Understanding Stock Volatility: What It Means and Why It Matters
Stock volatility measures how much a stock’s price fluctuates over time. High volatility means significant price swings, both up and down, while low volatility indicates more stable prices. Understanding volatility is crucial because it directly relates to investment risk. Investors with a high risk tolerance might favor highly volatile stocks seeking potentially higher returns, while those with lower risk tolerance prefer less volatile stocks for greater stability. The question of how do you calculate volatility of a stock is key to managing risk. For example, a technology stock like Tesla might exhibit high volatility due to its growth potential and sensitivity to market sentiment. In contrast, a utility company stock might show lower volatility, offering steadier, albeit potentially slower, returns. How do you calculate volatility of a stock accurately? This question is central to informed investment decisions. Different investors will have different approaches to answering this question based on their tolerance for risk. The ability to assess volatility helps shape investment strategies, aligning them with individual risk profiles and financial goals. Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is a critical skill for any investor. Knowing how to evaluate volatility allows for a more informed approach to portfolio construction and risk management.
Volatility is a critical factor in evaluating investment opportunities. High volatility can lead to significant losses, but it also presents opportunities for substantial gains. Conversely, low volatility often signifies lower risk, but also potentially lower returns. How do you calculate volatility of a stock? A common method, discussed later, involves using standard deviation, which quantifies the dispersion of a stock’s returns around its average. Investors use this information to assess the risk associated with a particular stock or portfolio. Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is essential for making well-informed investment choices. The answer involves analyzing historical price data and applying statistical methods. By accurately answering how do you calculate volatility of a stock, investors gain valuable insights into potential risks and rewards.
Successfully navigating the stock market requires a nuanced understanding of volatility. It’s not simply about avoiding volatility; it’s about incorporating volatility into your investment strategy. How do you calculate volatility of a stock efficiently and effectively? This knowledge is instrumental in diversifying your portfolio, mitigating risks, and potentially capitalizing on market opportunities. Investors should consider their risk tolerance and investment goals when making decisions. The question of how do you calculate volatility of a stock provides a quantifiable measure to guide those decisions. A comprehensive understanding of volatility, and how do you calculate volatility of a stock, enables investors to make more strategic and informed choices in their pursuit of financial objectives. Using this information allows investors to make educated decisions in line with their overall financial plan.
How to Calculate Stock Volatility Using Standard Deviation
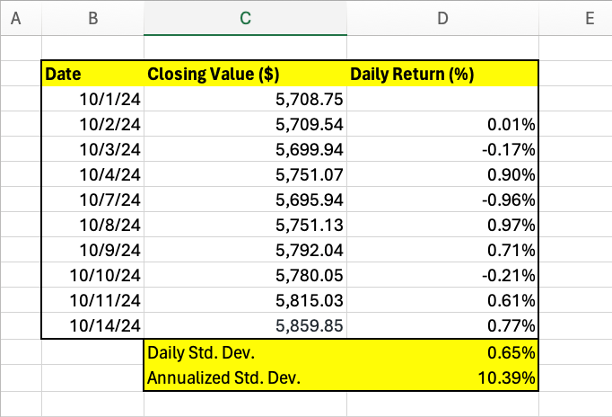
Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is crucial for informed investment decisions. Volatility, a measure of price fluctuation, is commonly calculated using standard deviation. This statistical method quantifies the dispersion of a stock’s price around its average. To calculate a stock’s volatility using standard deviation, one first needs historical stock price data. The more data points used, the more accurate the result will generally be. A common period is 252 trading days, representing one year. This allows for a comprehensive view of the stock’s price movements throughout the year.
The process begins by calculating the average (mean) of the stock’s closing prices over the chosen period. Next, for each price, subtract the mean to find the deviation from the average. Square each of these deviations. This removes negative values, ensuring that large positive or negative deviations have an equal effect on the volatility calculation. Then, sum all the squared deviations. Finally, divide this sum by (n-1), where n is the number of data points (days). This provides the variance. How do you calculate volatility of a stock after this step? The square root of the variance gives the standard deviation, which represents the stock’s volatility. A higher standard deviation indicates greater volatility, implying higher risk and potentially higher returns.
Let’s illustrate with a simplified example. Imagine a stock with five closing prices: $10, $12, $11, $13, $14. The average price is $12. The deviations are -2, 0, -1, 1, and 2. Squaring these yields 4, 0, 1, 1, and 4. Summing these gives 10. Dividing by 4 (n-1 = 5-1 = 4) gives a variance of 2.5. The square root of 2.5 is approximately 1.58. Therefore, the standard deviation, representing the stock’s volatility, is approximately $1.58. Remember, how do you calculate volatility of a stock accurately? The accuracy of this calculation directly depends on the quality and length of the historical data used. Using a longer time frame, such as several years, often produces a more reliable measure of volatility.
Interpreting Your Volatility Calculations: What the Numbers Mean
The standard deviation, calculated as shown in the previous section on how do you calculate volatility of a stock, represents the average amount a stock’s price deviates from its average price over a specific period. A higher standard deviation indicates greater price fluctuations and therefore higher volatility. Conversely, a lower standard deviation suggests less price movement and lower volatility. Understanding this is crucial for assessing risk. Investors should consider their own risk tolerance when interpreting these numbers. A high-volatility stock might offer higher potential returns but also carries a significantly higher risk of substantial losses. Conversely, a low-volatility stock may offer more stability but with potentially lower returns. How do you calculate volatility of a stock accurately? By carefully selecting your historical data and time period.
For example, a stock with a standard deviation of 10% over a year suggests its price typically fluctuates by about 10% from its average price annually. This means the stock’s price could reasonably range from 10% below to 10% above its average. A stock with a standard deviation of only 2% shows much less price fluctuation and considerably lower volatility. Remember, this is just one measure; other factors influence investment decisions. The use of historical data is fundamental to understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock but this data only reflects past performance; it doesn’t guarantee future outcomes. How do you calculate volatility of a stock considering future uncertainties? You can’t, with complete accuracy. Future performance is inherently unpredictable, influenced by countless factors. Understanding this limitation is paramount.
It’s vital to remember the relationship between risk and return when interpreting volatility calculations. Higher volatility often correlates with the potential for higher returns but also carries greater risk. Lower volatility typically equates to lower potential returns but also reduced risk. The ideal balance between risk and return is highly subjective and depends heavily on an investor’s individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. How do you calculate volatility of a stock in relation to your risk profile? You must first understand your own tolerance for potential losses before making any investment decisions. This crucial step guides your selection of assets. Remember to consider your personal investment timeframe and financial objectives when deciding which volatility levels suit your strategy. How do you calculate volatility of a stock’s alignment with your long-term goals? By thoroughly analyzing the stock’s historical volatility and comparing it to your risk tolerance.
Beyond Standard Deviation: Alternative Volatility Metrics
While standard deviation provides a fundamental understanding of how do you calculate volatility of a stock’s price fluctuations, other methods offer a more nuanced perspective. Beta, for instance, measures a stock’s volatility relative to the overall market. A beta of 1 indicates that the stock moves in line with the market. A beta greater than 1 suggests higher volatility than the market, while a beta less than 1 implies lower volatility. How do you calculate volatility of a stock using beta? It involves regressing the stock’s returns against the market’s returns. This calculation helps investors understand the stock’s systematic risk, or the risk inherent in the overall market.
Implied volatility, derived from options prices, reflects market participants’ expectations of future price fluctuations. Unlike standard deviation, which uses historical data, implied volatility looks forward. It’s a valuable tool for option pricing and trading, providing insights into how do you calculate volatility of a stock based on market sentiment. Options traders frequently utilize implied volatility to assess potential profit and loss scenarios and price their options strategies accordingly. Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock through implied volatility requires a grasp of option pricing models, such as the Black-Scholes model.
Finally, the choice of time period significantly influences volatility calculations. Using shorter timeframes, like daily data, will often show higher volatility than longer periods, such as monthly or yearly data. Investors should consider their investment horizon when selecting the appropriate time frame. A short-term investor might focus on daily or weekly data, while a long-term investor might use monthly or annual data. The selection of time period significantly influences the results and the interpretation of how do you calculate volatility of a stock. Different timeframes offer different insights into the risk profile of a stock, highlighting the importance of choosing the time horizon most relevant to one’s investment strategy.
Using Volatility in Your Investment Strategy: Practical Applications
Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is crucial for effective investment strategies. Investors can use volatility information to make informed decisions about asset allocation. A diversified portfolio, incorporating both high and low-volatility stocks, can help mitigate overall risk. High-volatility stocks, while riskier, offer the potential for higher returns. Low-volatility stocks provide stability and reduce portfolio fluctuations. The appropriate balance depends on individual risk tolerance and investment goals. How do you calculate volatility of a stock? By understanding its fluctuations, one can optimize their portfolio.
Volatility plays a significant role in risk management. Investors can use volatility measures to set stop-loss orders, limiting potential losses on individual stocks or the entire portfolio. Sophisticated investors also utilize options trading strategies to hedge against volatility. Options contracts, which derive their value from underlying assets, can be used to profit from or protect against price swings. Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is key to deploying such strategies effectively. The calculation of volatility helps in choosing the appropriate options strategies for managing risk.
Incorporating volatility data into investment decisions requires careful consideration. It’s essential to remember that past volatility doesn’t guarantee future performance. While understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock provides valuable insights, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. Fundamental analysis, examining a company’s financial health and prospects, and macroeconomic factors also significantly influence investment outcomes. Therefore, a comprehensive approach, combining quantitative measures like volatility with qualitative factors, produces well-rounded and robust investment strategies.
Factors Influencing Stock Volatility: Macro and Micro Factors
Numerous factors influence a stock’s volatility. Understanding these influences is crucial for investors seeking to manage risk and optimize returns. Macroeconomic factors, affecting the overall economy, significantly impact market sentiment and individual stock prices. Interest rate changes, for instance, directly influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, affecting investment and spending patterns. Economic growth or recession significantly affects corporate profitability, impacting stock valuations. Inflation, impacting purchasing power and production costs, also contributes to market uncertainty and volatility. How do you calculate volatility of a stock accurately considering these macroeconomic shifts? A thorough understanding of these broader economic trends is necessary for a comprehensive volatility assessment.
Beyond macroeconomic factors, company-specific microeconomic elements play a crucial role. Unexpected earnings announcements, exceeding or falling short of expectations, frequently trigger significant price swings. Industry trends, such as technological disruptions or regulatory changes, can reshape market competition and a company’s outlook. Significant management changes, such as the appointment of a new CEO or a shift in strategic direction, introduce uncertainty and influence investor confidence. Analyzing a company’s financial health, competitive position, and operational efficiency helps in anticipating potential volatility. Therefore, understanding how these microeconomic factors affect individual firms is essential for predicting and managing volatility. How do you calculate volatility of a stock when considering both macro and micro influences? This requires a multi-faceted approach combining quantitative analysis with qualitative assessments.
Successfully navigating market fluctuations requires considering both macro and micro influences on stock volatility. Macroeconomic factors paint a broad picture of the economic environment, while microeconomic factors offer insights into specific company dynamics. By carefully analyzing both, investors gain a more comprehensive understanding of the forces shaping stock prices and volatility. How do you calculate volatility of a stock effectively by integrating these diverse factors? The answer lies in a balanced approach, combining quantitative methods with insightful qualitative assessment to create a robust and informed investment strategy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating and Interpreting Volatility
One common pitfall is over-reliance on standard deviation alone when answering the question, “how do you calculate volatility of a stock?”. While standard deviation provides a valuable measure of price fluctuation, it shouldn’t be the sole factor in investment decisions. Investors should consider other metrics and contextual factors, such as trading volume and market conditions. A stock might show low volatility based on standard deviation, but high volume could indicate underlying instability. Ignoring such nuances leads to flawed assessments of risk. Remember that past volatility does not guarantee future performance; market dynamics shift constantly.
Another mistake is misinterpreting the implications of volatility for investment strategies. High volatility doesn’t automatically equate to poor investment. High-volatility stocks can offer substantial returns if appropriately managed within a diversified portfolio. Conversely, low volatility doesn’t guarantee safety. A seemingly stable stock might suddenly experience significant drops due to unforeseen circumstances. Understanding the context of volatility – its causes and potential consequences – is crucial. Investors should avoid making quick judgments based solely on a single volatility number. Thorough research and analysis are key to making informed decisions, understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is only the first step.
Finally, investors often overlook the importance of the time period used in volatility calculations. A shorter time frame, like a few months, may show significantly different volatility than a longer time frame, such as five years. The chosen period substantially influences the results, and the appropriate timeframe depends on the investor’s investment horizon and risk tolerance. Using an inappropriate time frame can provide a misleading representation of a stock’s actual volatility and impact investment strategies. Investors should consider how the calculation timeframe aligns with their investment objectives before making any conclusions about how do you calculate volatility of a stock and using that information.
Staying Informed: Resources and Further Learning
Mastering the intricacies of stock market volatility is an ongoing process. Understanding how do you calculate volatility of a stock is a crucial first step, but continuous learning is key to effective investment management. Investors should regularly update their knowledge of market trends and analytical techniques. This includes exploring more advanced statistical methods for evaluating risk and return. Expanding knowledge into different asset classes, such as bonds or real estate, provides a more holistic understanding of portfolio diversification. Further studies in portfolio optimization strategies and risk management techniques can significantly enhance investment performance. Exploring alternative investment vehicles or delving deeper into derivatives can provide new perspectives on managing volatility. How do you calculate volatility of a stock effectively is only one piece of the puzzle. A commitment to continuous professional development ensures informed and strategic decision-making in the dynamic world of finance. Consider studying behavioral finance to understand the psychological factors influencing investment decisions. This knowledge can improve your ability to manage your own emotional responses to market fluctuations. Understanding the influence of macroeconomic factors, like interest rate changes or inflation, on asset prices helps you anticipate market movements. This includes monitoring and analyzing global events, economic indicators, and industry-specific trends to refine your risk assessments. How do you calculate volatility of a stock efficiently supports your overall investment strategy, but shouldn’t be the only tool you use. The effective investor continuously seeks out new information and analysis techniques.
Successfully navigating the complexities of the stock market requires a multifaceted approach. While knowing how do you calculate volatility of a stock is important, it’s only a single element in a larger picture. Proactive learning should incorporate diverse areas of finance, such as understanding the intricacies of derivative instruments or sophisticated trading strategies. Investors benefit from enhancing their knowledge of quantitative analysis methods, exploring advanced statistical models to refine their risk assessments. A broader understanding of different asset classes, including commodities, alternative investments, or fixed-income securities, enables more informed diversification strategies. The pursuit of continuous learning isn’t just about enhancing investment outcomes; it’s about developing a deeper understanding of financial markets and building resilience to market volatility. Regularly reviewing your investment strategy and adjusting it to reflect changes in your risk tolerance or market conditions is crucial. This holistic approach, combined with a detailed knowledge of how do you calculate volatility of a stock, strengthens the foundation for informed and successful investment practices.
The ever-evolving nature of financial markets necessitates a continuous learning approach. Expanding your knowledge base beyond the mechanics of how do you calculate volatility of a stock will enhance your investment acumen. For example, consider delving into the nuances of technical analysis, which focuses on using charts and price patterns to predict market trends. A strong understanding of fundamental analysis is equally important, focusing on evaluating a company’s financial health and growth prospects. Staying abreast of geopolitical events and regulatory changes impacting financial markets allows for more informed decision-making. Enhancing your understanding of different trading strategies, including active and passive investment approaches, is another area to focus on. How do you calculate volatility of a stock accurately contributes to a robust investment strategy, but this knowledge must be complemented by a deep understanding of macro-economic trends and their potential impact on different asset classes. The ability to effectively analyze and interpret financial data, along with a thoughtful approach to risk management, are paramount in navigating the complexities of stock market volatility. This well-rounded skill set, along with regularly applying techniques such as how do you calculate volatility of a stock, equips investors with the confidence to make sound investment decisions.