Understanding the CD Market: Factors Affecting Pricing
The CD market has undergone significant changes in recent years, with the rise of digital music and streaming services altering consumer behavior and preferences. To effectively learn how to price a CD, it’s essential to understand the current state of the market and the factors that influence pricing. The shift towards digital music has led to a decline in CD sales, making it crucial to adapt pricing strategies to remain competitive. Additionally, the increasing competition from independent artists and labels has created a saturated market, further emphasizing the need for a well-thought-out pricing approach. By recognizing these market trends and factors, artists and labels can develop a pricing strategy that takes into account the evolving landscape of the music industry and appeals to their target audience.
Calculating Your Costs: Production, Distribution, and Marketing Expenses
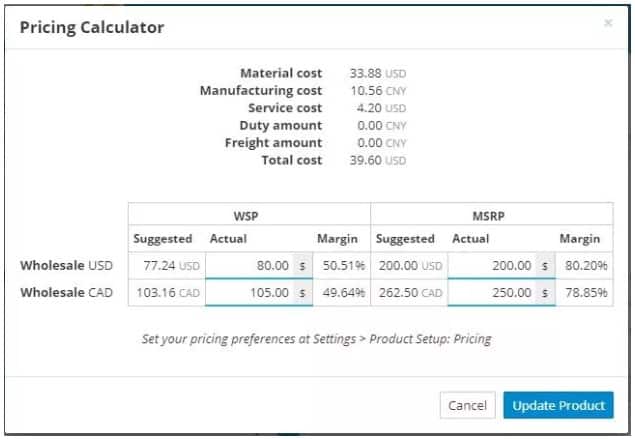
When learning how to price a CD, it’s essential to calculate the various costs associated with producing, distributing, and marketing the album. These costs can significantly impact the pricing strategy, and understanding them is crucial to determining a fair and competitive price. Manufacturing costs, including CD replication, packaging, and artwork, can range from $2 to $5 per unit, depending on the quantity and quality of the production. Distribution costs, such as shipping and storage, can add an additional $1 to $3 per unit. Marketing expenses, including advertising, promotion, and publicity, can vary widely depending on the scope and reach of the campaign. By accurately calculating these costs, artists and labels can determine a wholesale price that ensures a profit margin while remaining competitive in the market. This wholesale price will serve as the basis for determining the retail price, which will ultimately affect how to price a CD.
Researching Your Competition: Analyzing Similar Artists and Albums
When determining how to price a CD, researching similar artists and albums is crucial to understanding the competitive landscape of the market. By analyzing the pricing strategies of similar artists and albums, artists and labels can gain valuable insights into what consumers are willing to pay for music. This research can help identify gaps in the market, opportunities to differentiate, and potential price points that will resonate with the target audience. Start by identifying similar artists and albums in terms of genre, style, and target audience. Then, research their pricing strategies, including wholesale and retail prices, discounts, and promotions. Analyze online marketplaces, such as Amazon or iTunes, as well as physical retailers, to gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive pricing landscape. By understanding how similar artists and albums are priced, artists and labels can develop a pricing strategy that is competitive, yet profitable, and ultimately learn how to price a CD effectively.
Valuing Your Music: Pricing Strategies for Different Genres and Audiences
Different genres and audiences require unique pricing strategies when determining how to price a CD. For instance, classical music CDs may be priced higher due to their niche audience and perceived value. Jazz CDs, on the other hand, may be priced lower to appeal to a wider audience. Rock CDs, with their broad appeal, may be priced competitively to maximize sales. When pricing CDs for specific audiences, such as collectors or fans, artists and labels should consider the perceived value of the music and the target audience’s willingness to pay. For example, limited edition CDs or special releases may be priced higher for collectors who are willing to pay a premium for unique items. Fans, on the other hand, may be more price-sensitive and require competitive pricing to drive sales. By understanding the nuances of different genres and audiences, artists and labels can develop targeted pricing strategies that maximize revenue and appeal to their target market, ultimately learning how to price a CD effectively.
Considering the Retailer’s Perspective: Wholesale Pricing and Profit Margins
When determining how to price a CD, it’s essential to consider the retailer’s perspective, including wholesale pricing and profit margins. Retailers need to make a profit on the CDs they sell, so artists and labels must set wholesale prices that allow for a reasonable markup. A common practice is to set the wholesale price at 40-50% of the suggested retail price. This allows retailers to double their money while still providing a competitive price for consumers. Additionally, artists and labels should consider the retailer’s profit margins when setting prices. For example, if a retailer has a high overhead or operates on thin margins, they may require a lower wholesale price to remain competitive. By understanding the retailer’s perspective and incorporating their needs into the pricing strategy, artists and labels can increase the chances of their CDs being stocked and promoted by retailers, ultimately driving sales and revenue. This is a crucial aspect of learning how to price a CD effectively, as it directly impacts the availability and visibility of the music.
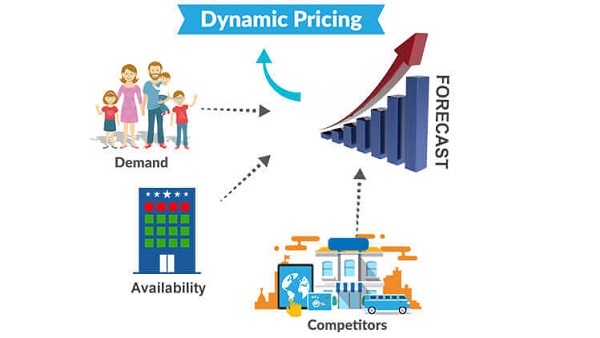
Dynamic Pricing: Adjusting Your Prices Based on Demand and Supply
Dynamic pricing is a crucial aspect of learning how to price a CD effectively. It involves adjusting prices based on demand, supply, and other market factors to maximize revenue and sales. By monitoring sales trends, artists and labels can identify opportunities to increase prices during periods of high demand or decrease prices during periods of low demand. For example, if a CD is selling well during the holiday season, the price can be increased to capitalize on the demand. Conversely, if sales are slow during the off-season, the price can be decreased to stimulate sales. Additionally, dynamic pricing can be used to respond to changes in the market, such as a competitor’s price drop or a shift in consumer behavior. By being flexible and adaptable with pricing, artists and labels can stay competitive and ensure their CDs remain attractive to consumers. This approach requires continuous monitoring of the market and sales data, but can lead to significant revenue increases and a more effective pricing strategy.
Bundling and Discounting: Strategies to Boost Sales and Revenue
When it comes to how to price a CD, bundling and discounting strategies can be effective ways to increase sales and revenue. By offering customers a package deal or a discounted price, artists and labels can incentivize purchases and drive sales. For example, offering a discount for bulk purchases can appeal to fans who want to buy multiple CDs or to retailers who want to stock up on inventory. Bundling CDs with merchandise, such as T-shirts or posters, can also increase the average sale value and provide an additional revenue stream. Another strategy is to offer limited-time discounts or promotions to create a sense of urgency and encourage customers to make a purchase. Additionally, artists and labels can consider offering exclusive content or bonus tracks to customers who purchase a CD at a certain price point. By getting creative with bundling and discounting strategies, artists and labels can attract more customers and increase revenue.
Monitoring and Adjusting: Continuously Evaluating Your Pricing Strategy
To ensure that your CD pricing strategy remains effective, it’s crucial to continuously monitor and adjust it as needed. This involves tracking sales data, consumer behavior, and market trends to identify areas for improvement. By regularly evaluating your pricing strategy, you can identify opportunities to optimize prices, increase revenue, and stay competitive in the market. For instance, if sales data shows that a particular CD is not selling well at its current price, you may need to adjust the price to make it more attractive to consumers. Additionally, monitoring consumer behavior and market trends can help you identify shifts in demand and adjust your pricing strategy accordingly. By staying flexible and adaptable, you can ensure that your CD pricing strategy remains effective and aligned with your business goals. Remember, learning how to price a CD is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and adjustment to stay ahead in the market.