Understanding the Income Statement: A Comprehensive Overview
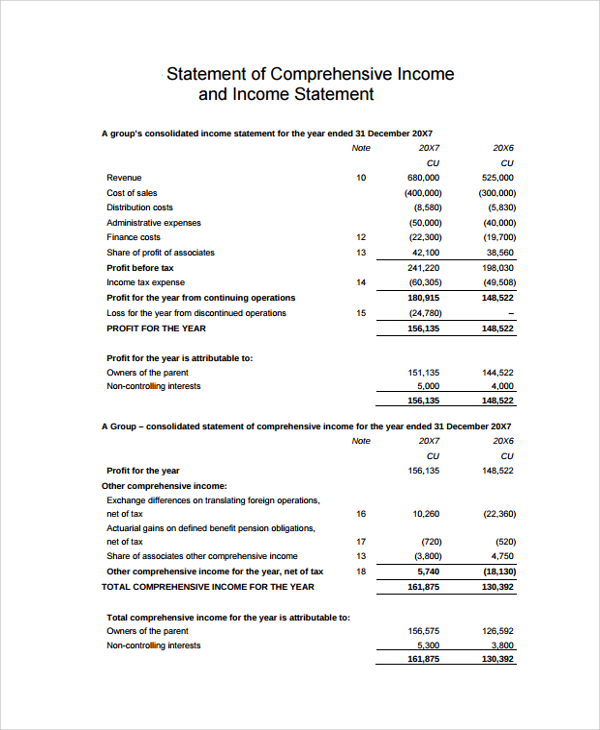
The income statement, a crucial financial report, provides stakeholders with a snapshot of a company’s financial performance over a specific period. It is a vital tool for investors, creditors, and management to assess a company’s ability to generate earnings and make informed decisions. The income statement is typically divided into three main sections: revenues, expenses, and net income. Revenues represent the income generated from a company’s primary business activities, while expenses include the costs incurred to generate those revenues. Net income, also known as the bottom line, represents the company’s profitability after deducting all expenses from revenues. When analyzing an income statement, it is essential to understand the different components and how they interact with each other. This includes identifying where is depreciation expense on income statement, as it plays a critical role in accurately reflecting a company’s financial position. By grasping the income statement’s structure and components, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health and make informed decisions.
What is Depreciation Expense and Why is it Important?
Depreciation expense is a critical component of a company’s financial reporting, representing the allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life. It is a non-cash item that accounts for the wear and tear of assets, such as buildings, machinery, and vehicles, which are used to generate revenue. The causes of depreciation expense are diverse, including physical deterioration, technological obsolescence, and changes in market conditions. Accurate calculation and reporting of depreciation expense are essential, as it directly impacts a company’s profitability and asset valuation. For instance, a company that underestimates depreciation expense may overstate its net income, leading to inaccurate financial analysis and decision-making. On the other hand, a company that accurately reports depreciation expense can better assess its financial performance and make informed decisions about investments and resource allocation. Understanding where is depreciation expense on income statement is vital to grasp the true financial position of a company.
How to Identify Depreciation Expense on the Income Statement
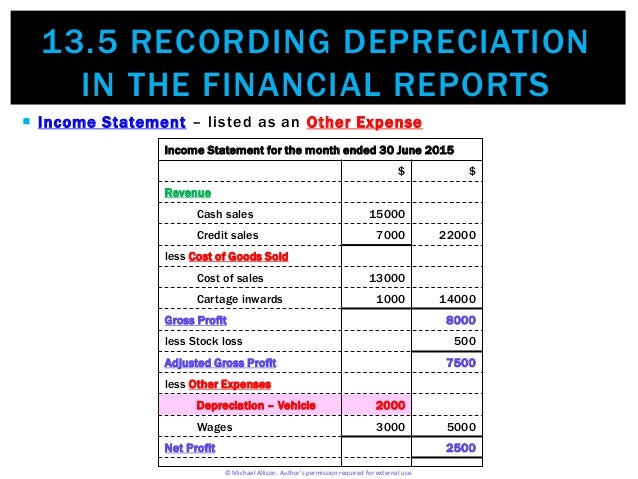
Locating depreciation expense on the income statement is a crucial step in understanding a company’s financial performance. To identify depreciation expense, follow these steps: first, review the income statement and look for the “Operating Expenses” or “Depreciation and Amortization” section. Depreciation expense is typically reported as a separate line item within this section. Next, examine the company’s footnotes or supplementary schedules, which provide detailed information about the depreciation expense calculation. Additionally, analyze the company’s financial data, such as the balance sheet and cash flow statement, to understand the impact of depreciation expense on its overall financial position. When searching for depreciation expense on the income statement, it is essential to know where is depreciation expense on income statement, as it can significantly influence a company’s reported profitability. By following these steps, stakeholders can accurately identify and analyze depreciation expense, gaining valuable insights into a company’s financial health and performance.
The Role of Depreciation Expense in Financial Analysis
Depreciation expense plays a vital role in financial analysis, as it significantly impacts a company’s profitability, cash flow, and investment decisions. When analyzing a company’s financial performance, it is essential to understand where is depreciation expense on income statement, as it can influence various financial metrics. For instance, depreciation expense affects profitability ratios, such as the return on assets (ROA) and return on equity (ROE), by reducing net income. Additionally, depreciation expense has a significant impact on cash flow, as it is a non-cash item that does not affect a company’s liquidity. In investment decisions, depreciation expense is crucial in evaluating a company’s capital expenditures and asset utilization. Furthermore, depreciation expense is used in various financial models, such as the discounted cash flow (DCF) model, to estimate a company’s intrinsic value. By accurately analyzing depreciation expense, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s financial health, competitiveness, and growth prospects. In financial analysis, understanding the significance of depreciation expense and its impact on financial metrics is crucial for making informed decisions.
Common Misconceptions About Depreciation Expense on the Income Statement
Despite its importance, depreciation expense is often misunderstood, leading to misconceptions and myths surrounding its reporting on the income statement. One common misconception is that depreciation expense is a cash flow item, when in fact it is a non-cash item that does not affect a company’s liquidity. Another myth is that depreciation expense is only relevant for companies with tangible assets, when in reality it applies to intangible assets as well. Additionally, some stakeholders believe that depreciation expense is not essential for financial analysis, when in fact it significantly impacts profitability ratios, cash flow, and investment decisions. It is crucial to understand where is depreciation expense on income statement to avoid these misconceptions. By clarifying the relationship between depreciation expense and other financial statement items, stakeholders can gain a more accurate understanding of a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions. For instance, depreciation expense is often confused with amortization expense, when in fact they are distinct concepts with different accounting treatments. By dispelling these misconceptions, stakeholders can unlock the secrets of financial reporting and make more informed decisions.
Real-World Examples of Depreciation Expense on the Income Statement
To illustrate the application of depreciation expense on the income statement, let’s consider a few real-world examples. For instance, a company like Apple Inc. reports depreciation expense on its income statement to reflect the wear and tear of its manufacturing equipment and machinery. In 2020, Apple reported depreciation expense of $4.4 billion, which represented a significant portion of its total operating expenses. Another example is a company like Delta Air Lines, which reports depreciation expense related to its aircraft and other assets. In 2020, Delta reported depreciation expense of $1.3 billion, which had a significant impact on its net income. By examining these real-world examples, it becomes clear where is depreciation expense on income statement and how it affects a company’s financial performance. Additionally, companies like Amazon and Microsoft also report depreciation expense on their income statements, highlighting the widespread application of this accounting concept. By analyzing these examples, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of depreciation expense and its significance in financial reporting.
Best Practices for Accounting and Reporting Depreciation Expense
Accurate and transparent reporting of depreciation expense is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions. To ensure compliance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements, companies should follow best practices for accounting and reporting depreciation expense. Firstly, companies should maintain accurate and detailed records of their assets, including their cost, useful life, and residual value. This information is essential for calculating depreciation expense and reporting it on the income statement. Secondly, companies should select the appropriate depreciation method, such as the straight-line method or the declining balance method, and apply it consistently across all assets. Thirdly, companies should regularly review and update their depreciation policies to ensure they remain relevant and compliant with changing accounting standards. Additionally, companies should provide clear and concise disclosures about their depreciation policies and methods in their financial reports, enabling stakeholders to understand where is depreciation expense on income statement and its impact on financial performance. By following these best practices, companies can ensure accurate and reliable reporting of depreciation expense, which is essential for informed decision-making and business success.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Depreciation Expense Reporting
In conclusion, accurate depreciation expense reporting is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions about a company’s financial performance and position. By understanding where is depreciation expense on income statement and its significance in financial reporting, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company’s profitability, asset valuation, and cash flow. Moreover, accurate depreciation expense reporting enables companies to comply with accounting standards and regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of financial misrepresentation and potential penalties. Furthermore, it facilitates comparability between companies, allowing stakeholders to make informed investment decisions. In today’s competitive business environment, accurate depreciation expense reporting is essential for business success, as it provides stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance and position. By recognizing the importance of accurate depreciation expense reporting, companies can ensure transparency, accountability, and reliability in their financial reporting, ultimately driving business growth and success.