Calculating Present Value: An Introductory Approach
Understanding present value is fundamental in financial decision-making, forming the bedrock for evaluating investments, projects, and various financial obligations. The core concept revolves around the idea that money available today is worth more than the same amount in the future, primarily due to its potential earning capacity. At the heart of calculating present value lies the discount rate, a crucial factor that essentially bridges the gap between future cash flows and their current worth. The discount rate, while seemingly a simple number, encapsulates several critical aspects. It reflects the opportunity cost—the return one could expect from an alternative investment of similar risk. Furthermore, it accounts for the inherent risk involved in future cash flows; higher risk often implies a higher discount rate to compensate for the uncertainty. Therefore, finding the correct discount rate is essential when calculating present value. It’s the mechanism by which the time value of money is assessed, allowing for a comparison of different investment opportunities over varying time horizons. This rate is not just a random figure; it’s an economically meaningful representation of the required return for an investment given the context.
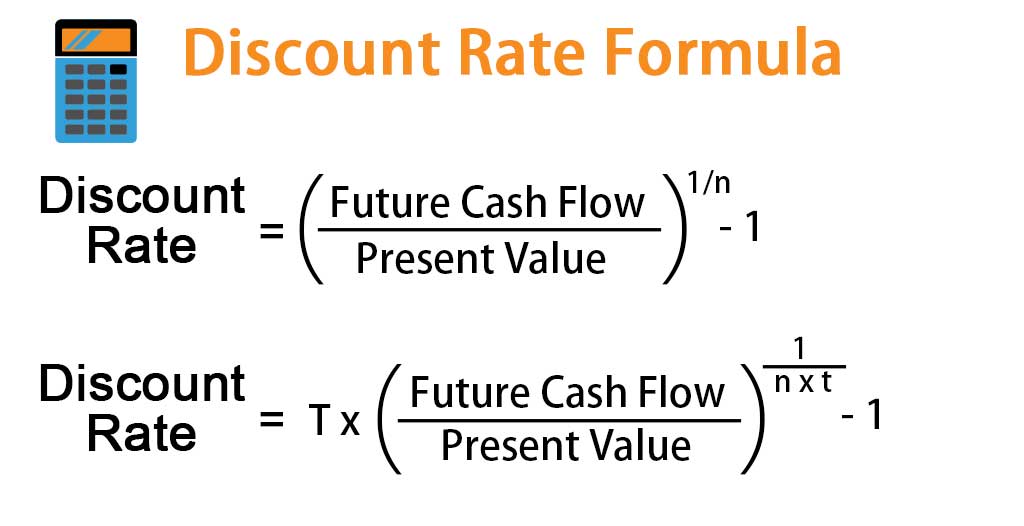
When delving into financial analysis, it is important to note that the discount rate is the interest rate used to determine the present value of future cash flows. This rate is an integral part of understanding how to find discount rate in excel. It is essential to select the correct rate, because it greatly impacts the results, and, in turn, the financial decisions that follow. The discount rate is used to evaluate if a potential investment or project is viable. For example, the discount rate is used to determine if the present value of future cash flows exceeds the initial investment. The rate can be determined by factors such as opportunity cost of capital or any required return given the risk involved. Moreover, this single number allows for the financial assessment of investments based on risk, time, and earning capacity.
Navigating the World of Financial Analysis With Excel
Excel stands as a powerful ally in the realm of financial analysis, offering a suite of functions that simplify complex calculations. Specifically, when it comes to understanding the time value of money, Excel provides the tools necessary to determine present value and, subsequently, how to find discount rate in excel. Excel’s capabilities extend beyond mere computation; it serves as a dynamic environment where financial models can be constructed, tested, and refined. The process of discounting future cash flows back to their present value is crucial in financial decision-making. This involves applying a discount rate, which effectively represents the rate of return required to compensate for the time value of money and the risk associated with future cash flows. Excel’s financial functions enable the easy manipulation of these parameters, providing a clear perspective on the present worth of anticipated earnings or costs.
The bridge between future financial events and their present-day worth is created through the process of discounting. For instance, consider a future cash inflow. Excel can help calculate how much that future sum is worth today, based on a chosen discount rate. This is the essence of present value calculation, and it’s directly relevant to understanding how to find discount rate in excel. The rate at which future cash flows are discounted is what determines the extent of this adjustment. Excel’s ability to accurately and quickly perform these calculations is extremely valuable for investors, financial analysts, and businesses that need to evaluate projects or opportunities. The software can also aid in sensitivity analysis where discount rates can be varied to see how this affects the outcome of financial valuations. It is critical to understand that these future cash flows are the money that is expected to be received at a point in the future, and the objective is to know what they are worth today.
Therefore, Excel functions like RATE and IRR (which will be discussed later) are the core elements in these calculations. Whether evaluating a potential investment, comparing different options, or even understanding the profitability of a project, Excel offers an accessible and reliable platform to manage all the financial analysis needs. It is also the starting point for anyone looking for the answer on how to find discount rate in excel. The transition from theoretical financial concepts to practical applications is made much easier with the help of spreadsheet software, making it an invaluable tool in the financial world.
Decoding The RATE Function for Discount Rate Calculations
The RATE function in Excel is a powerful tool for determining the discount rate, a crucial element in present value calculations. Understanding how to find discount rate in excel using this function is vital for various financial analyses. The RATE function helps calculate the periodic interest rate required to reach a specific future value (FV) from a present value (PV) over a given number of periods (Nper). Its basic syntax is `RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess])`. ‘nper’ represents the total number of payment periods, ‘pmt’ is the payment made each period, ‘pv’ is the present value, ‘fv’ is the future value (optional, defaults to 0), ‘type’ specifies when payments are due (0 for end of period, 1 for beginning, defaults to 0), and ‘guess’ is an optional initial guess for the interest rate. The function is particularly useful when analyzing investments with a fixed interest rate, such as bonds or loans, allowing for a clear understanding of the return or cost of capital involved. Knowing how to find discount rate in excel is important for making informed financial decisions. For instance, if you know the present value of an investment, the regular payments, and the desired future value, the RATE function efficiently determines the discount rate needed to achieve that future value. This process is invaluable for investment planning and asset valuation.
Real-world applications of the RATE function are numerous. Imagine assessing the feasibility of a project requiring an upfront investment and yielding future cash flows. By inputting the initial investment (PV), expected cash flows (PMT), and the project’s lifespan (Nper), the RATE function calculates the internal rate of return (IRR) — essentially, the discount rate at which the net present value of the project equals zero. This provides a clear benchmark for evaluating whether the project’s expected return justifies the initial investment. Similarly, when analyzing a loan, this function can help determine the actual interest rate. For example, you know your monthly payment, the loan amount, and the loan term. The RATE function helps discover the underlying interest rate applied by the lender, providing transparency in the borrowing cost. Efficiently using the RATE function in Excel greatly simplifies such calculations, making complex financial analysis considerably more accessible.
The RATE function’s flexibility extends to various scenarios where determining a discount rate is essential. For example, it can be used in evaluating the profitability of different investment options, comparing the attractiveness of loans with varying interest rates, and performing sensitivity analysis by changing input variables to observe their impact on the discount rate. Understanding how to find discount rate in excel enhances financial literacy and facilitates better decision-making in personal finance, business planning, and more broadly across various finance-related fields. The versatility and ease of use make the RATE function a valuable asset for anyone working with financial data. Mastering this function empowers individuals to take control of their financial analysis and enhance financial decisions by providing an efficient tool to understand the fundamental concept of discount rate. This, in turn, enables better comparisons between various financial opportunities.
Step-by-Step Instructions: Determining the Discount Rate With RATE Formula
To effectively demonstrate how to find discount rate in Excel using the RATE function, consider a practical scenario. Suppose you are evaluating an investment that requires an initial outlay of $1000 (this is your present value or PV) and promises a return of $1200 after 3 years (this is your future value or FV). To find the discount rate, you’ll use the RATE formula. First, open your Excel sheet and locate an empty cell where you want to display the calculated discount rate. In that cell, type the following formula: =RATE(nper, pmt, pv, [fv], [type], [guess]). Here’s how each part of the formula is defined: ‘nper’ is the total number of payment periods, in this case, 3 years; ‘pmt’ is the payment made each period—since this is a lump sum investment with no periodic payments, it’s 0; ‘pv’ represents the present value of the investment, which is -$1000 (note the negative sign, it indicates cash outflow); ‘fv’ is the future value or the expected investment value, which is $1200; the optional ‘type’ argument refers to whether payments are made at the beginning or end of the period, for simplicity we will skip this and the ‘guess’ argument too as Excel can make an approximation. The complete formula for our example would be =RATE(3,0,-1000,1200). After entering this formula and pressing Enter, Excel will calculate and display the discount rate, which will be expressed as a decimal. To display it as a percentage, you might need to format the cell.
Continuing with our step-by-step instructions on how to find discount rate in excel, once you’ve entered the formula =RATE(3,0,-1000,1200), Excel will return a numerical value. This value is the discount rate expressed as a decimal. To transform this value into a percentage, you simply need to select the cell with the calculated rate and click the percent style button located on the ‘Home’ tab in the number group, or use the keyboard shortcut ctrl + shift + %. Excel will format the numerical value to a more understandable percentage, for example, about 6.27%. This result indicates that the discount rate, which reflects the required return or the cost of capital for this investment, is approximately 6.27% per year. It’s crucial to remember that the present value (PV) must be entered as a negative value to indicate an initial investment or cash outflow. The future value (FV) should be positive because it is the expected future cash inflow. These sign conventions are vital for the RATE function to operate correctly and to find the discount rate accurately.
Let’s consider another example to further clarify how to find discount rate in Excel. Imagine you have a project that costs $5,000 today and is expected to yield $6,000 in two years. The ‘nper’ would be 2, the ‘pmt’ is still 0, ‘pv’ is -$5000, and ‘fv’ is $6000. The formula would therefore be =RATE(2,0,-5000,6000). After entering the formula, Excel will display the result as a decimal, and with percentage formatting, this translates to approximately 9.54%. This means that to achieve a future value of $6000 from an initial investment of $5000 over two years, the investment needs to grow at an annual discount rate of roughly 9.54%. Keep in mind that the accuracy of the result depends on the accuracy of your inputs, especially in scenarios with varying cash flows and durations. Always double-check that your present and future values, along with the number of periods, are correctly inputted. This methodical approach ensures precision in using the RATE function to find the discount rate effectively and correctly.
Practical Example: Determining the Yield for Investment Opportunity
Consider a practical scenario where an investor is evaluating a potential bond investment. The bond currently costs $900 (present value) and promises to pay $1000 at the end of a 5-year period (future value). To determine the yield, which is essentially the discount rate for this investment, the RATE function in Excel is the perfect tool. In Excel, inputting the following parameters into the RATE formula will reveal the yield: Nper (number of periods) as 5, PMT (payment) as 0 since there are no periodic payments, PV (present value) as -900 (entered as a negative value because it represents an outflow of cash), and FV (future value) as 1000. The formula is typically structured as =RATE(Nper, PMT, PV, FV). Plugging these values into Excel as =RATE(5,0,-900,1000) would return the discount rate, which in this case would be approximately 2.1%. This calculated rate represents the annual yield or return that the bond provides. Knowing how to find discount rate in excel in such situations allows for accurate comparisons of diverse investment opportunities. This yield is crucial for an investor to understand the profitability of this investment and its competitiveness compared to other opportunities.
Let’s consider a project evaluation scenario. A company invests $50,000 now and expects to receive $65,000 in 4 years without any interim payments. The question is: What is the implied discount rate or yield for this investment? Using the RATE function in Excel, the company can determine this rate by setting Nper to 4, PMT to 0 (because there are no periodic cash flows), PV to -50000 (the initial investment as an outflow), and FV to 65000. The Excel formula would be =RATE(4,0,-50000,65000). The result is approximately 6.7%. This value, the calculated discount rate, reveals the expected annual return of the project. The calculated discount rate is vital to evaluate if this return is satisfactory given the risk associated with the project and other alternative investment opportunities. This example illustrates another way how to find discount rate in excel to ensure a sound financial decision making process. The yield provided by the project will be directly compared with the company’s weighted average cost of capital.
Interpreting the calculated discount rate is critical. In both the bond and project example, this rate represents the return achieved or the yield. If the calculated discount rate is deemed acceptable given the perceived risk, then the investment is attractive. Otherwise the company or investor may decide to re-evaluate. For instance, if a similar risk bond has a yield higher than 2.1% in the first example, the investor may decide to pursue this alternative. Understanding how to find discount rate in excel and using it properly is key to make informed investment decisions. Therefore, in every real-world scenario, it’s crucial to evaluate the risk involved and its correlation to the discount rate to make the best financial decisions.
Alternative Approaches: Using the IRR function for Discount Rate
While the RATE function provides a straightforward method to determine the discount rate under specific circumstances, the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) function offers an alternative approach, particularly when dealing with a series of cash flows occurring at different times. The IRR function is invaluable when you need to calculate the discount rate for investments featuring a mix of inflows and outflows, a scenario frequently encountered in project analysis or evaluating complex financial instruments. Unlike the RATE function, which requires a single present value (PV), future value (FV) and a consistent payment per period, the IRR function requires only a series of cash flows and it calculates the discount rate that makes the net present value of those cash flows equal to zero. This distinction is crucial in understanding when to use each function. For example, if an investment involves an initial outlay followed by a series of varying returns over several periods, the IRR function is more suitable for finding the discount rate. This reflects a more realistic scenario for many real-world investment opportunities where cash flows are not uniform. This functionality is often used for project profitability analysis.
The key difference between the RATE and IRR functions lies in their application scenarios. The RATE function is best applied when dealing with a single investment with known present value, future value, and a fixed number of periods, as it directly calculates the implied discount rate assuming a constant rate. In contrast, the IRR function is designed to handle more complex scenarios involving multiple cash flows that are not necessarily uniform. For instance, when evaluating a new business venture where the cash flows are different in each year, the IRR is the best way to calculate the discount rate. The IRR represents the expected compound annual rate of return for a project or investment. To understand how to find discount rate in excel using the IRR, you input an array of cash flows, including the initial investment (negative value) and subsequent inflows, and Excel will calculate the discount rate that equates the present value of the inflows to the initial investment. This rate provides a crucial metric for assessing the profitability and viability of the investment. While both functions deal with finding a discount rate, their application is based on the cash flows and the specific parameters available.
When deciding on how to find discount rate in excel, particularly whether to use RATE or IRR, a careful review of the investment or project’s cash flow structure is needed. The RATE function is more straightforward for simpler scenarios, such as determining the yield of a bond with fixed payments. On the other hand, the IRR becomes indispensable when the cash flows are varied and not equally spaced or of equal value. For instance, consider a situation where a business invests capital, then receives varying returns in subsequent years. The IRR helps determine the actual yield the business is realizing, which can then be compared against benchmarks or alternative investment opportunities to help evaluate it. Understanding these differences ensures that the correct function is selected, which will lead to an accurate assessment of the investment opportunity. Although both functions help to determine what is known as discount rate, selecting the appropriate one ensures that decision-making is based on the most suitable analysis method.
Limitations and Considerations for Discount Rate Calculations
While Excel’s RATE and IRR functions provide powerful tools for calculating discount rates, it’s crucial to understand their limitations to ensure accurate financial analysis. One common pitfall arises from incorrect input values, which can lead to error messages or illogical results. For example, failing to input the correct sign convention for cash flows (positive for inflows, negative for outflows) will produce misleading outcomes when using the IRR function. It is also important to consider that the RATE function assumes regular, periodic cash flows, and may not be suitable for more complex scenarios with irregular timing. Furthermore, a common user error happens when trying to use the RATE function to solve for the discount rate when there are multiple cashflows, as it is only designed for uniform periodic cash flows. In such instances, the IRR function would be more appropriate. When using the IRR function, understand that the function works with an iterative process, it may be possible that it returns an error if no solution is found, or provide multiple possible solutions (even if one is more applicable). Therefore, when trying to determine how to find discount rate in excel, remember that accuracy is highly dependent on input data integrity and that the functions work under certain assumptions.
Another important consideration revolves around the interpretation of the calculated discount rate. Excel formulas provide a numerical rate, but they do not inherently capture the underlying factors that influence the discount rate. These factors include the level of risk associated with the investment, the prevailing inflation rate, and the opportunity cost of capital. For example, a higher-risk investment will generally warrant a higher discount rate to reflect the increased uncertainty of future returns, which is not something that the RATE or IRR function will automatically calculate. Likewise, inflation erodes the real value of future cash flows, and investors typically demand a higher rate of return to compensate for this. The discount rate must also consider the returns that could be earned on alternative investments; the opportunity cost. When considering how to find discount rate in excel, remember that the functions themselves do not consider these external factors, thus, users must make informed judgments and often rely on external models to determine the appropriate rate to use in those formulas. It’s also important to keep in mind that discount rates change over time due to market conditions. In summary, while Excel is a powerful calculation tool, users must be aware that these functions can not capture all the variables related to the correct discount rate, and therefore must always be combined with solid theoretical concepts for a proper financial analysis.
Conclusion: Embracing Discount Rate as A Crucial Financial Metric
The journey through understanding how to find discount rate in excel reveals its importance as a core concept in financial analysis. The RATE function and IRR function in Excel are tools that enable precise calculations, providing a clear pathway to understand the time value of money. This article detailed how to find discount rate in excel and how to use the RATE and IRR functions, showcasing that determining discount rates doesn’t require complex mathematical background when using the right approach. The use of Excel functions like RATE empowers users to move beyond manual calculations, providing a streamlined methodology for financial analysis. By calculating a discount rate, one can make informed investment choices, accurately assess project profitability, and understand the implications of financial decisions. Grasping the nuances of how to find discount rate in excel through these methods, particularly by using the RATE function, is essential for anyone involved in finance.
Throughout this guide, the emphasis has been on the practical use of Excel to calculate discount rates. Understanding how to find discount rate in excel is a practical application that offers tangible benefits, from evaluating investment returns to assessing the feasibility of financial opportunities. The power of Excel in financial analysis stems from its ability to handle complex calculations quickly and accurately. The exploration of both the RATE and IRR functions has broadened the user’s toolkit for dealing with different financial scenarios, like determining the yield of bonds, or assessing an investment’s rate of return. However, as discussed, it’s vital to understand the limitations of excel functions and the factors that influence the discount rate itself, such as risk and inflation; excel does not calculate these inputs. Therefore, while Excel provides a powerful mechanism to compute the discount rate, always contextualizing its outputs and having awareness of all involved factors is required.
The power of knowing how to find discount rate in excel using functions like RATE and IRR cannot be overstated. Financial literacy is strengthened by understanding these techniques, thus equipping users with the skills to manage, analyze, and comprehend financial data effectively. Applying the learned techniques and approaches provides a path to navigate the complexities of financial decision-making with greater precision and confidence. The ability to compute the discount rate effectively provides a more transparent and objective approach to financial analysis, enabling users to make informed choices aligned with their investment goals and risk tolerance. The knowledge acquired represents a fundamental skill in the realm of finance, paving the way for better decision-making and strategic planning.