of the market. By analyzing this data, investors can gain valuable insights into market trends, identify patterns, and mitigate risks. This, in turn, can lead to more informed investment decisions, improved portfolio performance, and increased returns. In essence, historical data serves as a guide for investors, helping them make sense of the market and make better decisions.
How to Access and Analyze Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data
Accessing and analyzing Nasdaq 100 index historical data is a crucial step in unlocking its potential for informed investment decisions. There are several sources where investors can obtain this data, including financial websites, data providers, and stock exchanges. Some popular sources include Quandl, Alpha Vantage, and the Nasdaq website itself. Once the data is obtained, investors can use various tools and techniques to analyze it, such as Excel, Python, or R. These tools enable investors to clean, manipulate, and visualize the data, making it easier to identify trends, patterns, and correlations. Additionally, investors can use data analysis techniques such as moving averages, regression analysis, and technical indicators to gain deeper insights into the data. By following these steps, investors can unlock the full potential of Nasdaq 100 index historical data and make more informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Composition and Calculation of the Nasdaq 100 Index
The Nasdaq 100 index is a market-capitalization-weighted index composed of the 100 largest and most actively traded non-financial stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. The index is calculated and maintained by Nasdaq, Inc. and is widely followed by investors as a benchmark for the technology-heavy Nasdaq market. The selection criteria for the Nasdaq 100 index include a minimum market capitalization of $500 million, a minimum average daily trading volume of 200,000 shares, and a listing on the Nasdaq exchange. The index is rebalanced quarterly to ensure that the weights of the constituent stocks remain aligned with their market capitalization. This process involves adjusting the number of shares of each stock in the index to reflect changes in their market capitalization. By understanding the composition and calculation of the Nasdaq 100 index, investors can gain valuable insights into the performance of the technology sector and make more informed investment decisions using Nasdaq 100 index historical data.
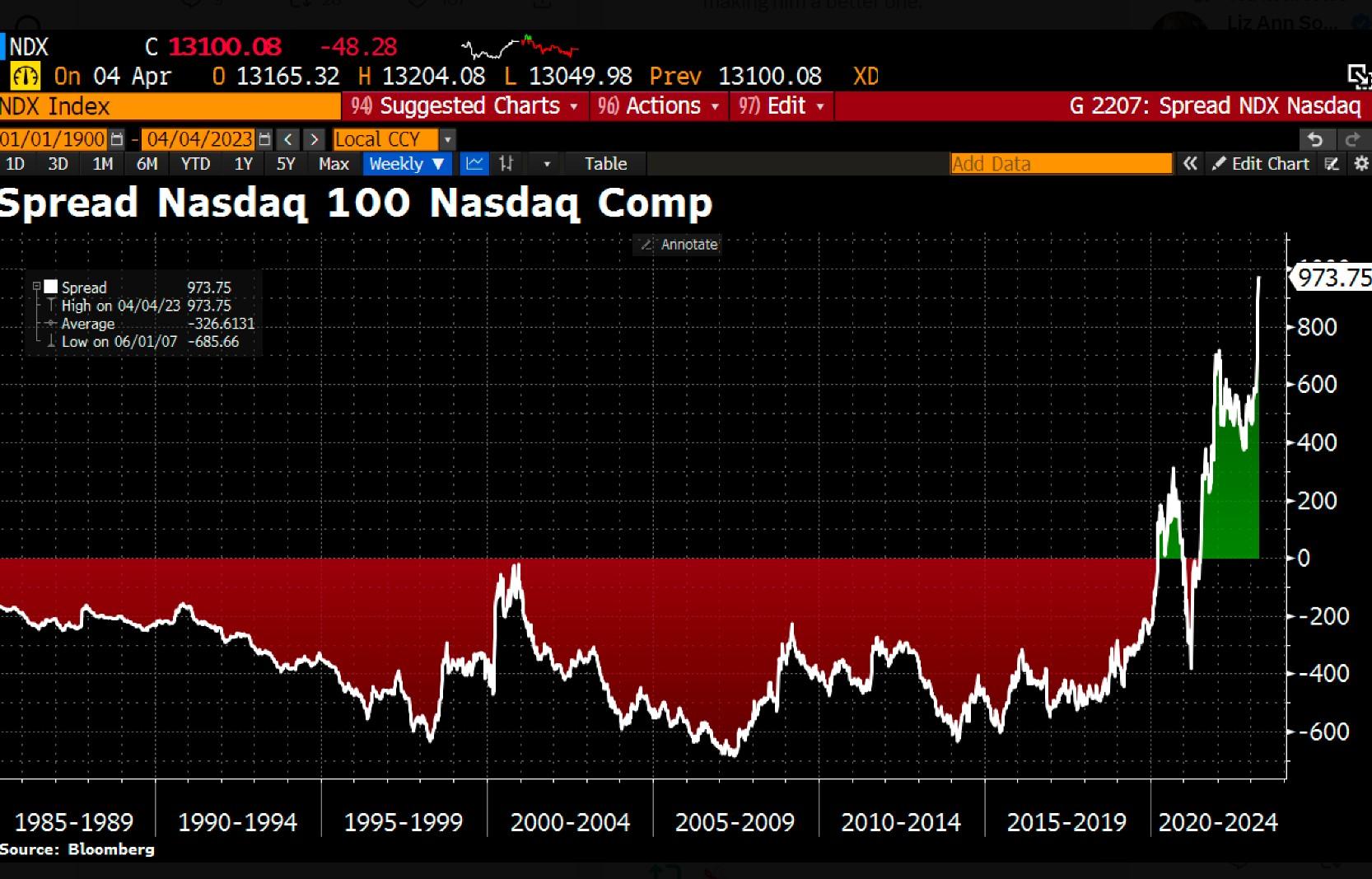
Key Trends and Insights from Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data
By analyzing Nasdaq 100 index historical data, investors can uncover valuable trends and insights that can inform their investment decisions. One key trend that emerges from historical data is the outperformance of the technology sector, which has driven the majority of the index’s growth over the past decade. Additionally, historical data reveals that the Nasdaq 100 index has historically been more volatile than other major indices, such as the S&P 500, due to its concentration of technology stocks. Furthermore, analysis of Nasdaq 100 index historical data shows that certain sectors, such as software and biotechnology, have consistently outperformed the broader market. Investors can also use historical data to identify patterns in market capitalization, dividend yields, and earnings growth, which can help inform their investment decisions. For example, historical data may reveal that companies with high dividend yields tend to outperform during periods of market volatility. By leveraging these insights, investors can develop a more informed investment strategy that takes into account the unique characteristics of the Nasdaq 100 index. By incorporating Nasdaq 100 index historical data into their analysis, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions.
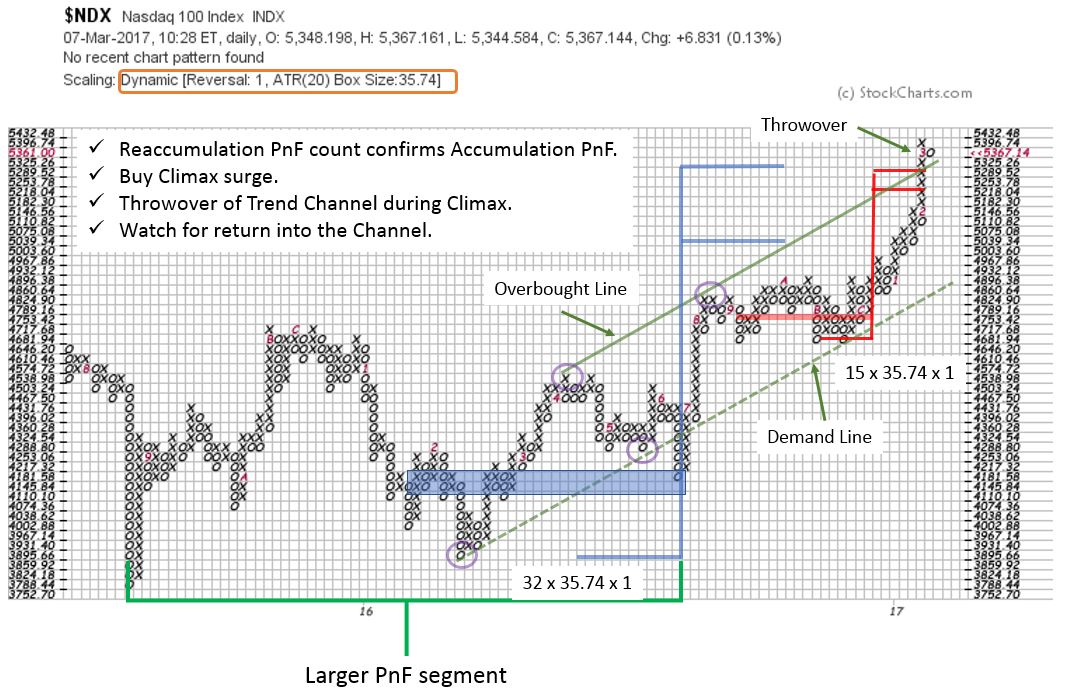
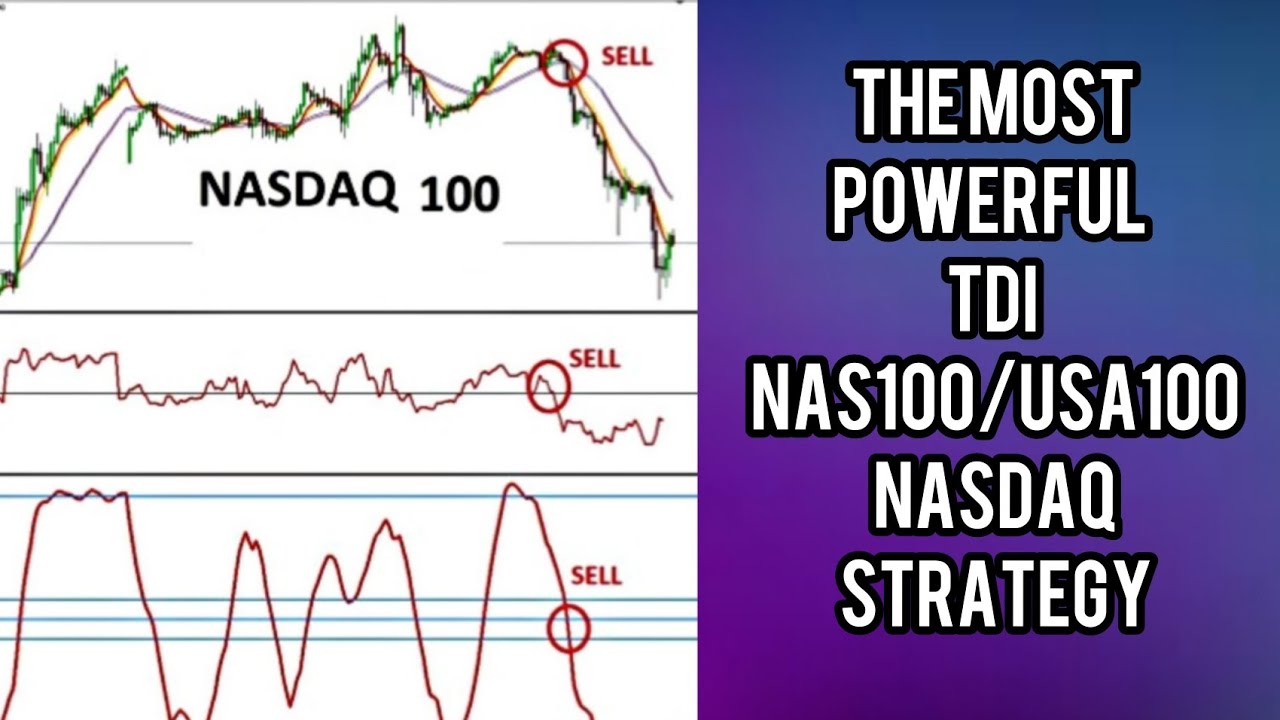
Using Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data for Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a crucial component of investment decision-making, and Nasdaq 100 index historical data plays a vital role in this process. By analyzing historical data, technical analysts can identify patterns and trends that can inform their trading decisions. One key application of Nasdaq 100 index historical data in technical analysis is the identification of chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, triangles, and wedges. These patterns can provide valuable insights into market sentiment and potential price movements. Additionally, historical data can be used to calculate technical indicators, such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands, which can help traders identify overbought and oversold conditions. Furthermore, Nasdaq 100 index historical data can be used to backtest trading strategies, allowing analysts to evaluate the effectiveness of different approaches and refine their techniques. By leveraging Nasdaq 100 index historical data in technical analysis, investors can gain a deeper understanding of market dynamics and make more informed trading decisions. For example, historical data may reveal that the Nasdaq 100 index tends to experience a seasonal rally in the fourth quarter, which can inform investment decisions during this period. By incorporating Nasdaq 100 index historical data into their technical analysis, investors can develop a more nuanced understanding of the market and improve their trading performance.
The Role of Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data in Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis is a crucial component of investment decision-making, and Nasdaq 100 index historical data plays a vital role in this process. By analyzing historical data, fundamental analysts can gain a deeper understanding of company performance, industry trends, and economic indicators. One key application of Nasdaq 100 index historical data in fundamental analysis is the evaluation of company performance. Historical data can provide valuable insights into a company’s revenue growth, profitability, and return on investment, allowing analysts to identify trends and patterns that can inform their investment decisions. Additionally, Nasdaq 100 index historical data can be used to analyze industry trends, such as the growth of the technology sector or the decline of the energy sector. This information can help analysts identify opportunities and risks in different industries and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, historical data can be used to analyze economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates, which can provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy. By incorporating Nasdaq 100 index historical data into their fundamental analysis, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions. For example, historical data may reveal that companies with high dividend yields tend to outperform during periods of economic uncertainty, which can inform investment decisions during times of market volatility. By leveraging Nasdaq 100 index historical data in fundamental analysis, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the market and improve their investment performance.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Working with Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data
When working with Nasdaq 100 index historical data, it’s essential to be aware of common pitfalls that can lead to inaccurate analysis and poor investment decisions. One of the most significant pitfalls is data quality issues, which can arise from incomplete or inaccurate data. This can lead to incorrect conclusions and a flawed understanding of market trends. To avoid this, it’s crucial to source high-quality data from reputable providers and to thoroughly clean and validate the data before analysis. Another common pitfall is survivorship bias, which occurs when only successful companies or investments are included in the analysis, while failed or delisted companies are excluded. This can lead to an overly optimistic view of the market and a failure to account for potential risks. To avoid survivorship bias, it’s essential to include all relevant data, including failed or delisted companies, in the analysis. Overfitting is another common pitfall, which occurs when a model is too complex and fits the noise in the data rather than the underlying patterns. This can lead to poor predictive performance and a failure to generalize to new data. To avoid overfitting, it’s essential to use robust modeling techniques and to regularly test and validate the model. Additionally, it’s important to avoid cherry-picking data or selectively presenting only the data that supports a particular hypothesis. This can lead to a biased view of the market and a failure to consider alternative perspectives. By being aware of these common pitfalls and taking steps to avoid them, investors can ensure that their analysis of Nasdaq 100 index historical data is accurate, reliable, and informative.
Best Practices for Integrating Nasdaq 100 Index Historical Data into Your Investment Strategy
Integrating Nasdaq 100 index historical data into an investment strategy requires a thoughtful and structured approach. One best practice is to utilize data visualization techniques to effectively communicate insights and trends from the data. This can include creating charts and graphs to illustrate sector performance, market capitalization, and dividend yields. By visualizing the data, investors can quickly identify patterns and trends that may not be immediately apparent from raw data. Another best practice is to incorporate risk management techniques into the investment strategy. This can include using Nasdaq 100 index historical data to identify potential risks and opportunities, and adjusting the portfolio accordingly. For example, an investor may use historical data to identify sectors that are highly correlated with each other, and adjust the portfolio to minimize risk. Additionally, investors can use Nasdaq 100 index historical data to optimize their portfolio through techniques such as mean-variance optimization. This involves using historical data to estimate the expected returns and volatility of different assets, and constructing a portfolio that maximizes returns while minimizing risk. By integrating Nasdaq 100 index historical data into an investment strategy, investors can make more informed decisions, manage risk, and optimize returns. Furthermore, investors can use Nasdaq 100 index historical data to backtest their investment strategies, evaluating their performance over time and making adjustments as needed. By following these best practices, investors can unlock the full potential of Nasdaq 100 index historical data and achieve their investment goals.