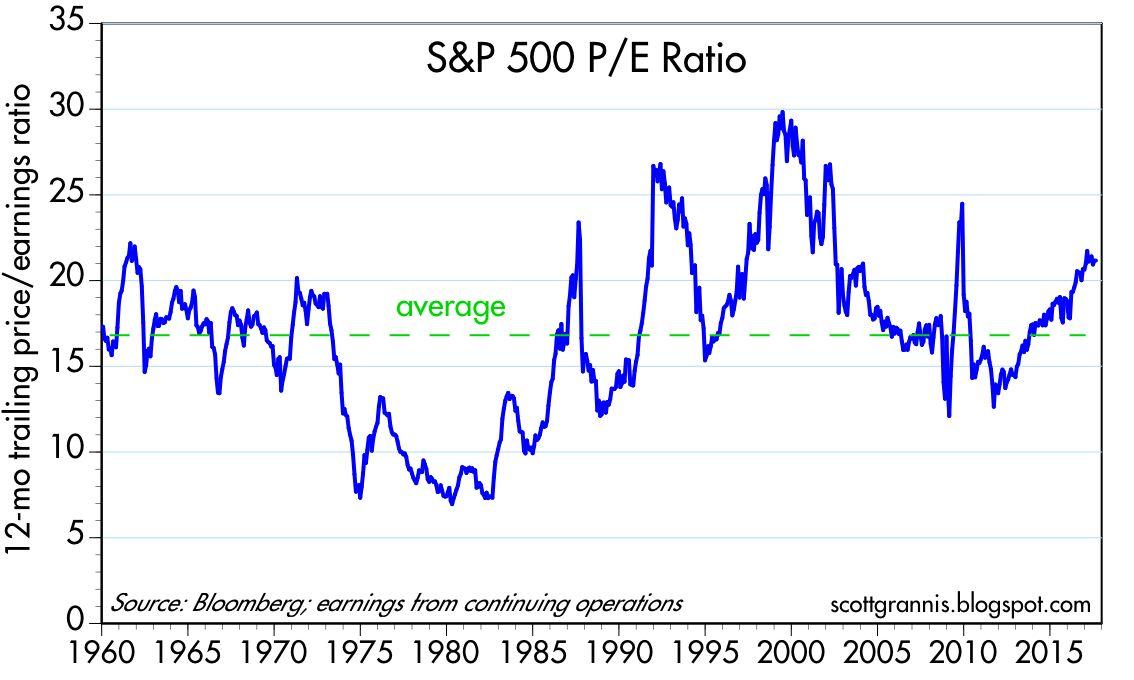
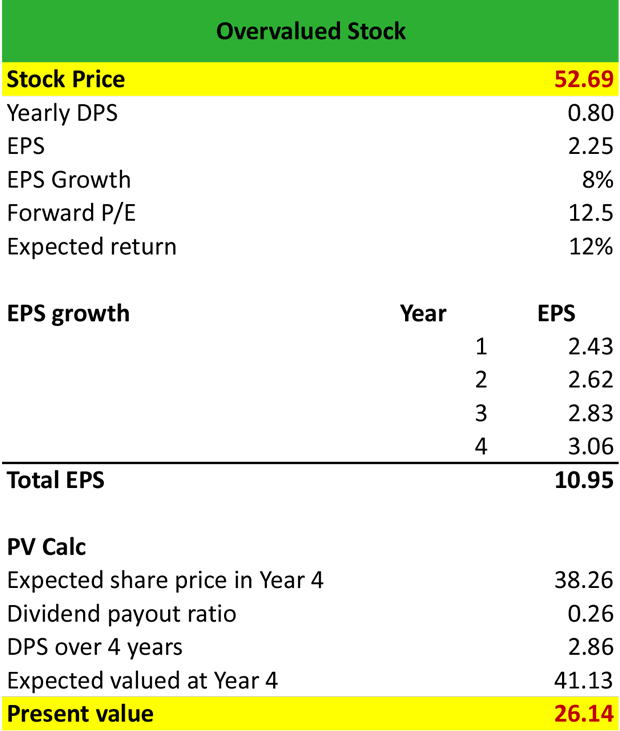
Why Historical PE Ratios Matter in Stock Analysis
Historical PE ratios by stock are a crucial component of stock analysis, providing valuable insights into a company’s valuation and performance over time. By examining historical PE ratios, investors can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s earnings growth, profitability, and market sentiment. This information can be used to identify trends, patterns, and anomalies that can inform investment decisions. For instance, a company with a consistently high historical PE ratio may indicate that the market has high expectations for its future performance, while a company with a low historical PE ratio may suggest that it is undervalued. Furthermore, historical PE ratios can be used to compare companies within the same industry, providing a benchmark for evaluating their relative performance. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their analysis, investors can make more informed decisions about which stocks to buy, sell, or hold, ultimately leading to more effective investment strategies.
How to Analyze Historical PE Ratios for Informed Investing
To effectively analyze historical PE ratios, investors should follow a step-by-step approach that includes calculating the ratio, identifying trends, and comparing companies within the same industry. The first step is to calculate the historical PE ratio by dividing the stock’s price by its earnings per share. This can be done using historical stock prices and earnings data, which can be obtained from financial databases or websites. Next, investors should identify trends in the historical PE ratio, such as whether it has been increasing or decreasing over time. This can provide insights into how the market has valued the company’s earnings in the past and whether it is likely to continue to do so in the future. Additionally, investors can use historical PE ratios to compare companies within the same industry, providing a benchmark for evaluating their relative performance. For example, an investor can compare the historical PE ratio of a company like Apple to that of its peers in the technology industry, such as Microsoft or Alphabet. By following this approach, investors can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s valuation and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, historical PE ratios by stock can be used to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate opportunities for investment. For instance, a company with a historically low PE ratio may be undervalued, while a company with a historically high PE ratio may be overvalued. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their analysis, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.
Uncovering Hidden Gems: Historical PE Ratios of Top Performing Stocks
Analyzing the historical PE ratios of top-performing stocks can provide valuable insights into the characteristics of successful companies and inform investment decisions. For instance, a review of the historical PE ratios of top-performing stocks in the technology industry, such as Amazon and Microsoft, reveals a pattern of consistently high ratios, indicating that the market has high expectations for their future performance. Similarly, an analysis of the historical PE ratios of top-performing stocks in the healthcare industry, such as Johnson & Johnson and Pfizer, shows a trend of relatively low ratios, suggesting that the market values their earnings at a lower multiple. By examining the historical PE ratios of top-performing stocks, investors can identify trends and patterns that can inform their investment decisions. For example, an investor may identify a company with a historical PE ratio that is lower than its peers, indicating that it may be undervalued. Conversely, an investor may identify a company with a historical PE ratio that is higher than its peers, suggesting that it may be overvalued. By incorporating historical PE ratios by stock into their analysis, investors can uncover hidden gems and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, analyzing the historical PE ratios of top-performing stocks can provide insights into the market’s expectations for a company’s future performance and help investors identify potential opportunities for investment. By examining the historical PE ratios of companies across various industries, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.
The Impact of Economic Cycles on Historical PE Ratios
Economic cycles, such as recessions and booms, have a significant impact on historical PE ratios. During recessions, historical PE ratios tend to be lower due to decreased earnings and investor risk aversion. Conversely, during booms, historical PE ratios tend to be higher due to increased earnings and investor optimism. Understanding how economic cycles affect historical PE ratios is crucial for investors, as it can inform their investment strategies and help them make more informed decisions. For example, during a recession, investors may identify undervalued stocks with low historical PE ratios, which could potentially increase in value as the economy recovers. On the other hand, during a boom, investors may identify overvalued stocks with high historical PE ratios, which could potentially decrease in value as the economy slows down. By analyzing historical PE ratios in the context of economic cycles, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions. Furthermore, historical PE ratios by stock can be used to identify patterns and trends that are specific to certain economic cycles, providing valuable insights for investors. For instance, an analysis of historical PE ratios during the 2008 financial crisis reveals a pattern of decreasing ratios, indicating a decrease in investor confidence. Conversely, an analysis of historical PE ratios during the subsequent recovery period reveals a pattern of increasing ratios, indicating an increase in investor confidence. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their analysis, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the stock market and make more informed investment decisions.
Comparing Historical PE Ratios Across Industries
Comparing historical PE ratios across industries can provide valuable insights into the unique characteristics and trends of each industry. By analyzing historical PE ratios of companies within different industries, investors can identify patterns and trends that can inform their investment decisions. For instance, an analysis of historical PE ratios in the technology industry reveals a pattern of high ratios, indicating that investors are willing to pay a premium for companies with high growth potential. In contrast, an analysis of historical PE ratios in the energy industry reveals a pattern of lower ratios, indicating that investors are more cautious in their valuations. By comparing historical PE ratios across industries, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the market’s expectations for each industry and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, historical PE ratios by stock can be used to identify industry-specific trends and patterns, providing valuable insights for investors. For example, an analysis of historical PE ratios of companies within the healthcare industry reveals a trend of increasing ratios, indicating that investors are becoming more optimistic about the industry’s growth prospects. Conversely, an analysis of historical PE ratios of companies within the retail industry reveals a trend of decreasing ratios, indicating that investors are becoming more cautious about the industry’s growth prospects. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their analysis, investors can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.
Using Historical PE Ratios to Identify Overvalued and Undervalued Stocks
Historical PE ratios can be a powerful tool for identifying overvalued and undervalued stocks. By analyzing historical PE ratios by stock, investors can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s valuation and make more informed investment decisions. Overvalued stocks typically have high historical PE ratios, indicating that investors are willing to pay a premium for the company’s shares. Conversely, undervalued stocks typically have low historical PE ratios, indicating that investors are undervaluing the company’s shares. For example, a company with a historical PE ratio of 30 may be considered overvalued if its industry average is 20, while a company with a historical PE ratio of 10 may be considered undervalued if its industry average is 15. By identifying these discrepancies, investors can make more informed investment decisions and potentially capitalize on mispricings in the market. Furthermore, historical PE ratios can be used in conjunction with other metrics, such as earnings growth and dividend yield, to create a more comprehensive picture of a company’s valuation. For instance, a company with a high historical PE ratio but strong earnings growth may be considered a good investment opportunity, while a company with a low historical PE ratio but weak earnings growth may be considered a poor investment opportunity. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their analysis, investors can develop a more nuanced understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.
Limitations and Potential Biases of Historical PE Ratios
While historical PE ratios can be a valuable tool for investors, they are not without limitations and potential biases. One of the primary limitations of historical PE ratios is that they are based on past data, which may not accurately reflect a company’s current or future performance. Additionally, historical PE ratios can be influenced by factors such as accounting practices, industry trends, and economic cycles, which can impact their accuracy and reliability. For example, a company that has undergone significant changes in its business model or accounting practices may have historical PE ratios that are not representative of its current valuation. Furthermore, historical PE ratios can be biased towards companies with high growth rates or those that are in industries with high valuations, which can lead to inaccurate comparisons and investment decisions. Another limitation of historical PE ratios is that they do not take into account other important factors such as dividend yield, earnings growth, and debt-to-equity ratio, which can provide a more comprehensive picture of a company’s valuation. To mitigate these limitations and biases, investors should use historical PE ratios in conjunction with other metrics and analysis tools, such as fundamental analysis and technical analysis, to gain a more complete understanding of a company’s valuation and potential for growth. By understanding the limitations and potential biases of historical PE ratios, investors can use them more effectively to inform their investment decisions and avoid potential pitfalls. For instance, historical PE ratios by stock can be used to identify trends and patterns in a company’s valuation over time, but they should be used in conjunction with other metrics to get a more complete picture of the company’s valuation. By combining historical PE ratios with other analysis tools, investors can develop a more nuanced understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.
Integrating Historical PE Ratios into Your Investment Strategy
To maximize the benefits of historical PE ratios, it’s essential to incorporate them into a comprehensive investment strategy. This involves combining historical PE ratios with other metrics and analysis tools to gain a more complete understanding of a company’s valuation and potential for growth. One approach is to use historical PE ratios as a screening tool to identify potential investment opportunities. For example, investors can use historical PE ratios to identify companies with low valuations relative to their industry or sector, and then conduct further analysis to determine if these companies are undervalued or overvalued. Historical PE ratios can also be used in conjunction with other metrics, such as dividend yield and earnings growth, to create a more comprehensive picture of a company’s valuation. Additionally, investors can use historical PE ratios to monitor trends and patterns in a company’s valuation over time, and adjust their investment strategy accordingly. For instance, if a company’s historical PE ratio is trending upwards, it may indicate that the company is becoming overvalued, and investors may want to consider selling or reducing their position. On the other hand, if a company’s historical PE ratio is trending downwards, it may indicate that the company is becoming undervalued, and investors may want to consider buying or increasing their position. By incorporating historical PE ratios into their investment strategy, investors can make more informed investment decisions and potentially achieve better returns. Furthermore, historical PE ratios by stock can be used to compare the valuation of different companies within the same industry, and identify potential investment opportunities. By combining historical PE ratios with other analysis tools, investors can develop a more nuanced understanding of the stock market and make more effective investment decisions.