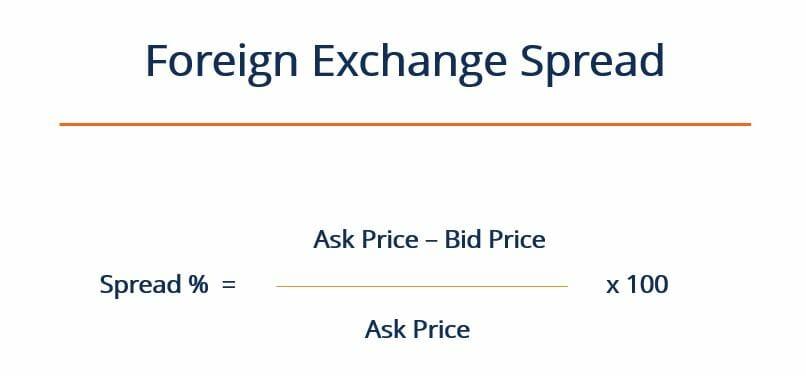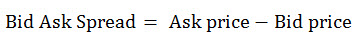What is a Bid-Ask Spread and Why Does it Matter?
In the world of trading, understanding the bid-ask spread is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The bid-ask spread, also known as the bid-offer spread, is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. This seemingly simple concept has a profound impact on trading outcomes, and grasping its significance is essential for traders of all levels. By understanding how to calculate bid ask spread, investors can better navigate the complexities of the market and make more informed trading decisions. In essence, the bid-ask spread represents the cost of trading, and being aware of it can help traders minimize losses and maximize gains.
The Anatomy of a Bid-Ask Spread: Breaking it Down
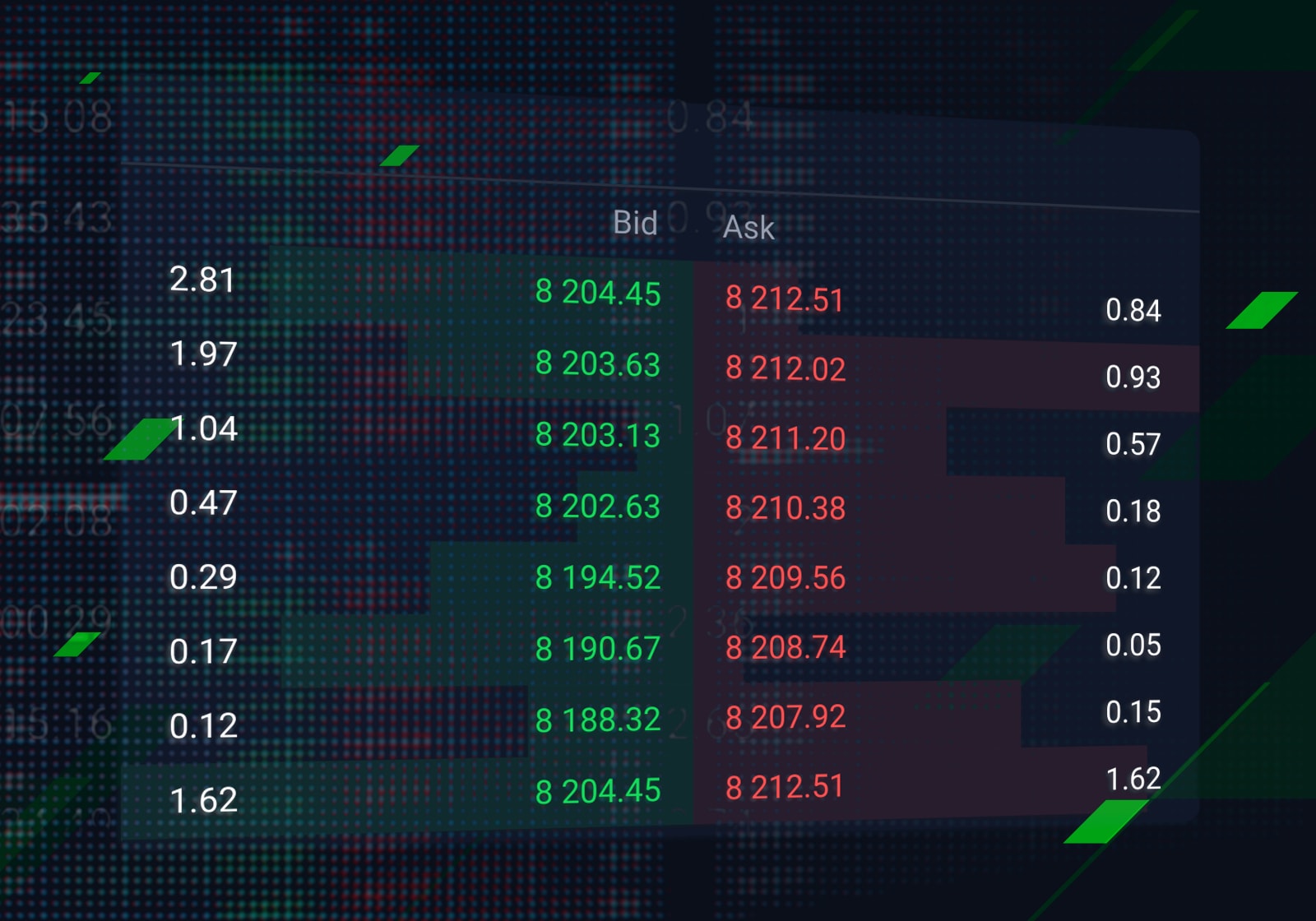
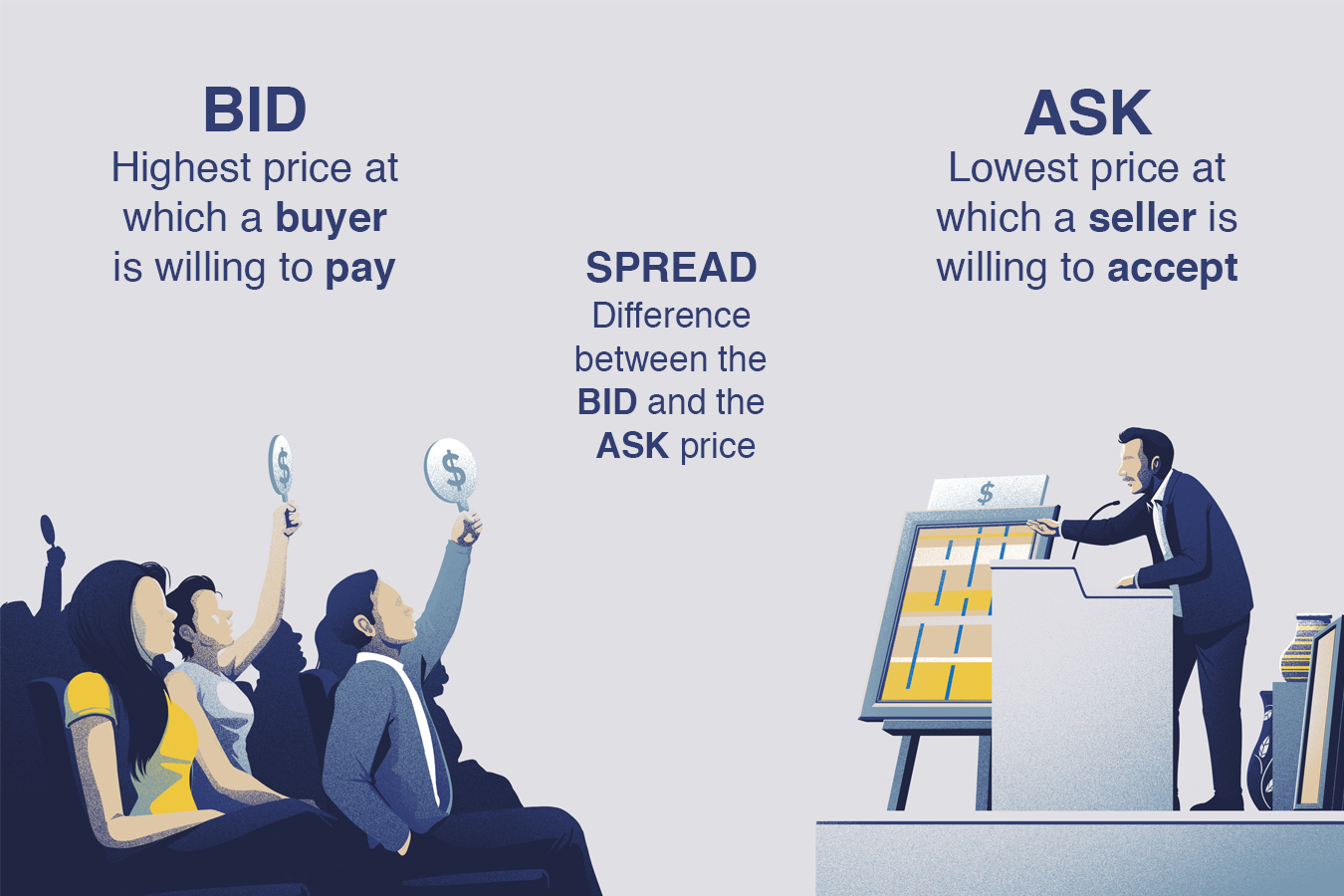
A bid-ask spread is comprised of three essential components: the bid price, ask price, and the spread itself. Understanding each component is crucial for grasping the concept of bid-ask spreads. The bid price represents the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security, while the ask price is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. The spread, which is the difference between the bid and ask prices, represents the cost of trading. For instance, if the bid price for a stock is $50 and the ask price is $55, the bid-ask spread would be $5. This spread represents the profit made by the market maker or broker for facilitating the trade. By understanding how to calculate bid ask spread, investors can better comprehend the dynamics of the market and make more informed trading decisions.
How to Calculate the Bid-Ask Spread: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating the bid-ask spread is a straightforward process that requires understanding the bid and ask prices. The formula to calculate the bid-ask spread is: Bid-Ask Spread = Ask Price – Bid Price. To illustrate this, let’s consider an example. Suppose the bid price for a stock is $40 and the ask price is $45. Using the formula, the bid-ask spread would be: Bid-Ask Spread = $45 – $40 = $5. This means that the market maker or broker is making a profit of $5 for facilitating the trade. When learning how to calculate bid ask spread, it’s essential to understand that the spread can vary depending on market conditions and the type of security being traded. By mastering this calculation, investors can better navigate the complexities of the market and make more informed trading decisions.
Factors Affecting the Bid-Ask Spread: What You Need to Know
The bid-ask spread is influenced by several factors that can impact trading decisions. One of the primary factors is market volatility. In highly volatile markets, the bid-ask spread tends to increase as market makers and brokers seek to compensate for the increased risk. This is because they need to adjust their prices quickly to reflect the changing market conditions. Another crucial factor is liquidity, which refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold. In markets with low liquidity, the bid-ask spread tends to be higher due to the reduced number of buyers and sellers. Order flow is another significant factor, as it can influence the supply and demand dynamics of the market. For instance, a surge in buy orders can lead to an increase in the ask price, while a surge in sell orders can lead to a decrease in the bid price. Understanding how to calculate bid ask spread is essential, but it’s equally important to recognize the factors that influence the spread. By doing so, investors can make more informed trading decisions and adapt to changing market conditions.
Real-World Examples: Calculating Bid-Ask Spreads in Different Markets
To illustrate the concept of bid-ask spreads in different markets, let’s consider some real-world examples. In the stock market, suppose we want to buy 100 shares of Apple Inc. (AAPL). The current bid price is $175.50, and the ask price is $176.50. Using the formula, the bid-ask spread would be: Bid-Ask Spread = $176.50 – $175.50 = $1.00. This means that the market maker or broker is making a profit of $1.00 for facilitating the trade. In the options market, the bid-ask spread can be more complex due to the various strike prices and expiration dates. For instance, suppose we want to buy a call option on Google (GOOGL) with a strike price of $1,500 and an expiration date of one month. The current bid price is $20.50, and the ask price is $21.50. Using the formula, the bid-ask spread would be: Bid-Ask Spread = $21.50 – $20.50 = $1.00. In the forex market, the bid-ask spread is typically quoted in pips, which are the smallest units of currency price movement. For example, suppose we want to buy EUR/USD at a current bid price of 1.1000 and an ask price of 1.1020. Using the formula, the bid-ask spread would be: Bid-Ask Spread = 1.1020 – 1.1000 = 20 pips. These examples demonstrate how to calculate bid ask spread in different markets, highlighting the importance of understanding this concept in various trading scenarios.
The Impact of Bid-Ask Spreads on Trading Strategies
The bid-ask spread has a significant impact on various trading strategies, and understanding its effects is crucial for making informed trading decisions. In day trading, the bid-ask spread can eat into profits, especially when trading low-volume stocks or illiquid markets. For instance, if a day trader buys a stock at the ask price and sells it at the bid price, the spread can result in a loss, even if the stock price hasn’t moved. In swing trading, the bid-ask spread can affect the timing of trades. If the spread is wide, it may be more challenging to enter or exit a trade at a favorable price, which can impact the overall profitability of the trade. In position trading, the bid-ask spread can influence the overall cost of holding a position. A wide spread can increase the cost of buying and selling a stock, which can erode profits over time. Furthermore, the bid-ask spread can also impact trading decisions, such as when to enter or exit a trade. For example, if the spread is wide, a trader may choose to wait for a more favorable price or adjust their trading strategy to minimize the impact of the spread. By understanding how to calculate bid ask spread and its impact on trading strategies, traders can make more informed decisions and optimize their trading performance.
Minimizing the Bid-Ask Spread: Tips and Strategies
To minimize the bid-ask spread, traders can employ several strategies that help reduce trading costs and improve overall performance. One effective approach is to use limit orders instead of market orders. Limit orders allow traders to specify the exact price at which they want to buy or sell a security, which can help avoid the bid-ask spread. Additionally, traders can avoid trading during times of high market volatility or low liquidity, when the bid-ask spread tends to be wider. Timing trades carefully can also help minimize the spread. For instance, traders can try to execute trades during times of high liquidity, such as during market open or close, when the spread is typically narrower. Another strategy is to use dark pools or alternative trading systems, which can provide better prices and lower spreads. Furthermore, traders can consider using trading algorithms or automated trading systems that can help optimize trade execution and minimize the bid-ask spread. By understanding how to calculate bid ask spread and implementing these strategies, traders can reduce trading costs and improve their overall trading performance.
Conclusion: Mastering the Bid-Ask Spread for Trading Success
In conclusion, understanding the bid-ask spread is a crucial aspect of trading that can significantly impact trading decisions and overall performance. By grasping the concept of bid-ask spreads, traders can make more informed decisions, minimize trading costs, and optimize their trading strategies. Whether it’s day trading, swing trading, or position trading, understanding how to calculate bid ask spread and its implications can be the key to success. By implementing the strategies and tips outlined in this article, traders can reduce the bid-ask spread and improve their trading performance. Remember, mastering the bid-ask spread is not a one-time task, but rather an ongoing process that requires continuous learning and adaptation. By staying informed and up-to-date on the latest market trends and bid-ask spread dynamics, traders can stay ahead of the curve and achieve long-term trading success.