What is a Forward Rate and Why is it Important?
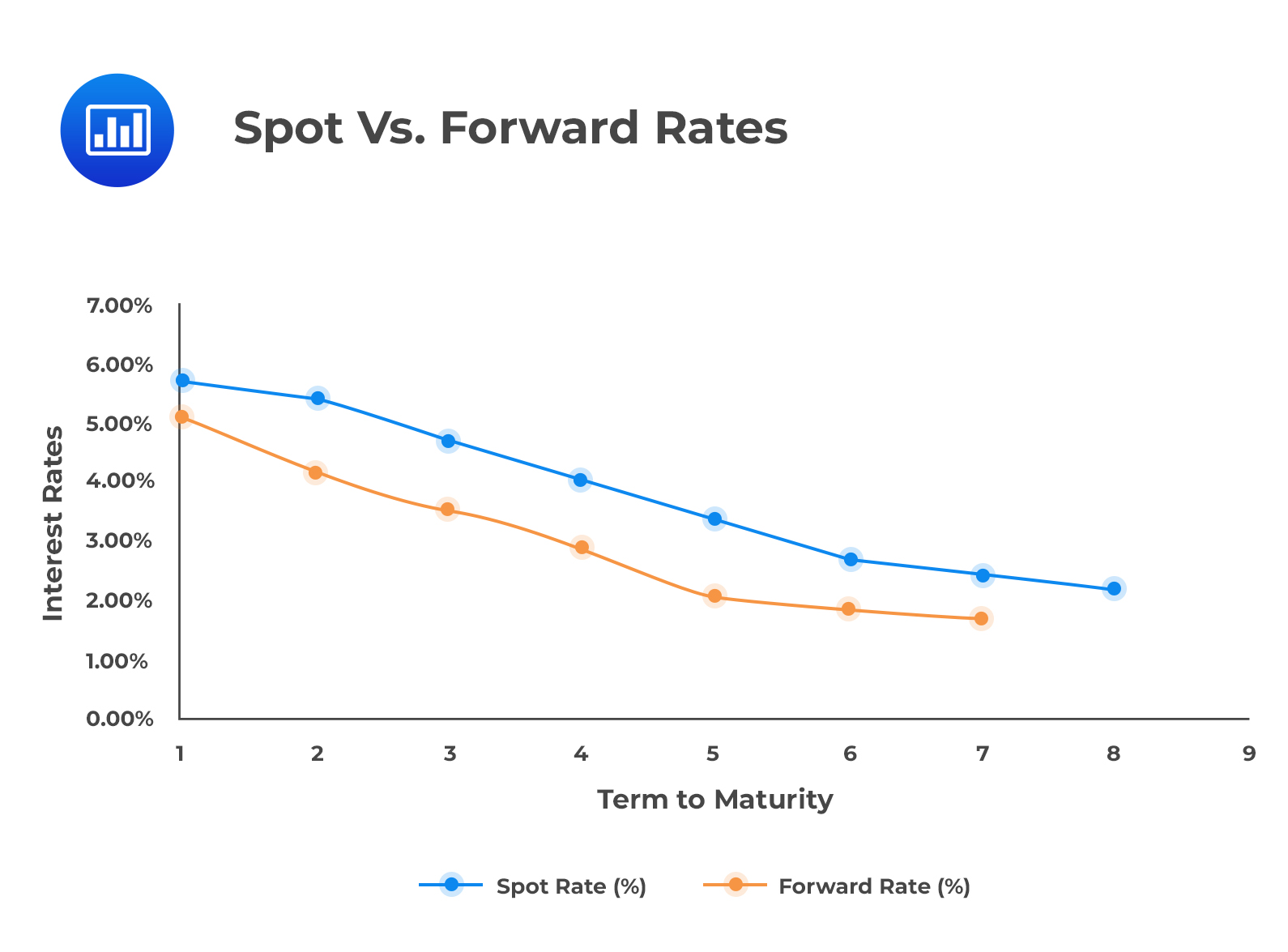
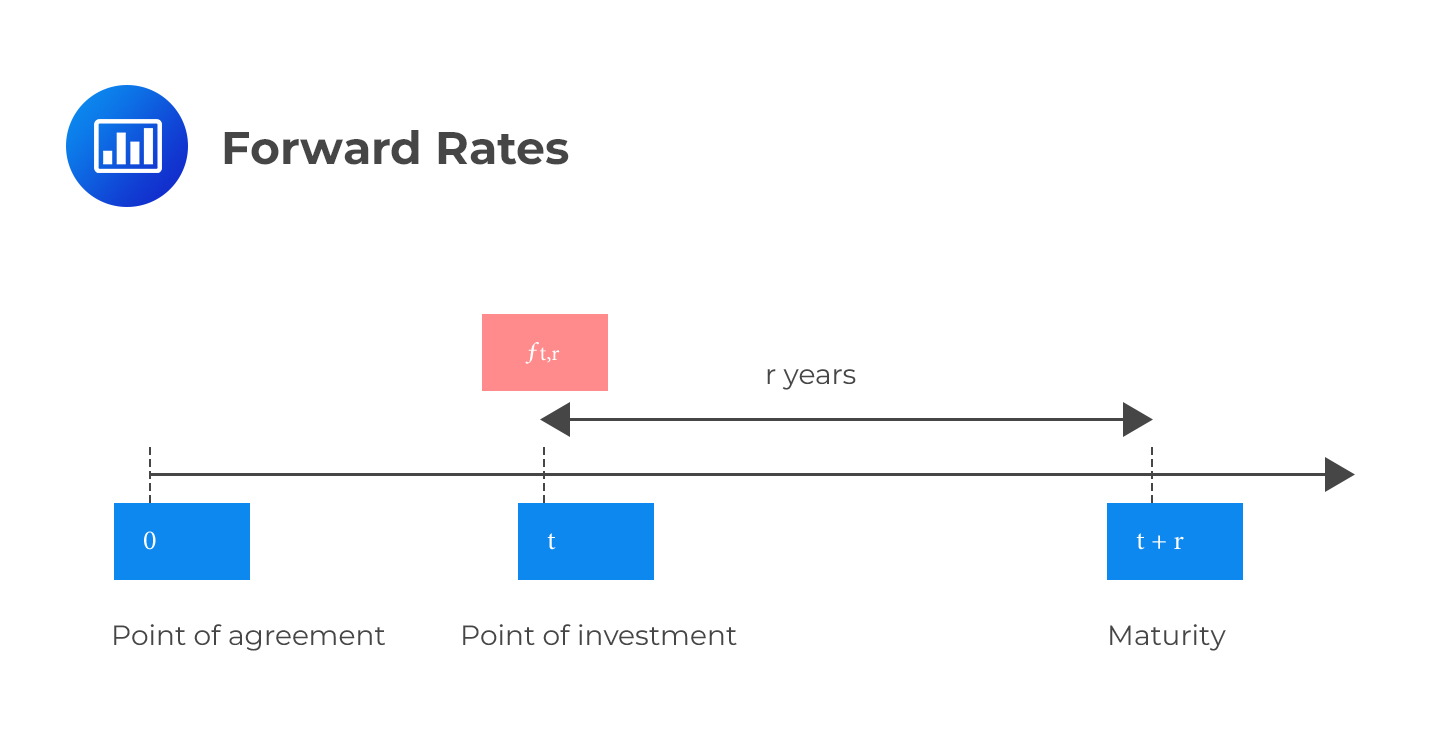
In the foreign exchange market, forward rates play a crucial role in facilitating international trade and investment. A forward rate is an exchange rate agreed upon today for an exchange that will take place at a future date, differing from the spot rate, which is the current exchange rate. This distinction is vital, as forward rates provide a forecast of future spot rates, enabling market participants to plan and strategize their investments accordingly.
The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, as it helps businesses and investors manage their foreign exchange exposure. By understanding forward rates, market participants can better navigate the complexities of exchange rate fluctuations, reducing the risk of losses due to adverse exchange rate movements. In fact, forward rates are essential in international trade, as importers and exporters need to hedge against exchange rate fluctuations to ensure profitability.
Forward rates are also significant in investment decisions, as they provide a valuable tool for managing exchange rate risks and optimizing investment strategies. Investors can use forward rates to inform their investment decisions, taking into account the potential impact of exchange rate changes on their returns. As a result, understanding forward rates is crucial for businesses and investors operating in the global market, as it enables them to make informed decisions and maximize their returns.
The forward rate from spot rate is a powerful tool for managing exchange rate risks and optimizing investment strategies. By grasping the concept of forward rates, market participants can better navigate the complexities of exchange rate fluctuations, reducing the risk of losses due to adverse exchange rate movements. As the global market continues to evolve, the importance of forward rates will only continue to grow, making it essential for businesses and investors to understand this critical concept.
Calculating Forward Rates from Spot Rates: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating forward rates from spot rates is a crucial step in understanding the dynamics of foreign exchange markets. The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and mastering this calculation is essential for businesses and investors operating in the global market.
The formula to calculate the forward rate from the spot rate is as follows:
F = S x (1 + r_d / (1 + r_f))^(t)
Where:
F = Forward rate
S = Spot rate
r_d = Domestic interest rate
r_f = Foreign interest rate
t = Time to maturity
This formula takes into account the interest rates of both the domestic and foreign currencies, as well as the time to maturity of the forward contract. By plugging in the relevant values, market participants can calculate the forward rate and make informed investment decisions.
For example, let’s say the spot rate for EUR/USD is 1.1000, the domestic interest rate is 2%, and the foreign interest rate is 1%. If we want to calculate the 1-year forward rate, we would plug in the values as follows:
F = 1.1000 x (1 + 0.02 / (1 + 0.01))^1
F = 1.1212
This means that the 1-year forward rate for EUR/USD is 1.1212, indicating that the euro is expected to appreciate against the US dollar over the next year.
By understanding how to calculate forward rates from spot rates, market participants can better navigate the complexities of foreign exchange markets and make informed investment decisions. The forward rate from spot rate is a powerful tool for managing exchange rate risks and optimizing investment strategies, and mastering this calculation is essential for success in international finance.
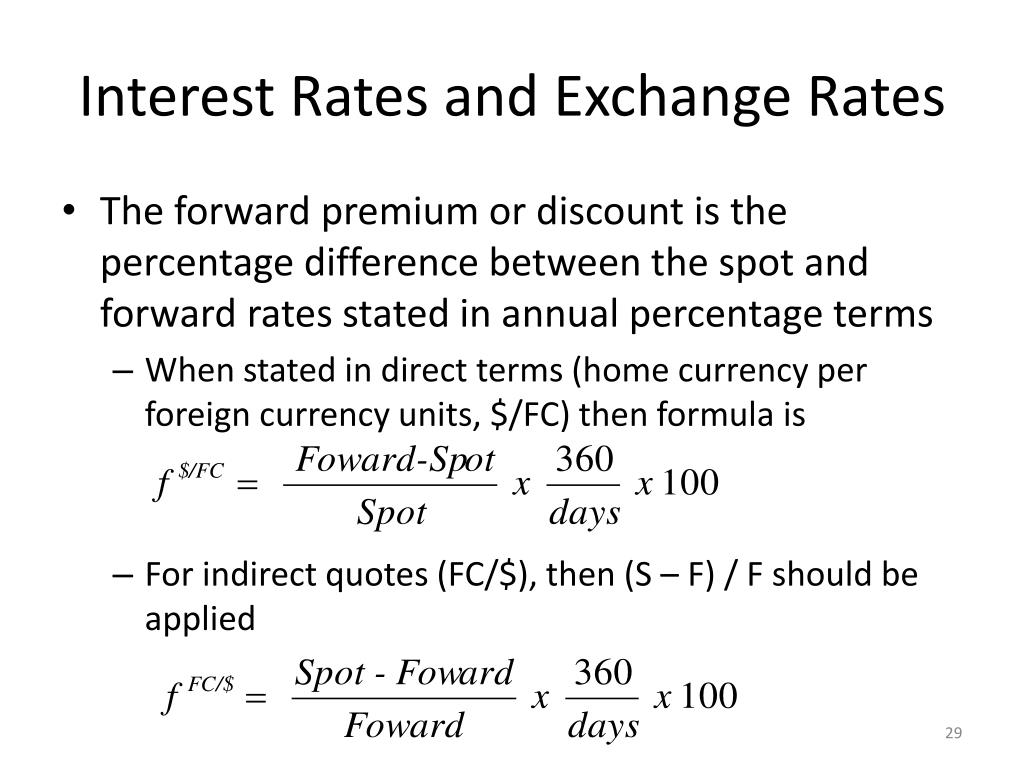
How to Determine the Forward Premium or Discount
In the context of forward exchange rates, a forward premium or discount refers to the difference between the forward rate and the spot rate. This concept is crucial in international finance, as it helps investors and businesses understand the expected changes in exchange rates and make informed investment decisions.
The forward premium or discount can be calculated using the following formula:
Premium/Discount = (Forward Rate – Spot Rate) / Spot Rate
Where:
Premium/Discount = Forward premium or discount
Forward Rate = Forward exchange rate
Spot Rate = Spot exchange rate
For example, let’s say the spot rate for EUR/USD is 1.1000, and the 1-year forward rate is 1.1212. To calculate the forward premium, we would plug in the values as follows:
Premium = (1.1212 – 1.1000) / 1.1000
Premium = 0.0192 or 1.92%
This means that the euro is expected to appreciate against the US dollar by 1.92% over the next year, resulting in a forward premium.
The implications of a forward premium or discount on investment decisions are significant. A forward premium indicates that the currency is expected to appreciate, making it a more attractive investment opportunity. On the other hand, a forward discount indicates that the currency is expected to depreciate, making it a less attractive investment opportunity.
By understanding how to determine the forward premium or discount, investors and businesses can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their returns. The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and mastering this calculation is essential for success in the global market.
The Role of Interest Rates in Forward Exchange Rates
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining forward exchange rates. The relationship between interest rates and forward exchange rates is complex, and understanding this relationship is essential for investors and businesses operating in international markets.
In general, when interest rates in a country increase, the value of its currency appreciates, and when interest rates decrease, the value of its currency depreciates. This is because higher interest rates attract foreign investors, causing an increase in demand for the currency and, subsequently, an appreciation in its value.
The impact of interest rates on forward exchange rates can be seen in the following ways:
When interest rates in the domestic country are higher than in the foreign country, the forward rate will be higher than the spot rate, resulting in a forward premium. This is because investors are willing to pay a premium to invest in the domestic country with higher interest rates.
On the other hand, when interest rates in the domestic country are lower than in the foreign country, the forward rate will be lower than the spot rate, resulting in a forward discount. This is because investors are less willing to invest in the domestic country with lower interest rates.
For example, let’s say the spot rate for EUR/USD is 1.1000, and the 1-year interest rate in the US is 2%, while the 1-year interest rate in the EU is 1%. To calculate the 1-year forward rate, we would use the formula:
F = S x (1 + r_d / (1 + r_f))^(t)
Where:
F = Forward rate
S = Spot rate
r_d = Domestic interest rate
r_f = Foreign interest rate
t = Time to maturity
Plugging in the values, we get:
F = 1.1000 x (1 + 0.02 / (1 + 0.01))^1
F = 1.1212
This means that the 1-year forward rate for EUR/USD is 1.1212, indicating a forward premium due to the higher interest rate in the US.
By understanding the role of interest rates in forward exchange rates, investors and businesses can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their returns. The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and mastering this calculation is essential for success in the global market.
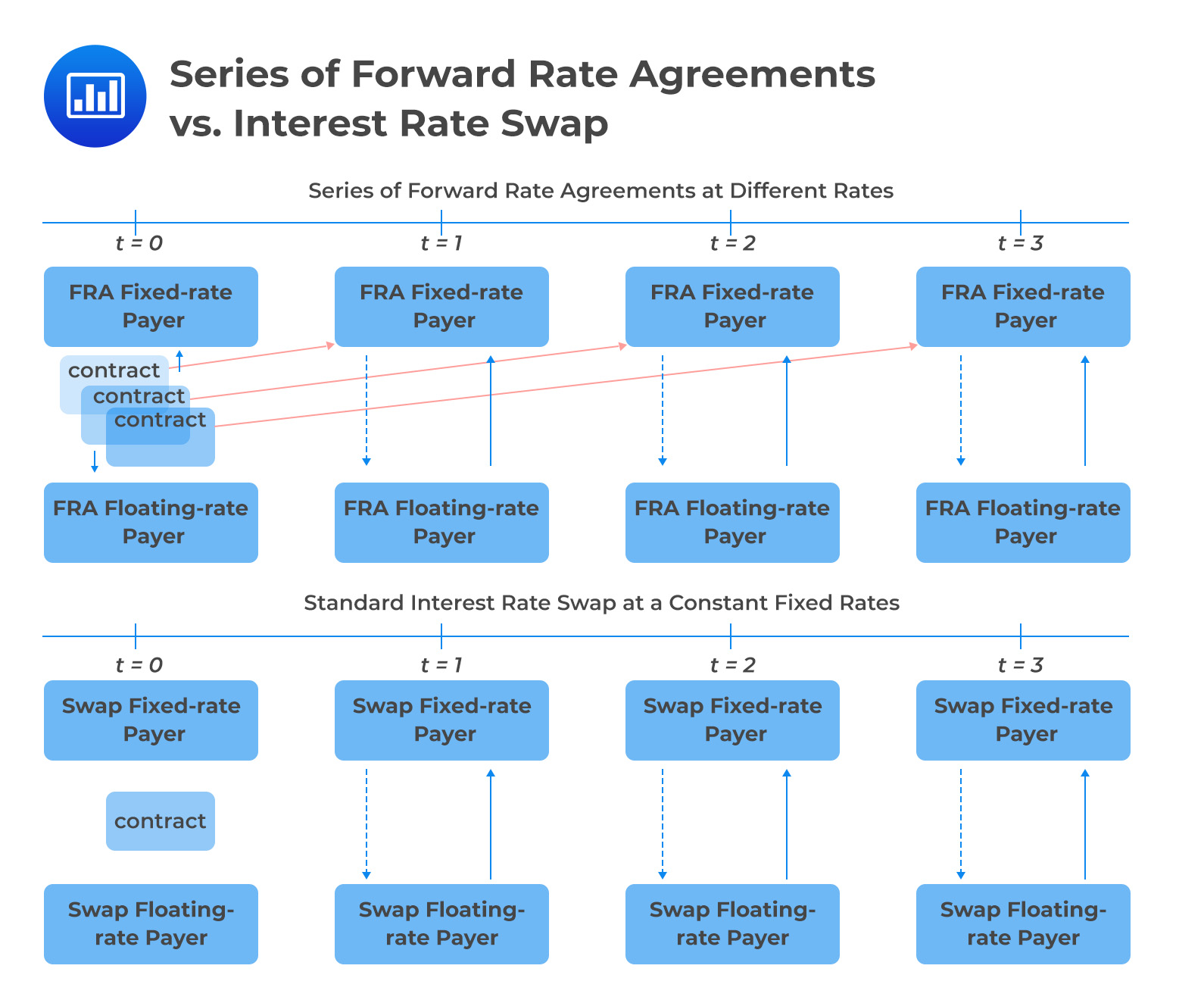
Forward Rate Agreements: A Risk Management Tool
Forward rate agreements (FRAs) are a type of financial derivative that allows businesses and investors to hedge against exchange rate risks. An FRA is a contractual agreement between two parties to exchange a fixed amount of currency at a predetermined forward rate on a specific date in the future.
FRAs are commonly used by companies that engage in international trade or investment, as they provide a way to manage foreign exchange risk. For example, an importer may use an FRA to lock in a fixed exchange rate for a future shipment of goods, ensuring that they know exactly how much they will pay in their local currency.
The benefits of FRAs include:
– Hedging against exchange rate risks: FRAs allow businesses to fix their exchange rates in advance, reducing the uncertainty and volatility associated with currency fluctuations.
– Reducing currency exposure: By locking in a fixed exchange rate, businesses can reduce their exposure to currency risks and avoid potential losses.
– Improving cash flow management: FRAs can help businesses to better manage their cash flow by providing a fixed exchange rate for future transactions.
– Enhancing budgeting and forecasting: By knowing exactly how much they will pay or receive in their local currency, businesses can improve their budgeting and forecasting processes.
In addition to their benefits, FRAs are also flexible and can be tailored to meet the specific needs of businesses. They can be used to hedge against exchange rate risks for a variety of currencies and can be structured to meet specific time horizons and transaction sizes.
By understanding how FRAs work and their benefits, businesses and investors can better manage their exchange rate risks and make more informed investment decisions. The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and mastering this calculation is essential for success in the global market.
Real-World Applications of Forward Rates in Finance
Forward rates play a crucial role in various real-world financial transactions, including import/export businesses, international investments, and currency speculation. Understanding how forward rates are used in these transactions is essential for businesses and investors to make informed decisions.
In import/export businesses, forward rates are used to hedge against exchange rate risks. For example, an importer may use a forward rate to lock in a fixed exchange rate for a future shipment of goods, ensuring that they know exactly how much they will pay in their local currency. This helps to reduce the uncertainty and volatility associated with currency fluctuations.
In international investments, forward rates are used to manage currency risks. For instance, an investor may use a forward rate to convert their investment returns from a foreign currency to their local currency, ensuring that they receive a fixed amount of currency. This helps to reduce the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their investment returns.
In currency speculation, forward rates are used to bet on future exchange rate movements. For example, a speculator may use a forward rate to buy a currency at a fixed rate, expecting that the currency will appreciate in value. If the currency appreciates, the speculator can sell it at the higher rate, earning a profit.
The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and understanding how to calculate it is essential for businesses and investors to make informed decisions. By using forward rates, businesses and investors can manage their exchange rate risks, reduce uncertainty, and increase their returns.
In addition to these applications, forward rates are also used in other financial transactions, such as foreign exchange swaps, options, and futures. They are an essential tool for businesses and investors operating in international markets, and understanding how to use them effectively is crucial for success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with Forward Rates
When working with forward rates, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes or misconceptions that can lead to inaccurate calculations, poor investment decisions, and significant financial losses. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Incorrectly assuming that forward rates are the same as spot rates: Forward rates and spot rates are two different concepts, and confusing them can lead to incorrect calculations and poor investment decisions. It’s essential to understand the difference between the two and how to calculate forward rates from spot rates.
Failing to consider the impact of interest rates on forward rates: Interest rates have a significant impact on forward rates, and failing to consider this impact can lead to inaccurate calculations. It’s essential to understand the relationship between interest rates and forward rates and how changes in interest rates affect the forward rate.
Not accounting for forward premium or discount: Forward premium or discount is a critical concept in forward rates, and failing to account for it can lead to inaccurate calculations. It’s essential to understand how to calculate forward premium or discount and its implications on investment decisions.
Not using forward rate agreements (FRAs) effectively: FRAs are a risk management tool that can help businesses and investors hedge against exchange rate risks. However, not using them effectively can lead to poor investment decisions and significant financial losses. It’s essential to understand how FRAs work and their benefits in hedging against exchange rate risks.
Not considering the forward rate from spot rate in investment decisions: The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and not considering it in investment decisions can lead to poor investment decisions and significant financial losses. It’s essential to understand how to calculate forward rates from spot rates and its implications on investment decisions.
By avoiding these common mistakes, businesses and investors can ensure that they make informed investment decisions and minimize their exposure to exchange rate risks.
Mastering Forward Rates for Informed Investment Decisions
In conclusion, understanding forward rates is crucial for businesses and investors operating in international markets. Forward rates play a vital role in managing exchange rate risks, making informed investment decisions, and maximizing returns. By grasping the concept of forward rates, including how to calculate them from spot rates, determining forward premium or discount, and understanding the role of interest rates, businesses and investors can make informed decisions and minimize their exposure to exchange rate risks.
The forward rate from spot rate is a critical concept in international finance, and mastering it is essential for success in today’s globalized economy. By avoiding common mistakes and misconceptions, businesses and investors can ensure that they make informed investment decisions and achieve their financial goals.
In today’s fast-paced and volatile financial markets, understanding forward rates is no longer a luxury, but a necessity. With the increasing globalization of trade and investment, the importance of forward rates will only continue to grow. By mastering forward rates, businesses and investors can stay ahead of the curve, make informed decisions, and thrive in an increasingly complex and interconnected world.