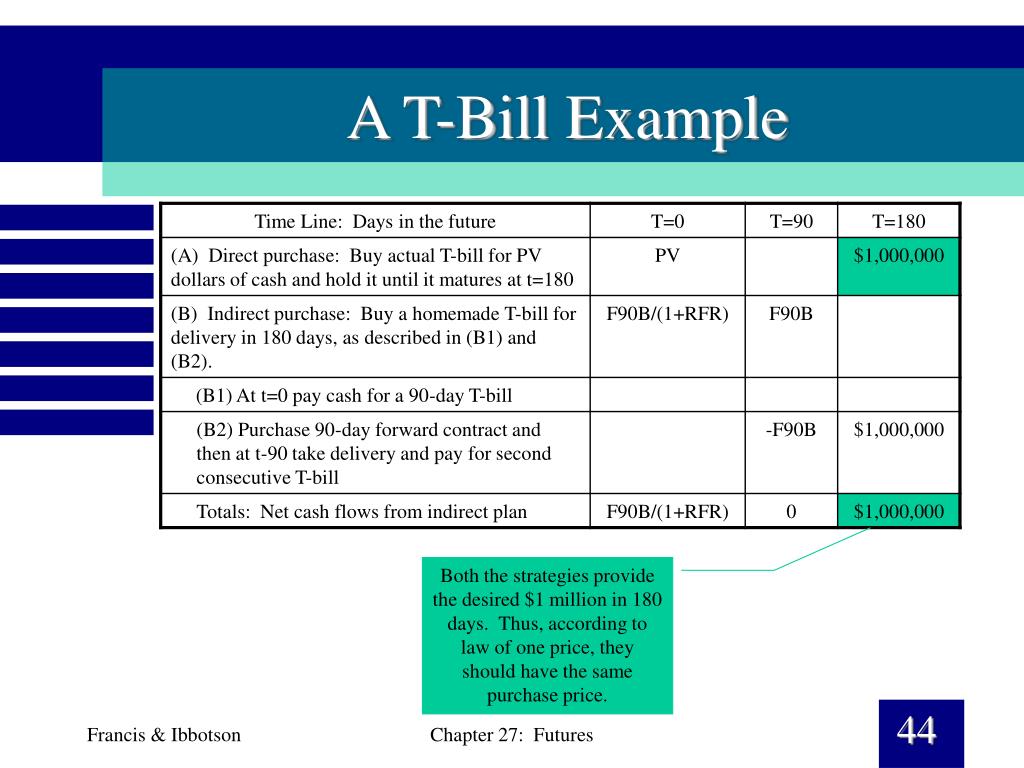
What is a Treasury Bill and How Does it Work?
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) are a type of short-term government debt security issued by the US Department of the Treasury. They are considered one of the safest investment options, offering a low-risk way to invest in the US economy. T-Bills are backed by the full faith and credit of the US government, making them an attractive option for investors seeking a secure return. With maturities ranging from a few weeks to a year, T-Bills provide a flexible investment opportunity for individuals, businesses, and institutions alike. Understanding how T-Bills work is essential for investors looking to capitalize on their benefits, including learning how to calculate T-Bill return. By grasping the mechanics of T-Bills, investors can make informed decisions about their investment portfolios and optimize their returns. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the world of T-Bills, exploring the different types, calculating returns, and providing expert tips for maximizing T-Bill returns.
Understanding the Different Types of Treasury Bills
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) come in various maturities, each offering unique characteristics and benefits. The four main types of T-Bills are 4-week, 13-week, 26-week, and 52-week bills. The 4-week T-Bill is the shortest-term option, providing a quick and low-risk investment opportunity. The 13-week and 26-week T-Bills offer a slightly longer investment horizon, while the 52-week T-Bill provides a longer-term investment option. Each type of T-Bill has its own distinct features, such as varying interest rates and returns, which are essential to understand when deciding how to calculate T-Bill return. For instance, longer-term T-Bills typically offer higher returns, but also come with slightly higher risks. By understanding the differences between each type of T-Bill, investors can make informed decisions about their investment portfolios and optimize their returns.
The Formula for Calculating T-Bill Return
Calculating the return on a T-Bill investment is a straightforward process. The formula to calculate T-Bill return is: (Face Value – Purchase Price) / Purchase Price. This formula takes into account the face value of the T-Bill, which is the amount the investor will receive at maturity, and the purchase price, which is the amount the investor pays for the T-Bill. For example, let’s say an investor purchases a 26-week T-Bill with a face value of $1,000 for $980. To calculate the return, the investor would use the formula: ($1,000 – $980) / $980 = 2.04%. This means the investor can expect a 2.04% return on their investment. Understanding how to calculate T-Bill return is essential for investors looking to maximize their returns and make informed investment decisions. By grasping this concept, investors can better navigate the world of T-Bill investments and optimize their portfolios.
Factors Affecting T-Bill Returns
When it comes to understanding how to calculate T-Bill return, it’s essential to consider the various factors that influence T-Bill returns. These factors can significantly impact investment decisions and ultimately affect the overall performance of a T-Bill investment portfolio. One of the primary factors affecting T-Bill returns is interest rates. When interest rates rise, the returns on T-Bills also increase, making them a more attractive investment option. On the other hand, when interest rates fall, T-Bill returns decrease, making them less appealing to investors. Inflation is another critical factor that affects T-Bill returns. During periods of high inflation, T-Bill returns may not keep pace with inflation, resulting in a decrease in purchasing power. Economic conditions, such as recession or growth, also play a significant role in shaping T-Bill returns. In times of economic uncertainty, investors may flock to T-Bills as a safe-haven asset, driving up demand and increasing returns. By understanding these factors and how they impact T-Bill returns, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
How to Calculate T-Bill Return Using Discount Yield
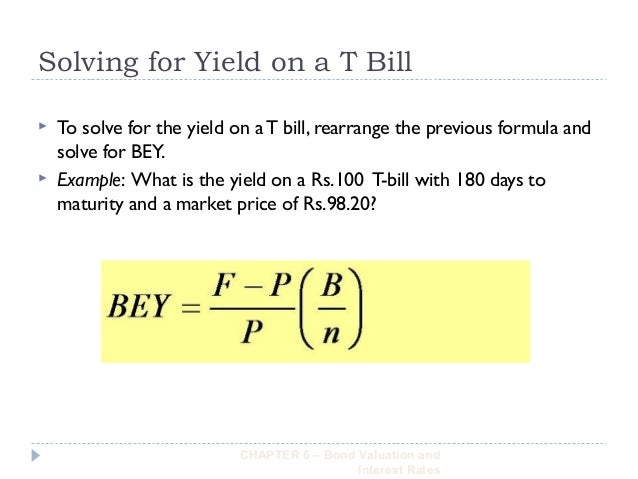
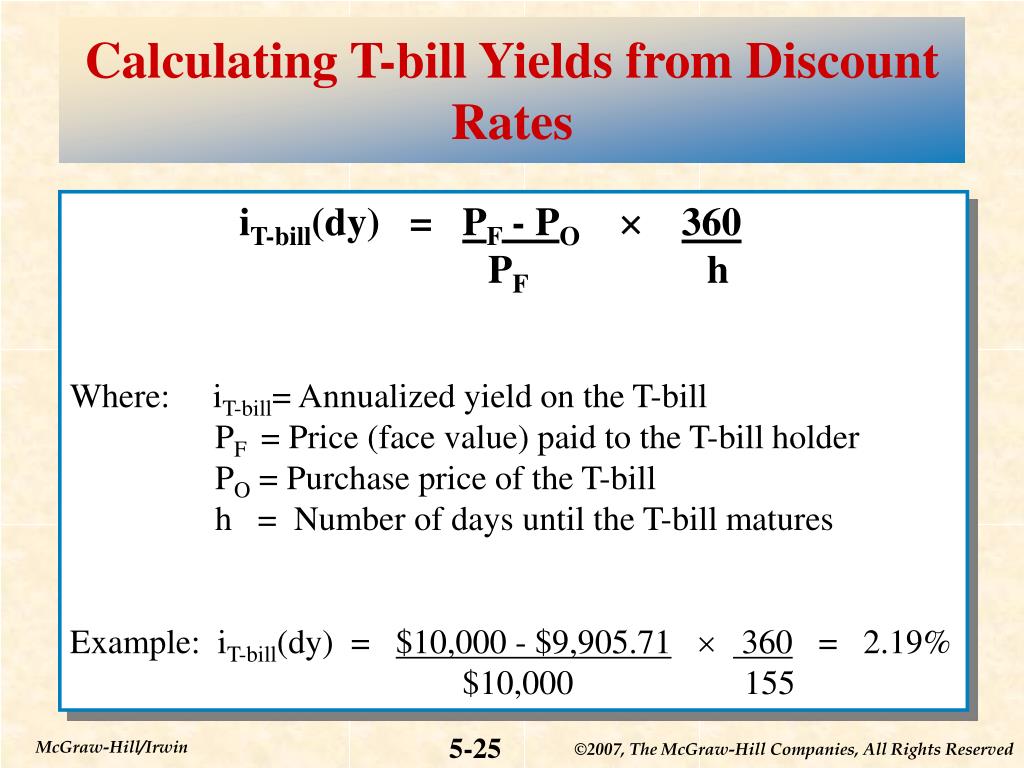
When it comes to calculating the return on a T-Bill investment, investors have two options: the simple return method and the discount yield method. While the simple return method provides a straightforward calculation, the discount yield method offers a more accurate representation of the T-Bill’s return. To calculate the discount yield, investors need to know the face value, purchase price, and term of the T-Bill. The formula for discount yield is: (Face Value – Purchase Price) / Purchase Price x (360 / Days to Maturity). For example, let’s say an investor purchases a 26-week T-Bill with a face value of $1,000 for $980. To calculate the discount yield, the investor would use the formula: ($1,000 – $980) / $980 x (360 / 182) = 2.15%. This means the investor can expect a 2.15% return on their investment. Understanding how to calculate T-Bill return using the discount yield method is essential for investors looking to maximize their returns and make informed investment decisions. By grasping this concept, investors can better navigate the world of T-Bill investments and optimize their portfolios.
Real-World Examples of T-Bill Investments
Understanding how to calculate T-Bill return is crucial, but it’s equally important to see how T-Bills can be applied in real-world investment scenarios. Let’s consider a few examples. Suppose an investor has $10,000 to invest and wants to diversify their portfolio with T-Bills. They could invest $2,000 in a 4-week T-Bill, $3,000 in a 13-week T-Bill, and $5,000 in a 26-week T-Bill. By doing so, they can take advantage of the different maturity periods and returns offered by each T-Bill. Another scenario could be an investor who wants to park their money for a short period while waiting for a more lucrative investment opportunity. In this case, a 4-week T-Bill could provide a low-risk, short-term investment solution. By incorporating T-Bills into a diversified investment portfolio, investors can reduce risk, increase returns, and achieve their long-term financial goals. For instance, an investor could allocate 20% of their portfolio to T-Bills, 30% to stocks, and 50% to bonds. This diversification strategy can help mitigate risk and increase potential returns. By understanding how to calculate T-Bill return and incorporating T-Bills into a diversified investment portfolio, investors can make informed investment decisions and achieve financial success.
Tips for Maximizing T-Bill Returns
While T-Bills are considered a low-risk investment option, there are still ways to maximize returns and optimize investment strategies. One effective approach is laddering, which involves investing in multiple T-Bills with staggered maturity dates. This strategy allows investors to take advantage of changing interest rates and minimize the impact of inflation. For example, an investor could invest in a 4-week, 13-week, 26-week, and 52-week T-Bill simultaneously, creating a ladder of investments that mature at different times. Another strategy is diversification, which involves spreading investments across different asset classes, including T-Bills, stocks, and bonds. By diversifying a portfolio, investors can reduce risk and increase potential returns. Timing investments is also crucial, as T-Bill returns can be affected by changes in interest rates and economic conditions. Investors should consider the current market conditions and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. Additionally, investors can take advantage of the compounding effect by reinvesting the returns from their T-Bill investments. By following these expert tips and strategies, investors can maximize their T-Bill returns and achieve their long-term financial goals. Understanding how to calculate T-Bill return is essential, but it’s equally important to know how to apply this knowledge in real-world investment scenarios.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of T-Bill Investing
In conclusion, understanding how to calculate T-Bill return is a crucial aspect of investing in Treasury Bills. By grasping the concepts of T-Bill mechanics, types, and return calculations, investors can make informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies. It’s essential to consider the factors that affect T-Bill returns, such as interest rates, inflation, and economic conditions, and to incorporate T-Bills into a diversified investment portfolio. By following expert tips and strategies, such as laddering, diversification, and timing investments, investors can maximize their T-Bill returns and achieve their long-term financial goals. Remember, calculating T-Bill return is not a complex task, and with practice and patience, investors can master the art of T-Bill investing. By applying the knowledge and concepts discussed in this article, investors can unlock the secrets of Treasury Bill investments and reap the benefits of this low-risk investment option. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding how to calculate T-Bill return is a valuable skill that can help you navigate the world of finance with confidence.