Grasping the Basics of Price Swings in Stocks
Stock volatility is a critical concept for investors to understand. It describes the degree of variation in a stock’s trading price over a specific period. In essence, it measures how much and how quickly a stock price tends to fluctuate. Stock volatility is a statistical measure. It quantifies the dispersion of returns for a particular security or market index. Understanding stock volatility is crucial because it provides insights into the potential risk and reward associated with investing in a specific stock. Learning how to calculate stock volatility is essential to asses investment risks.
A volatile stock experiences significant price swings. These swings can occur rapidly and unpredictably. Conversely, a less volatile stock exhibits more stable and predictable price movements. The degree of stock volatility influences investment decisions. Investors often use volatility as an indicator of risk. Higher volatility typically suggests a riskier investment. The risk is that the stock price could decline sharply. However, higher volatility also presents the potential for greater returns. This is because the stock price could also increase significantly. For investors, understanding how to calculate stock volatility helps in managing risk tolerance.
Why is understanding stock volatility important? It allows investors to make more informed decisions. This knowledge enables investors to better assess the potential risks and rewards. They can align investments with their financial goals and risk tolerance. For example, a risk-averse investor might prefer low-volatility stocks. A more aggressive investor might seek opportunities in high-volatility stocks. Ultimately, understanding how to calculate stock volatility and interpreting its implications are essential skills for any investor. These skills contribute to a more strategic and successful investment approach. These skills can lead to better investment outcomes. Learning how to calculate stock volatility equips investors with a valuable tool for navigating the complexities of the stock market.
How to Determine Stock Volatility: Common Methods Explained
Understanding how to calculate stock volatility is crucial for investors seeking to manage risk and make informed decisions. Several methods exist, but two primary approaches dominate: historical volatility and implied volatility. Each offers unique insights into the potential price fluctuations of a stock.
Historical volatility provides a backward-looking perspective. It measures the degree of price fluctuation of a stock over a specific period. To determine how to calculate stock volatility using this method, one typically calculates the standard deviation of the stock’s returns. This involves gathering historical price data, computing the returns for each period (e.g., daily or weekly), and then calculating the standard deviation of those returns. A higher standard deviation indicates greater historical volatility. The formula for standard deviation can be complex, but spreadsheet software and financial tools simplify the process. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility historically allows investors to assess past price behavior and make informed decisions.
Implied volatility, on the other hand, is forward-looking. It is derived from the prices of options contracts on the underlying stock. Implied volatility reflects the market’s expectation of future volatility over the life of the option. Option prices are influenced by several factors. These factors include the current stock price, the strike price of the option, the time until expiration, and the expected volatility of the stock. Sophisticated models, such as the Black-Scholes model, are used to back out the implied volatility from the option price. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility, as implied by option prices, is valuable because it provides insight into market sentiment and expectations. While historical volatility reflects what has already happened, implied volatility attempts to predict what might happen. IVolatility.com is an example of a specialized platform that provides implied volatility data and analytics. Comparing historical and implied volatility can be insightful. A significant divergence between the two may suggest that the market expects a change in the stock’s volatility regime.
Calculating Historical Volatility: A Step-by-Step Approach
Understanding how to calculate stock volatility, specifically historical volatility, involves a straightforward process. This calculation relies on past price movements to estimate future price fluctuations. Investors can then use it to assess potential risks. The steps below provide a detailed guide on how to calculate stock volatility. This enables informed investment decisions.
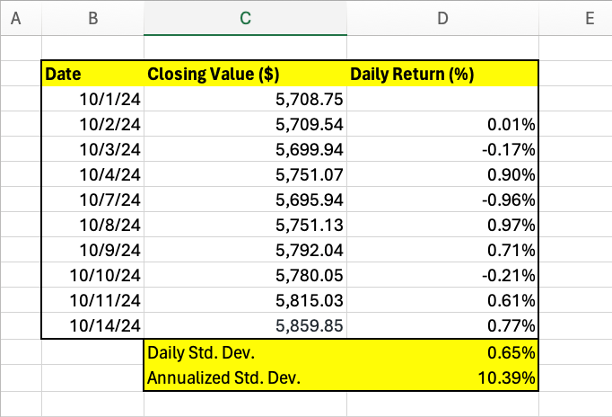
First, gather historical price data for the stock. Obtain daily closing prices for a specific period (e.g., the past year). Publicly available sources, like financial websites or APIs, are excellent resources. Ensure the data is accurate and reliable. Next, calculate daily returns. Use logarithmic returns for superior accuracy. The formula for calculating daily return is: `(Price(today) – Price(yesterday)) / Price(yesterday)`. For example, if a stock closed at $150 today and $145 yesterday, the daily return is approximately 0.0345 or 3.45%. Subsequently, determine the standard deviation of the daily returns. This measures the dispersion of the returns around the average return. Spreadsheet software or statistical packages can assist with this calculation. The standard deviation represents the volatility of the stock over the observed period. Lastly, annualize the standard deviation. Multiply the daily standard deviation by the square root of the number of trading days in a year (typically 252). This converts the daily volatility into an annualized figure, facilitating easier comparison with other investments. For example, if the daily standard deviation is 0.01 (1%), the annualized volatility would be approximately 0.1587 (15.87%). Annualizing is important because it provides a standardized measure of volatility across different time periods. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility and annualizing it allows for better comparison and risk assessment.
Consider this example to further illustrate how to calculate stock volatility. Assume a stock has the following closing prices for five consecutive days: $100, $101, $102, $101, and $103. First, calculate the daily returns: (101-100)/100 = 0.01, (102-101)/101 = 0.0099, (101-102)/102 = -0.0098, (103-101)/101 = 0.0198. Then, calculate the standard deviation of these returns, which is approximately 0.0125. Finally, annualize this by multiplying by the square root of 252: 0.0125 * √252 ≈ 0.1984. Therefore, the annualized historical volatility is approximately 19.84%. Knowing how to calculate stock volatility using historical data provides valuable insights for investment analysis. Remember that historical volatility is not a predictor of future volatility. It’s merely an indicator based on past performance.
Interpreting Volatility Metrics: What Does the Number Mean?
Understanding how to interpret volatility metrics is crucial for investors. Volatility, in essence, reflects the degree of price fluctuation for a stock or market index. A high volatility figure suggests that the price can change dramatically over a short period. Conversely, a low volatility figure indicates more stable and predictable price movements. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility and what the resulting metrics signify is key to risk management and investment strategy.
The relationship between volatility and risk is directly proportional. Higher volatility generally equates to higher risk. This is because there’s a greater chance of significant losses in a short timeframe. However, higher volatility also presents the potential for higher rewards. Rapid price increases can lead to substantial profits for investors who are willing to take on the added risk. Therefore, interpreting volatility requires a balanced perspective, considering both potential gains and potential losses. Different sectors and individual stocks exhibit varying levels of typical volatility. For instance, technology stocks often experience higher volatility than established blue-chip companies due to factors like rapid innovation and changing market trends. Knowing how to calculate stock volatility for different assets allows for a comparative analysis, helping investors build diversified portfolios that align with their risk tolerance.
When analyzing volatility, consider the context of the specific stock or market. A volatility of 20% might be considered high for a stable utility stock, but it could be normal for a high-growth tech stock. Investors can use volatility metrics to assess the potential risk and reward of an investment. This information is valuable in making informed decisions about asset allocation and portfolio construction. Keep in mind that understanding how to calculate stock volatility is just one piece of the puzzle. It should be combined with other fundamental and technical analyses to form a comprehensive investment strategy. By combining an understanding of how to calculate stock volatility with other analytical approaches, investors can better manage risk and maximize their potential returns in the stock market.
Tools and Resources for Analyzing Stock Volatility
Analyzing stock volatility effectively requires the right tools and resources. Several options are available to investors seeking to understand how to calculate stock volatility and interpret its implications. These tools range from readily accessible financial websites to sophisticated financial analysis software, each offering unique functionalities. Understanding the capabilities of these resources is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The following paragraphs present several options for further analysis.
One category of helpful resources includes financial websites. Many reputable sites, such as Google Finance and Yahoo Finance, provide historical stock prices and volatility data. These platforms often display volatility metrics alongside other key financial indicators. This allows investors to quickly assess a stock’s price fluctuations and compare it to its peers. These websites are generally free to use, making them an accessible starting point for volatility analysis. They provide readily available data necessary to understand how to calculate stock volatility. Spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets is another valuable tool for performing custom volatility calculations. Users can import historical stock price data and apply statistical formulas to calculate standard deviation, a key component in determining historical volatility. While requiring some technical proficiency, spreadsheet software offers flexibility in tailoring the analysis to specific needs. These can also assist in understanding how to calculate stock volatility via manual calculation.
For more advanced analysis, specialized financial analysis software is also available. These programs often offer features like real-time data feeds, advanced charting capabilities, and sophisticated statistical tools. Some platforms also provide implied volatility data, derived from options prices. These professional-grade tools cater to experienced traders and analysts who require in-depth insights into market volatility. IVolatility.com is one example of such specialized platform. Regardless of the chosen tool, investors should remember that no single method guarantees investment success. A comprehensive understanding of financial markets, combined with disciplined risk management, is crucial for navigating the complexities of stock volatility. Using these tools will improve understanding on how to calculate stock volatility, but does not guarantee profits.
Factors That Influence Market Volatility
Numerous external factors exert influence over stock volatility. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the market effectively. It’s important to know how to calculate stock volatility and what impacts it.
Economic news plays a significant role. Interest rate changes announced by central banks can trigger substantial market reactions. For example, an unexpected interest rate hike might lead to a sell-off in stocks, increasing volatility. Inflation reports also matter. Higher-than-expected inflation figures can cause uncertainty, leading to increased volatility as investors reassess their positions. Furthermore, political events contribute to market swings. Elections, policy changes, and geopolitical tensions can all create uncertainty and impact investor sentiment. The more investors understand how to calculate stock volatility, the more prepared they will be for such events. Company-specific news is another key driver. Earnings reports often lead to significant price movements, especially if the results deviate considerably from expectations. Product announcements, mergers, and acquisitions can also affect a company’s stock price and contribute to overall market volatility. Market sentiment, driven by fear and greed, significantly impacts stock prices. Negative news can trigger fear, leading to widespread selling and increased volatility. Conversely, positive news can fuel greed, resulting in a buying frenzy and potentially unsustainable price increases. All of these factors underscore how to calculate stock volatility to use it when evaluating investments.
These events can trigger increased or decreased volatility. Negative economic data, political instability, or disappointing earnings reports can lead to a surge in volatility as investors react to the uncertainty. Conversely, positive economic news, political stability, or strong corporate performance can result in decreased volatility as investor confidence grows. It is essential to monitor these factors closely to anticipate potential shifts in market volatility and adjust investment strategies accordingly. The capacity to know how to calculate stock volatility gives the investor an advantage to be considered. Recognizing these influences enables investors to make informed decisions and manage risk effectively.
Using Volatility in Investment Strategies
Investors can leverage volatility information to shape their investment strategies. How to calculate stock volatility data provides insights for various investment approaches. For example, options traders heavily rely on implied volatility. This is used to price options contracts, reflecting the market’s expectation of future price swings. The higher the implied volatility, the more expensive the options tend to be, due to the increased probability of the underlying asset experiencing significant price movements. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility is important in options trading.
Risk-averse investors may choose to avoid high-volatility stocks. These stocks can experience significant price drops in short periods. Conversely, more aggressive investors might view high volatility as an opportunity. They aim to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations. They seek higher potential returns. How to calculate stock volatility can highlight potential high-reward, high-risk investments. Investors should align their strategy with their personal risk tolerance.
Volatility can also play a crucial role in position sizing. This refers to determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to a particular investment. When an investor identifies a high-volatility stock they wish to invest in, they may reduce the size of their position. This limits potential losses if the stock price declines sharply. Conversely, for lower-volatility stocks, investors might take larger positions. This aims to maximize returns while staying within their risk tolerance. How to calculate stock volatility helps investors to make more informed decisions. It is also important to understand the risks associated with these investments.
Limitations of Volatility Analysis in Stock Assessment
Relying solely on volatility analysis has limitations when assessing stocks. Volatility, particularly historical volatility, is a backward-looking measure. It reflects past price fluctuations and may not accurately predict future price movements. Implied volatility, derived from option prices, represents market expectations. These expectations may not always materialize. Therefore, relying exclusively on volatility to make investment decisions can be misleading.
One key limitation is that past performance is not indicative of future results. A stock with low historical volatility may suddenly experience significant price swings due to unforeseen events. Conversely, a stock with high historical volatility might become more stable over time. Furthermore, volatility doesn’t tell the whole story. It only quantifies the magnitude of price changes, not the reasons behind them. Understanding company fundamentals is crucial. How to calculate stock volatility is a valuable skill, but it must be paired with a deep understanding of other factors. These factors include industry trends, macroeconomic conditions, and company-specific news. Ignoring these aspects can lead to poor investment choices. Understanding how to calculate stock volatility provides a piece of the puzzle. It’s essential to consider the bigger picture.
Therefore, a comprehensive stock assessment requires a multifaceted approach. In addition to understanding how to calculate stock volatility, investors should analyze financial statements, assess management quality, and evaluate the competitive landscape. Macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and economic growth can significantly impact stock prices. Political events, regulatory changes, and technological disruptions can also influence investment outcomes. By integrating volatility analysis with these other considerations, investors can make more informed and well-rounded investment decisions. Remember that learning how to calculate stock volatility is just one step in a complex and ongoing process. Employing a holistic view will dramatically improve investment success.