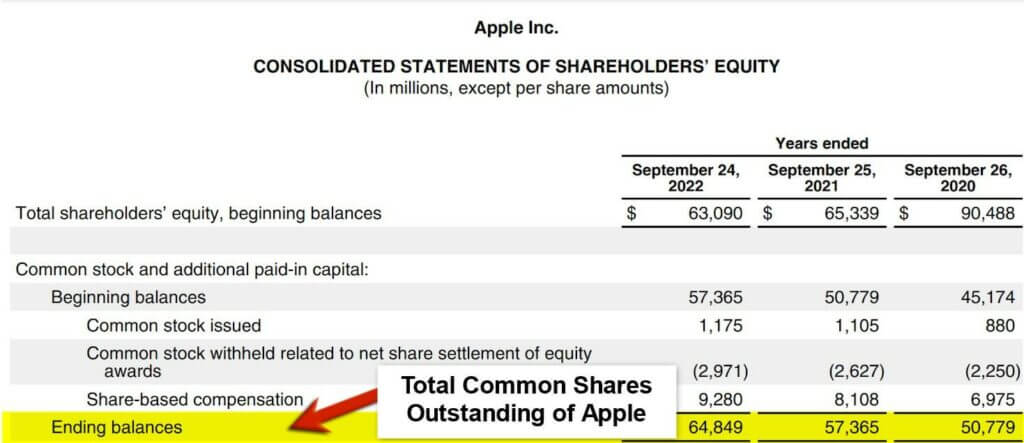
Understanding the Basics of Shares Outstanding
In the world of finance and investing, understanding the concept of shares outstanding is crucial for making informed decisions. Shares outstanding represent the total number of shares of a company’s stock that are currently held by its shareholders. This figure is essential for investors, analysts, and companies alike, as it provides a snapshot of the company’s ownership structure and market capitalization. When evaluating a company’s performance, shares outstanding serve as a key metric, helping to determine the total value of the company’s outstanding shares. In essence, shares outstanding are the backbone of a company’s financial health, and accurately calculating this figure is vital for stakeholders to make informed decisions. As we delve deeper into the world of share calculation, it’s essential to grasp the basics of shares outstanding, laying the foundation for a comprehensive understanding of how to calculate diluted shares outstanding, a crucial aspect of financial analysis.
The Importance of Accurate Share Counting
Accurate share counting is crucial for investors, analysts, and companies alike. Inaccurate calculations can lead to a distorted view of a company’s financial health, resulting in poor investment decisions and potential losses. Moreover, incorrect share counts can also impact a company’s ability to raise capital, as investors may be deterred by inaccurate or unreliable financial information. Furthermore, companies may face regulatory issues and reputational damage if they fail to provide accurate share counts. Therefore, it is essential to understand the importance of accurate share counting and how it can impact a company’s overall performance. By grasping the significance of accurate share counting, investors and analysts can better navigate the complexities of financial analysis, including how to calculate diluted shares outstanding, and make more informed decisions.
How to Calculate Basic Shares Outstanding
Calculating basic shares outstanding is a straightforward process that provides a snapshot of a company’s current ownership structure. The formula to calculate basic shares outstanding is:
Basic Shares Outstanding = Total Shares Issued – Treasury Shares
Where:
Total Shares Issued represents the total number of shares issued by the company, and
Treasury Shares represent the number of shares held in the company’s treasury.
For example, let’s say a company has issued 1 million shares and has 200,000 shares held in its treasury. The basic shares outstanding would be:
Basic Shares Outstanding = 1,000,000 – 200,000 = 800,000 shares
This figure represents the total number of shares currently held by shareholders, excluding treasury shares. Understanding how to calculate basic shares outstanding is essential for investors and analysts, as it provides a foundation for more advanced calculations, such as how to calculate diluted shares outstanding. By grasping this fundamental concept, stakeholders can better analyze a company’s financial health and make more informed investment decisions.
What are Diluted Shares Outstanding?
Diluted shares outstanding represent the total number of shares that would be outstanding if all convertible securities, such as options, warrants, and convertible debt, were exercised or converted into common shares. This concept is crucial for investors and analysts, as it provides a more comprehensive picture of a company’s potential ownership structure and market capitalization. Dilution occurs when a company issues new shares, reducing the ownership percentage of existing shareholders and potentially decreasing the value of their shares.
Several types of securities can lead to dilution, including:
– Stock options granted to employees or executives
– Warrants issued to investors or lenders
– Convertible debt, such as bonds or loans
– Restricted stock units (RSUs) or performance shares
Understanding diluted shares outstanding is essential for stakeholders, as it helps them assess the potential impact of dilution on shareholder value. By grasping this concept, investors and analysts can better evaluate a company’s financial health and make more informed decisions. In the next section, we will explore how to calculate diluted shares outstanding, providing a step-by-step guide to help stakeholders master this critical calculation.
The Formula for Calculating Diluted Shares Outstanding
The formula for calculating diluted shares outstanding is a bit more complex than the basic shares outstanding formula. It takes into account the potential conversion of convertible securities into common shares. The formula is:
Diluted Shares Outstanding = Basic Shares Outstanding + Additional Shares from Convertible Securities
Where:
Basic Shares Outstanding represents the total number of shares currently outstanding, and
Additional Shares from Convertible Securities represents the number of shares that would be issued if all convertible securities were exercised or converted.
To calculate the additional shares from convertible securities, you need to consider the following:
– Options: Use the treasury stock method to calculate the additional shares. This method assumes that the company will use the proceeds from the exercise of options to repurchase shares at the current market price.
– Warrants: Add the number of shares that would be issued if all warrants were exercised.
– Convertible debt: Add the number of shares that would be issued if all convertible debt were converted into common shares.
– Restricted stock units (RSUs) or performance shares: Add the number of shares that would be issued if all RSUs or performance shares were vested.
For example, let’s say a company has 1 million basic shares outstanding, 200,000 options outstanding with a strike price of $20, and 100,000 warrants outstanding with an exercise price of $30. The current market price is $40. Using the treasury stock method, the additional shares from options would be 150,000 (200,000 x ($40 – $20) / $40). The additional shares from warrants would be 100,000. Therefore, the diluted shares outstanding would be:
Diluted Shares Outstanding = 1,000,000 + 150,000 + 100,000 = 1,250,000 shares
By understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding, investors and analysts can gain a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s potential ownership structure and market capitalization. This knowledge can help stakeholders make more informed investment decisions and better assess the potential impact of dilution on shareholder value.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Diluted Shares
Calculating diluted shares outstanding can be a complex process, and even small mistakes can lead to significant errors. To ensure accuracy, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can occur during the calculation process. Here are some common errors to watch out for:
– Failing to account for all convertible securities: Make sure to include all types of convertible securities, such as options, warrants, and convertible debt, in your calculation.
– Incorrectly valuing convertible securities: Ensure that you use the correct valuation method for each type of convertible security, such as the treasury stock method for options.
– Ignoring the impact of dilution on shareholder value: Remember that diluted shares outstanding can have a significant impact on shareholder value, so it’s essential to consider this when making investment decisions.
– Not updating calculations regularly: Diluted shares outstanding can change over time due to changes in convertible securities or market conditions, so it’s essential to regularly update your calculations.
– Relying on incomplete or inaccurate data: Ensure that you have access to complete and accurate data on a company’s convertible securities and market conditions to ensure accurate calculations.
To avoid these mistakes, it’s essential to have a thorough understanding of the formula for calculating diluted shares outstanding and to carefully follow each step of the calculation process. Additionally, staying up-to-date with changes in a company’s convertible securities and market conditions can help ensure accuracy and provide a more comprehensive understanding of a company’s potential ownership structure and market capitalization.
By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, investors and analysts can ensure accurate calculations and make more informed investment decisions. Remember, understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding is crucial for making informed investment decisions and assessing the potential impact of dilution on shareholder value.
Real-World Examples of Diluted Shares Outstanding
To illustrate the concept of diluted shares outstanding, let’s examine some real-world examples of companies that have experienced dilution. These examples will help demonstrate the impact of diluted shares on shareholder value and market capitalization.
Example 1: Tesla, Inc.
In 2020, Tesla, Inc. issued 2.2 million shares of common stock to raise capital for its expansion plans. This increased the company’s basic shares outstanding from 180 million to 182.2 million. However, Tesla also had 10 million options outstanding, which, if exercised, would increase the diluted shares outstanding to 192.2 million. This represents a 6.2% increase in diluted shares outstanding, which could potentially dilute shareholder value.
Example 2: Amazon, Inc.
In 2019, Amazon, Inc. issued 1.5 million shares of common stock to acquire a minority stake in a rival company. This increased the company’s basic shares outstanding from 490 million to 491.5 million. However, Amazon also had 20 million restricted stock units (RSUs) outstanding, which, if vested, would increase the diluted shares outstanding to 511.5 million. This represents a 4.3% increase in diluted shares outstanding, which could impact shareholder value.
Example 3: Netflix, Inc.
In 2018, Netflix, Inc. issued 5 million shares of common stock to raise capital for its content production. This increased the company’s basic shares outstanding from 420 million to 425 million. However, Netflix also had 15 million options outstanding, which, if exercised, would increase the diluted shares outstanding to 440 million. This represents a 4.5% increase in diluted shares outstanding, which could dilute shareholder value.
These examples demonstrate how diluted shares outstanding can impact shareholder value and market capitalization. By understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding, investors and analysts can better assess the potential impact of dilution on a company’s share price and make more informed investment decisions.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Share Calculation
In conclusion, understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding is a crucial aspect of finance and investing. By grasping the concepts of basic and diluted shares outstanding, investors and analysts can make more informed decisions about their investments. Accurate share counting is essential to avoid misrepresentation of a company’s financial health and to ensure that investors are not misled.
Throughout this article, we have explored the importance of accurate share counting, the formula for calculating basic shares outstanding, and the concept of diluted shares outstanding. We have also discussed common mistakes to avoid when calculating diluted shares and provided real-world examples of companies that have experienced dilution.
By mastering the art of share calculation, investors and analysts can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health and make more informed decisions about their investments. Remember, understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding is key to unlocking the secrets of shareholder equity and making informed investment decisions.
By applying the concepts and formulas outlined in this article, investors and analysts can confidently navigate the world of finance and investing, making informed decisions that drive success. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding how to calculate diluted shares outstanding is an essential skill that will serve you well in your financial journey.