What is Term SOFR and Why Does it Matter?
In the world of finance, benchmark rates play a crucial role in determining lending and borrowing costs. One such rate is Term SOFR, a forward-looking rate that has gained significant attention in recent years. But what exactly is Term SOFR, and why does it matter in the financial industry? To understand the significance of Term SOFR, it’s essential to delve into its definition, history, and applications. Term SOFR, or Secured Overnight Financing Rate, is a benchmark rate that measures the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities. This rate serves as a reference point for financial institutions, corporations, and individuals to determine the interest rates they charge or pay on loans and investments. The importance of Term SOFR lies in its ability to provide a more accurate and transparent representation of the market’s expectations of future interest rates. This, in turn, affects the entire financial ecosystem, influencing the cost of credit, the value of investments, and the overall health of the economy. As the financial industry continues to evolve, understanding how Term SOFR is calculated and applied becomes increasingly important for making informed decisions.
The Evolution of SOFR: From LIBOR to a New Era
The financial industry has witnessed a significant shift in recent years, with the transition from the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) to the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) as the new benchmark rate. This change marks a significant milestone in the evolution of financial markets, driven by the need for a more robust and reliable rate that better reflects the underlying market conditions. The flaws in LIBOR, including its vulnerability to manipulation and lack of transparency, led to a concerted effort by regulatory bodies and industry stakeholders to develop a new benchmark rate. SOFR, with its overnight repo-based methodology, offers a more accurate and transparent representation of the market’s expectations of future interest rates. The adoption of SOFR has far-reaching implications for financial institutions, corporations, and individuals, as it affects the pricing of loans, investments, and derivatives. Understanding the reasons behind this transition and the benefits of SOFR is crucial for navigating the complexities of the modern financial landscape. As the industry continues to adapt to this new era, grasping how Term SOFR is calculated and applied becomes increasingly important for making informed decisions.
How to Calculate Term SOFR: A Step-by-Step Guide
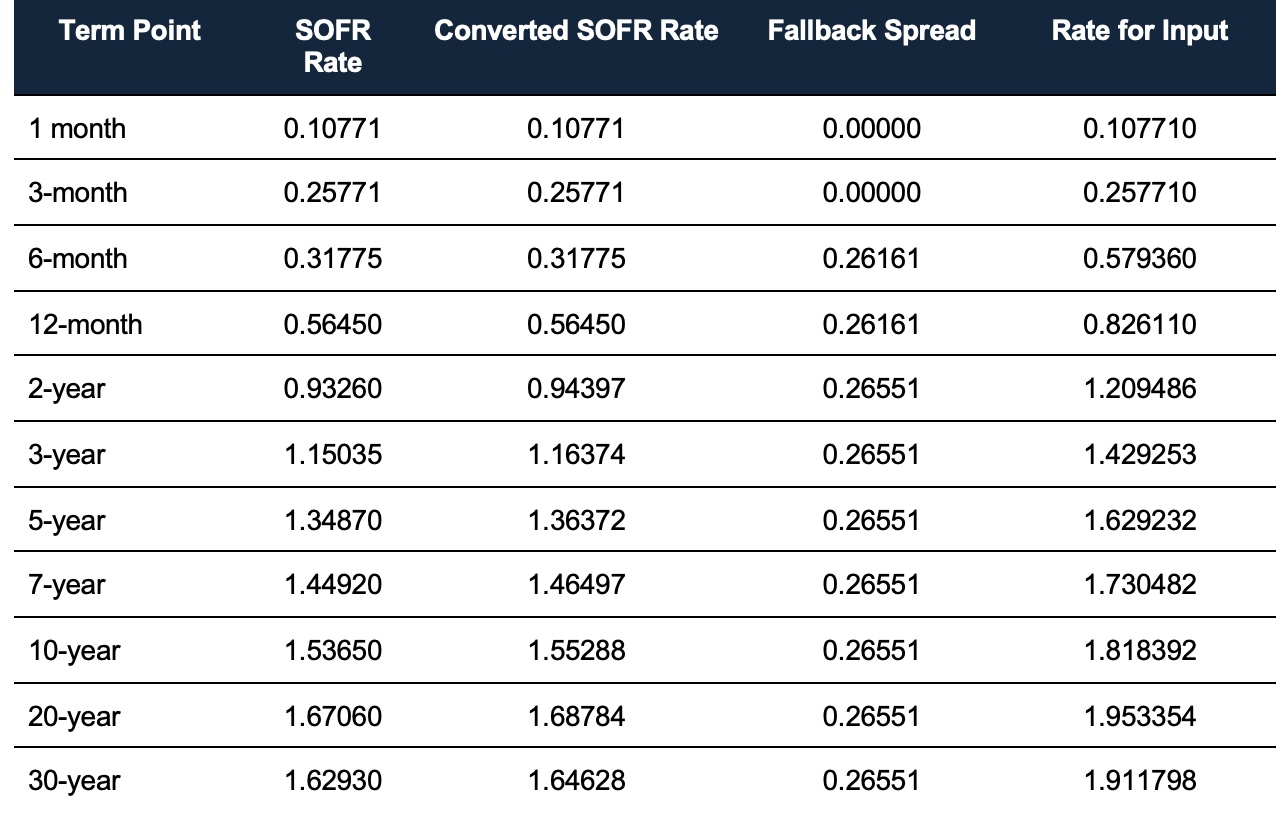
Calculating Term SOFR is a complex process that involves several inputs and formulas. To understand how Term SOFR is calculated, it’s essential to break down the process into its constituent parts. The calculation of Term SOFR involves three primary components: the overnight SOFR rate, the forward-looking term premium, and the credit spread. The overnight SOFR rate is calculated by the New York Federal Reserve based on the transactions in the Treasury repo market. The forward-looking term premium, on the other hand, is derived from a combination of market inputs, including futures rates, swap rates, and other market data. The credit spread, which represents the premium charged for borrowing over the risk-free rate, is also an essential component of the Term SOFR calculation. To calculate Term SOFR, the following formula is used: Term SOFR = Overnight SOFR Rate + Forward-Looking Term Premium + Credit Spread. Understanding how to calculate Term SOFR is crucial for financial institutions, corporations, and individuals seeking to navigate the complexities of the modern financial landscape. By grasping the intricacies of Term SOFR calculation, market participants can make more informed decisions about lending, borrowing, and investing. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s essential to consider the various inputs and formulas involved in the process.
Understanding the Components of Term SOFR
Term SOFR is a complex benchmark rate that consists of three primary components: the overnight SOFR rate, the forward-looking term premium, and the credit spread. Each of these components plays a crucial role in determining the final Term SOFR rate. The overnight SOFR rate, calculated by the New York Federal Reserve, represents the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by Treasury securities. This rate is based on the transactions in the Treasury repo market and serves as the foundation for the Term SOFR calculation. The forward-looking term premium, on the other hand, reflects the market’s expectations of future interest rates. This component is derived from a combination of market inputs, including futures rates, swap rates, and other market data. The credit spread, which represents the premium charged for borrowing over the risk-free rate, is the final component of Term SOFR. This spread is influenced by factors such as the borrower’s creditworthiness, the loan’s term, and the overall market conditions. Understanding the individual components of Term SOFR is essential for grasping how it is calculated and applied in financial markets. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s crucial to consider the interplay between these components and their impact on the final rate.
The Role of the New York Fed in Term SOFR Calculation
The New York Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in the calculation and publication of Term SOFR rates. As the administrator of the SOFR benchmark, the New York Fed is responsible for collecting and analyzing data from various sources, including the Treasury repo market, to calculate the overnight SOFR rate. This rate serves as the foundation for the Term SOFR calculation. The New York Fed also publishes the Term SOFR rates on a daily basis, providing market participants with a reliable and transparent benchmark rate. The methodology used by the New York Fed to calculate Term SOFR involves a combination of quantitative models and expert judgment, ensuring that the rate reflects the market’s expectations of future interest rates. The frequency of updates is also critical, with the New York Fed publishing Term SOFR rates daily, allowing market participants to adjust their lending and borrowing decisions accordingly. Understanding the role of the New York Fed in Term SOFR calculation is essential for grasping how the rate is determined and applied in financial markets. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s essential to consider the critical role played by the New York Fed in providing a reliable and transparent benchmark rate.
Real-World Applications of Term SOFR: Case Studies and Examples
Term SOFR has far-reaching implications for financial markets, and its applications are diverse and multifaceted. One of the primary uses of Term SOFR is in loan pricing, where it serves as a benchmark rate for determining interest rates on loans. For instance, a bank may use Term SOFR as a reference rate to set the interest rate on a commercial loan, ensuring that the rate is competitive and reflective of market conditions. In addition to loan pricing, Term SOFR is also used in risk management, where it helps financial institutions to assess and manage their exposure to interest rate risk. By using Term SOFR as a benchmark rate, institutions can better understand the potential impact of changes in interest rates on their portfolios and make informed decisions to mitigate risk. Furthermore, Term SOFR is used in investment decisions, such as in the valuation of securities and the assessment of investment opportunities. For example, an investor may use Term SOFR as a discount rate to value a bond, ensuring that the valuation is accurate and reflective of market conditions. Understanding how Term SOFR is used in real-world applications is essential for grasping its significance in financial markets. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s crucial to consider the practical implications of the rate and its applications in loan pricing, risk management, and investment decisions.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions in Term SOFR Calculation
Despite its widespread adoption, Term SOFR calculation is not without its challenges and misconceptions. One common challenge is data quality issues, where inaccurate or incomplete data can lead to incorrect Term SOFR calculations. For instance, if the input data for the overnight SOFR rate is incorrect, it can have a ripple effect on the entire calculation, resulting in an inaccurate Term SOFR rate. Another common challenge is incorrect assumptions, where market participants may make incorrect assumptions about the term premium or credit spread, leading to inaccurate calculations. To overcome these challenges, it’s essential to have a deep understanding of the Term SOFR calculation process and to carefully validate the input data. Additionally, market participants should be aware of common misconceptions surrounding Term SOFR calculation, such as the assumption that Term SOFR is a simple extension of the overnight SOFR rate. In reality, Term SOFR is a complex rate that requires a thorough understanding of its components and calculation methodology. By understanding these common challenges and misconceptions, market participants can ensure accurate and reliable Term SOFR calculations, which is critical for informed decision-making in financial markets. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s essential to consider these potential pitfalls and take steps to mitigate them.
Best Practices for Implementing Term SOFR in Your Organization
Implementing Term SOFR in a financial institution requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance. To ensure a seamless transition, it’s essential to follow best practices that address risk management, system integration, and operational efficiency. One key best practice is to develop a comprehensive risk management strategy that takes into account the unique characteristics of Term SOFR, including its volatility and sensitivity to market conditions. This involves identifying potential risks, assessing their impact, and developing mitigation strategies to minimize their effects. Another best practice is to integrate Term SOFR into existing systems and processes, ensuring that the new benchmark rate is accurately calculated and applied across all relevant business lines. This may involve updating legacy systems, developing new interfaces, and training staff on the new rate. Additionally, financial institutions should establish robust governance and oversight processes to ensure that Term SOFR is calculated and used consistently across the organization. By following these best practices, financial institutions can ensure a successful implementation of Term SOFR, which is critical for maintaining competitiveness and managing risk in today’s fast-paced financial markets. When asking “how is Term SOFR calculated?”, it’s essential to consider the broader implications of the rate and how it can be effectively implemented in a financial institution.