Understanding the LIBOR Rate: A Key to Financial Markets
The London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) is a crucial benchmark rate that plays a vital role in shaping the global financial landscape. As a widely followed indicator of short-term interest rates, LIBOR influences the cost of borrowing and the attractiveness of investments. The 3-month LIBOR rate, in particular, is a key driver of short-term interest rates, with its fluctuations having a ripple effect on financial markets. A thorough understanding of the LIBOR rate is essential for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates. In this article, we will delve into the significance of the LIBOR rate, exploring its history, trends, and practical applications in finance, including its role in shaping the libor rate history 3 month.
How to Navigate the Complex World of Short-Term Interest Rates
Understanding short-term interest rates, including the 3-month LIBOR rate, is crucial for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to make informed decisions in today’s complex financial landscape. With the libor rate history 3 month serving as a benchmark for short-term borrowing costs, it is essential to grasp the intricacies of short-term interest rates to navigate the market effectively. To analyze and interpret rate fluctuations, it is vital to consider a range of factors, including economic indicators, monetary policy decisions, and market sentiment. By developing a deep understanding of short-term interest rates, market participants can better position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks in an ever-changing financial environment. In this article, we will provide tips and insights on how to navigate the complex world of short-term interest rates, including the 3-month LIBOR rate, and explore its significance in shaping the libor rate history 3 month.
A Brief History of the 3-Month LIBOR Rate: Trends and Insights
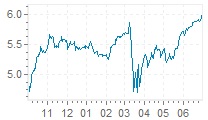
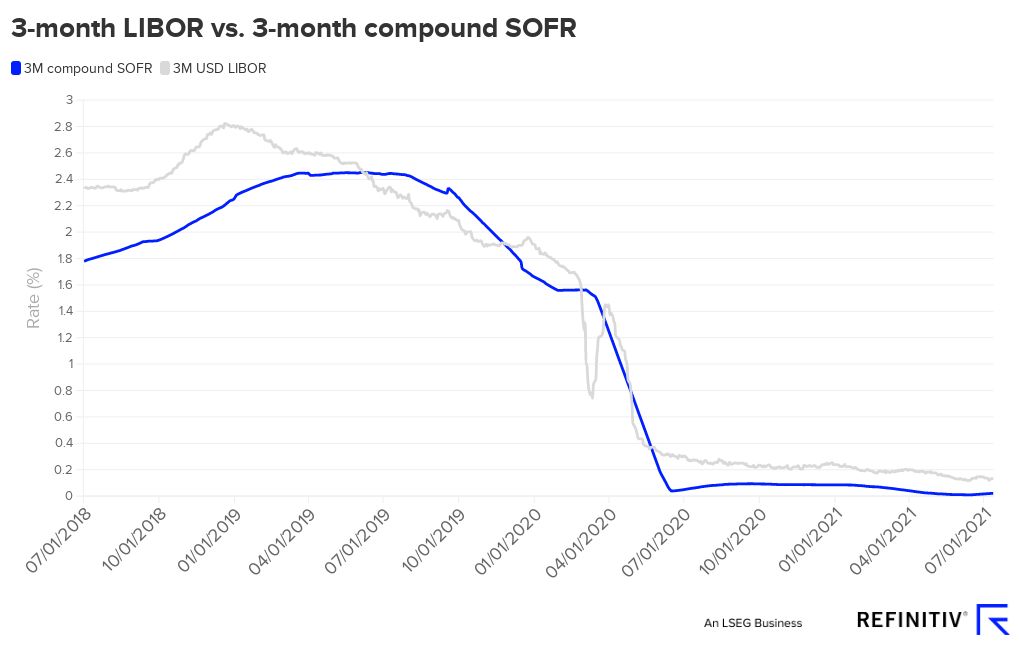
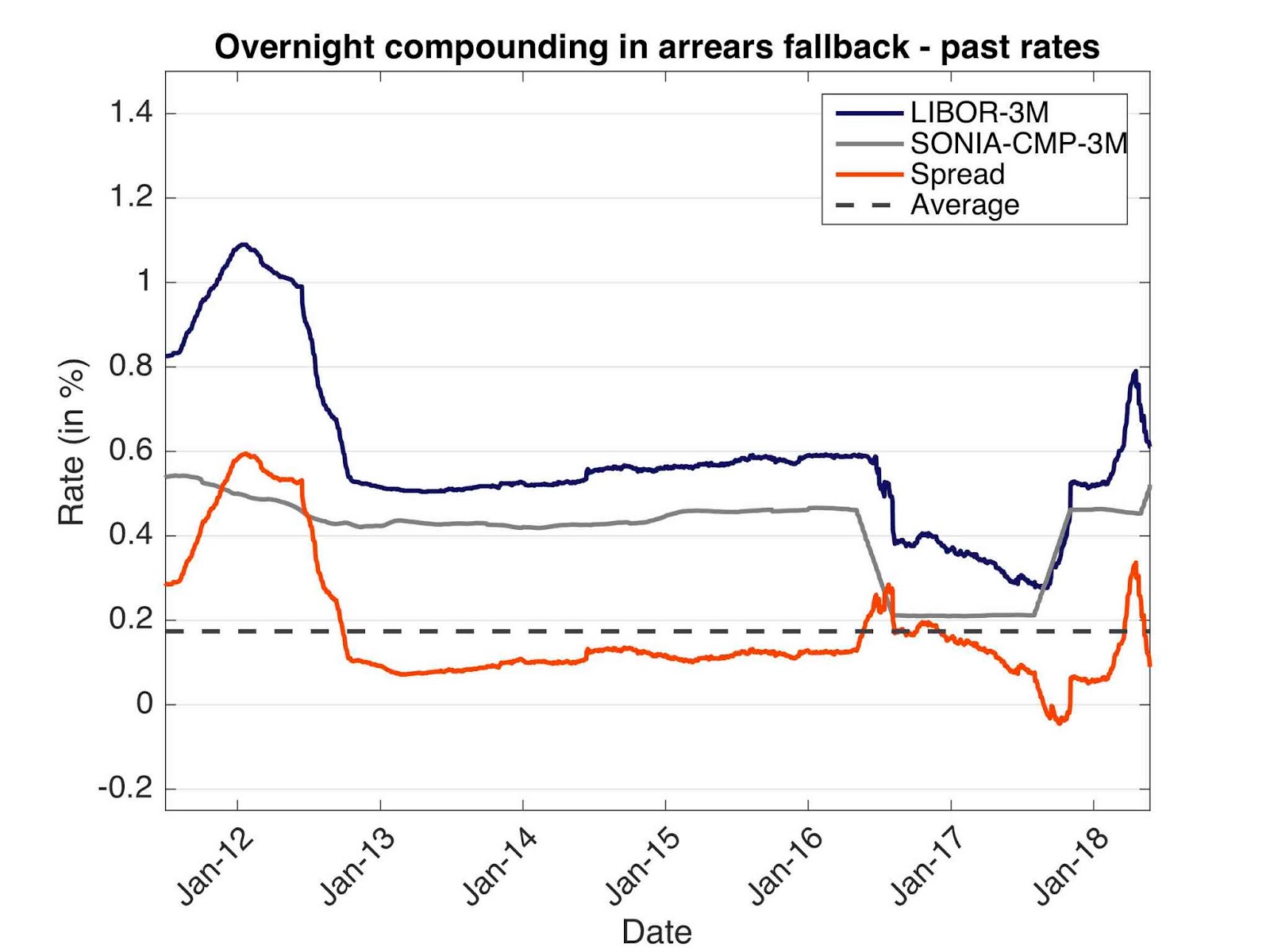
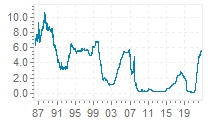
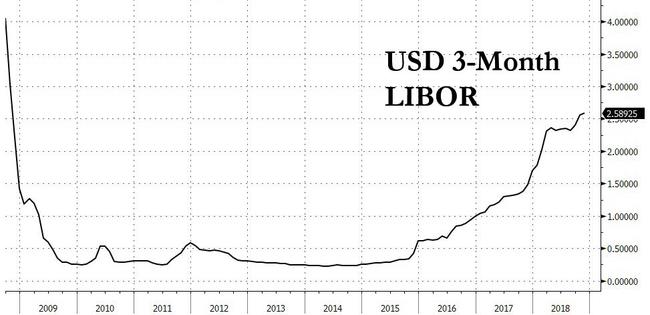
The 3-month LIBOR rate has a rich history, with its trajectory shaped by a complex array of economic, financial, and geopolitical factors. Since its inception, the libor rate history 3 month has been influenced by key events, trends, and milestones that have had a profound impact on global financial markets. In the 1980s, the 3-month LIBOR rate experienced a significant surge, driven by high inflation and monetary policy tightening. The 1990s saw a decline in the rate, as central banks implemented policies to stimulate economic growth. The early 2000s were marked by a period of stability, before the global financial crisis of 2008 led to a sharp decline in the rate. Since then, the 3-month LIBOR rate has experienced a slow recovery, influenced by quantitative easing and other unconventional monetary policies. Understanding the libor rate history 3 month is essential for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates and make informed decisions in today’s fast-paced financial environment.
The Impact of Economic Indicators on the 3-Month LIBOR Rate
The 3-month LIBOR rate is closely tied to various economic indicators, which have a profound impact on its trajectory. Gross Domestic Product (GDP), inflation rates, and unemployment rates are just a few of the key indicators that influence the libor rate history 3 month. For instance, a strong GDP growth rate can lead to an increase in the 3-month LIBOR rate, as it signals a robust economy and higher borrowing costs. On the other hand, high inflation rates can also drive up the 3-month LIBOR rate, as lenders demand higher returns to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, low unemployment rates can lead to a decrease in the 3-month LIBOR rate, as it indicates a slackening in labor market conditions and reduced borrowing costs. Understanding the complex relationships between these economic indicators and the 3-month LIBOR rate is crucial for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to make informed decisions in today’s dynamic financial environment.
What Drives Changes in the 3-Month LIBOR Rate?
Changes in the 3-month LIBOR rate are driven by a complex array of factors, including monetary policy decisions, market sentiment, and global economic events. Monetary policy decisions, such as changes in interest rates or quantitative easing, can have a significant impact on the libor rate history 3 month. For instance, a central bank’s decision to raise interest rates can lead to an increase in the 3-month LIBOR rate, as lenders demand higher returns to compensate for the increased cost of borrowing. Market sentiment, including investor confidence and risk appetite, also plays a crucial role in shaping the 3-month LIBOR rate. During times of economic uncertainty, investors may become risk-averse, leading to a decrease in the 3-month LIBOR rate as lenders become more cautious. Global economic events, such as recessions or geopolitical tensions, can also influence the 3-month LIBOR rate, as they impact the overall economic outlook and borrowing costs. Understanding the complex interplay between these factors is essential for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates.
The Role of Central Banks in Shaping the 3-Month LIBOR Rate
Central banks play a crucial role in influencing the 3-month LIBOR rate through their monetary policy decisions and tools. By adjusting interest rates, implementing quantitative easing, or engaging in forward guidance, central banks can shape the libor rate history 3 month and impact borrowing costs. For instance, during times of economic downturn, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, leading to a decrease in the 3-month LIBOR rate. Conversely, during periods of high inflation, central banks may raise interest rates to curb inflationary pressures, resulting in an increase in the 3-month LIBOR rate. Additionally, central banks’ communication strategies, such as forward guidance, can also influence market expectations and shape the 3-month LIBOR rate. Understanding the role of central banks in shaping the 3-month LIBOR rate is essential for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions seeking to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates.
Practical Applications of the 3-Month LIBOR Rate in Finance
The 3-month LIBOR rate has numerous practical applications in finance, making it a crucial component of various financial instruments and products. One of the most significant applications is in the derivatives market, where the 3-month LIBOR rate serves as a benchmark for interest rate swaps and options. This allows companies to hedge against potential interest rate risks and manage their exposure to fluctuations in the libor rate history 3 month. Additionally, the 3-month LIBOR rate is used to determine the interest rates on loans, such as commercial mortgages and credit cards, affecting the borrowing costs for individuals and businesses. Furthermore, the 3-month LIBOR rate influences the returns on investment products, such as certificates of deposit and treasury bills, making it an essential factor in investment decisions. Understanding the practical applications of the 3-month LIBOR rate is vital for financial institutions, investors, and borrowers seeking to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates and make informed decisions.
Looking Ahead: Predicting Future Trends in the 3-Month LIBOR Rate
As the global economy continues to evolve, the 3-month LIBOR rate is likely to be influenced by emerging market trends and technological advancements. One potential trend is the increasing adoption of alternative reference rates, such as the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR), which may eventually replace the libor rate history 3 month as the benchmark for short-term interest rates. Additionally, the growing importance of fintech and digital lending platforms may lead to new applications of the 3-month LIBOR rate in finance. Furthermore, the ongoing shift towards sustainable and environmentally responsible investing may also impact the 3-month LIBOR rate, as investors increasingly prioritize ESG considerations in their investment decisions. By understanding these potential future trends and developments, investors, borrowers, and financial institutions can better position themselves to navigate the complexities of short-term interest rates and make informed decisions in an ever-changing financial landscape.