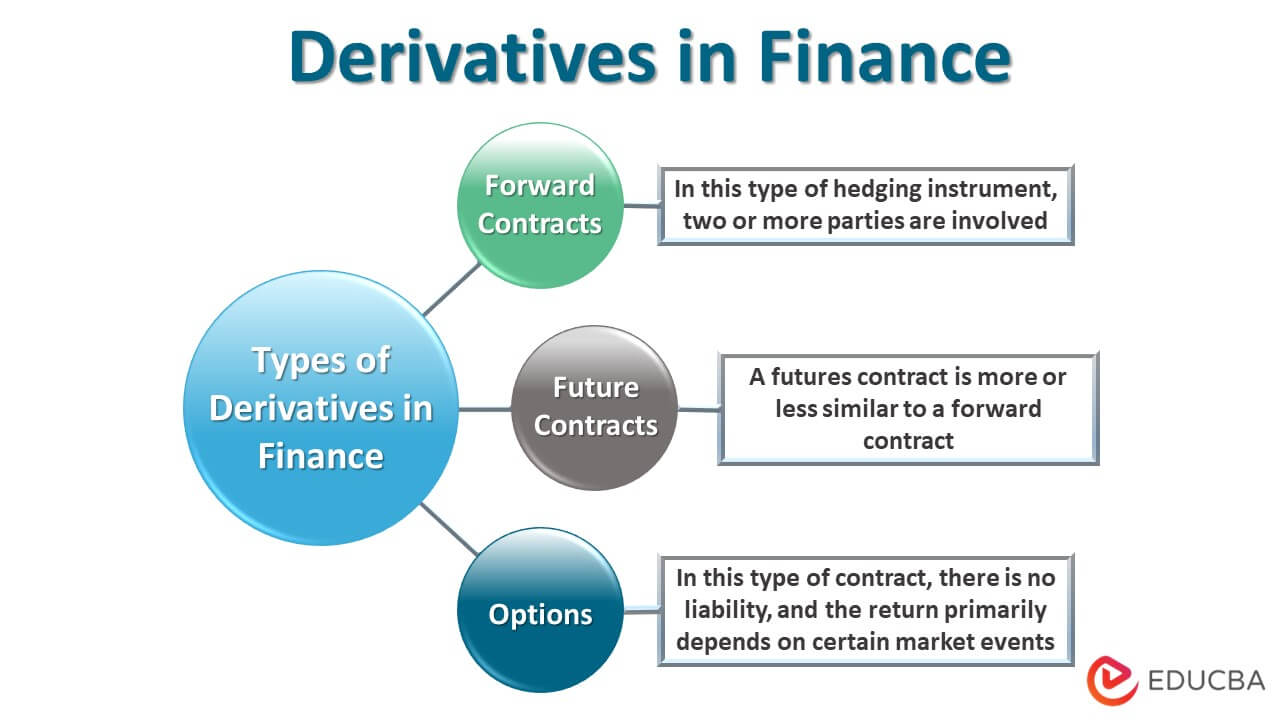
Navigating the Complex World of Derivatives
In modern finance, financial derivatives have become an essential tool for investors and financial institutions alike. A financial derivatives a quantitative finance view is crucial to understanding the intricacies of these complex instruments. Financial derivatives, which include options, futures, forwards, and swaps, are contracts that derive their value from underlying assets, such as stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies. The importance of financial derivatives lies in their ability to facilitate risk management, improve market efficiency, and increase investment opportunities. However, their complexity and nuances require a deep understanding of mathematical and statistical concepts, making a quantitative finance perspective indispensable. By grasping the intricacies of financial derivatives, investors and financial professionals can make informed decisions, optimize portfolio performance, and navigate the intricate world of derivatives with confidence.
How to Master the Art of Derivative Pricing
In the realm of financial derivatives, accurate pricing is crucial for effective risk management and informed investment decisions. A financial derivatives a quantitative finance view emphasizes the importance of understanding the fundamental principles of derivative pricing. The Black-Scholes model, binomial models, and finite difference methods are essential tools in the pricing of derivatives. The Black-Scholes model, for instance, provides a framework for pricing options and other derivatives based on the underlying asset’s price, volatility, and time to expiration. Binomial models, on the other hand, offer a more flexible approach to pricing, allowing for the incorporation of multiple factors and scenarios. Finite difference methods, meanwhile, provide a numerical approach to pricing, enabling the valuation of complex derivatives. By grasping these principles, investors and financial professionals can develop a deeper understanding of derivative pricing, enabling them to make more informed decisions and optimize their investment strategies.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/derivative.finalJPEG-5c8982d646e0fb00010f11c9.jpg)
The Mathematics Behind Derivative Valuation
At the heart of financial derivatives lies a complex web of mathematical concepts that underpin their valuation. A financial derivatives a quantitative finance view recognizes the importance of stochastic calculus, probability theory, and numerical methods in understanding the behavior of derivatives. Stochastic calculus, for instance, provides a framework for modeling the random fluctuations of underlying assets, enabling the valuation of derivatives in a probabilistic setting. Probability theory, meanwhile, offers a rigorous approach to quantifying uncertainty, allowing investors to assess the likelihood of different outcomes. Numerical methods, such as finite difference and Monte Carlo simulations, provide a practical means of approximating complex mathematical models, enabling the valuation of exotic derivatives. By grasping these mathematical concepts, investors and financial professionals can develop a deeper understanding of derivative valuation, enabling them to make more informed investment decisions and optimize their risk management strategies. For example, in the context of options pricing, stochastic calculus can be used to model the underlying asset’s price dynamics, while probability theory can be employed to quantify the probability of exercise. Numerical methods can then be used to approximate the option’s value, providing a robust estimate of its fair value.

Risk Management Strategies for Derivative Portfolios
Effective risk management is crucial in derivative portfolios, as it enables investors to mitigate potential losses and maximize returns. A financial derivatives a quantitative finance view emphasizes the importance of adopting a robust risk management strategy to navigate the complexities of derivative markets. Hedging, diversification, and dynamic replication are popular risk management strategies employed in derivative portfolios. Hedging involves taking positions in multiple derivatives to offset potential losses, while diversification involves spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce exposure to specific risks. Dynamic replication, on the other hand, involves continuously adjusting the portfolio’s composition to maintain a desired risk profile. Each strategy has its benefits and limitations, and investors must carefully consider their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and market conditions when selecting a risk management approach. For instance, hedging can provide protection against specific risks, but may also limit potential gains. Diversification can reduce overall portfolio risk, but may not provide adequate protection against systemic risks. Dynamic replication can offer flexibility and adaptability, but may require frequent rebalancing and incur higher transaction costs. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each strategy, investors can develop a tailored risk management approach that aligns with their investment goals and risk preferences, ultimately enhancing their ability to navigate the complex world of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view.

Quantitative Models for Derivative Trading
In the realm of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view, quantitative models play a crucial role in informing trading decisions and optimizing portfolio performance. Statistical arbitrage, pairs trading, and volatility trading are popular quantitative models employed in derivative trading. Statistical arbitrage, for instance, involves identifying mispricings in the market by analyzing statistical relationships between different assets. Pairs trading, on the other hand, involves identifying two highly correlated assets and taking advantage of deviations in their price ratio. Volatility trading, meanwhile, involves exploiting differences in implied and realized volatility to generate profits. Each model is based on specific assumptions and has its limitations. For example, statistical arbitrage assumes that mispricings will eventually converge to their mean, while pairs trading assumes that the correlation between assets will remain stable. Volatility trading, meanwhile, assumes that implied volatility will eventually converge to realized volatility. By understanding the underlying assumptions and limitations of each model, traders can develop a more nuanced approach to derivative trading, leveraging the power of quantitative finance to inform their investment decisions and optimize their returns. In the context of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view, these models can be used to identify profitable trading opportunities, manage risk, and enhance overall portfolio performance.

Real-World Applications of Financial Derivatives
In the realm of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view, derivatives are used in a variety of ways to manage risk, speculate on market movements, and exploit pricing inefficiencies. One of the most common applications of financial derivatives is hedging, which involves taking a position in a derivative to offset potential losses or gains in an underlying asset. For example, an airline company may use fuel derivatives to hedge against potential increases in fuel prices. Another application of financial derivatives is speculation, where investors take a position in a derivative to profit from potential price movements in an underlying asset. Arbitrage, meanwhile, involves exploiting pricing inefficiencies between two or more markets to generate profits. For instance, an investor may use currency derivatives to exploit differences in exchange rates between two countries. In each of these applications, a deep understanding of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view is crucial to making informed investment decisions and managing risk effectively. By grasping the complexities of derivatives and their various applications, investors and financial institutions can unlock the full potential of these powerful financial instruments and achieve their investment objectives.

The Future of Financial Derivatives: Trends and Innovations
The field of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view is rapidly evolving, driven by advances in technology, changes in market conditions, and shifting regulatory landscapes. One of the most significant trends in the industry is the increasing adoption of fintech, which is revolutionizing the way financial derivatives are traded, cleared, and settled. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also being applied to improve derivative pricing, risk management, and trading strategies. Additionally, blockchain technology is being explored for its potential to increase transparency, reduce counterparty risk, and enhance the overall efficiency of derivative markets. Furthermore, the growing importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors is leading to the development of new derivative products that allow investors to manage ESG-related risks and opportunities. As the financial derivatives landscape continues to evolve, a deep understanding of these trends and innovations will be crucial for investors, financial institutions, and regulators seeking to unlock the full potential of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view.

Conclusion: The Quantitative Finance View of Financial Derivatives
In conclusion, financial derivatives a quantitative finance view play a vital role in modern finance, offering a powerful tool for managing risk, speculating on market movements, and exploiting pricing inefficiencies. By grasping the fundamental principles of derivative pricing, the mathematical concepts underlying derivative valuation, and the various risk management strategies employed in derivative portfolios, investors and financial institutions can unlock the full potential of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view. Furthermore, understanding the real-world applications of financial derivatives, including hedging, speculation, and arbitrage, is crucial for making informed investment decisions and managing risk effectively. As the field of financial derivatives continues to evolve, driven by advances in technology, changes in market conditions, and shifting regulatory landscapes, a deep understanding of these complex instruments will be essential for success in the world of finance. By adopting a quantitative finance perspective, investors and financial institutions can navigate the complex world of derivatives with confidence, unlocking the power of financial derivatives a quantitative finance view to achieve their investment objectives.