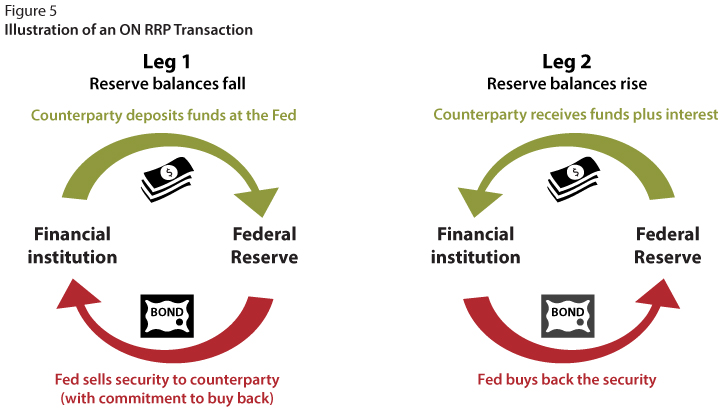
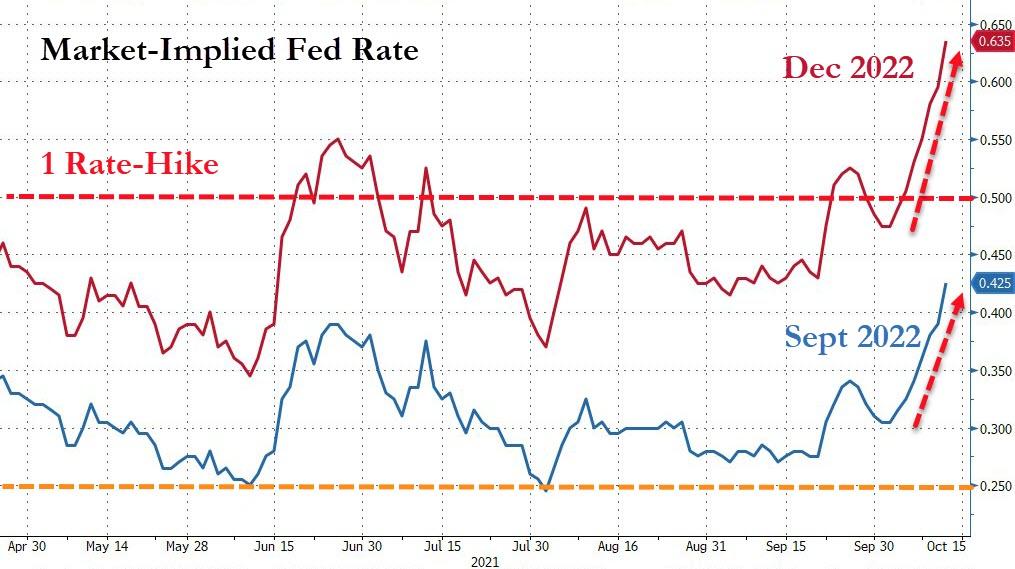
Navigating the Complex World of Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve’s interest rate decisions play a crucial role in shaping the economy, influencing inflation, employment, and economic growth. Understanding the Fed’s actions is vital for investors, businesses, and individuals alike, as it can affect the overall direction of the economy. The probability of a fed interest rate hike is a critical factor in this equation, as it can signal a shift in the Fed’s monetary policy stance. The Fed’s dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and price stability means that its interest rate decisions are closely tied to the performance of the labor market and inflation rates. By grasping the intricacies of monetary policy, individuals can better navigate the complex landscape of economic indicators and make informed decisions about their investments and financial strategies.
How to Read the Tea Leaves: Identifying Key Indicators of a Rate Hike
When assessing the likelihood of a fed interest rate hike, it’s essential to understand the key economic indicators that the Federal Reserve considers. The Fed closely monitors GDP growth, inflation rates, and labor market conditions to determine whether the economy is growing at a sustainable pace. A strong labor market, characterized by low unemployment rates and rising wages, can increase the likelihood of a rate hike. Similarly, a surge in inflation rates above the Fed’s 2% target can prompt the central bank to tighten monetary policy. By analyzing these indicators, investors and economists can gain valuable insights into the Fed’s decision-making process and the probability of a rate hike.
The Role of Inflation Expectations in Shaping Rate Hike Probability
Inflation expectations play a crucial role in shaping the Fed’s decision-making process and, subsequently, the likelihood of a fed interest rate hike. When inflation expectations rise, it can signal to the Fed that the economy is growing at a pace that may lead to higher inflation, prompting the central bank to consider tightening monetary policy. Conversely, low inflation expectations can suggest that the economy is growing at a slow pace, reducing the likelihood of a rate hike. The Fed closely monitors inflation expectations through various measures, including the University of Michigan’s Consumer Sentiment Index and the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Survey of Consumer Expectations. By understanding the dynamics of inflation expectations, investors and economists can gain valuable insights into the Fed’s thinking and the probability of a rate hike.
What the Bond Market is Telling Us About Rate Hike Chances
The bond market is a valuable indicator of the fed interest rate hike probability, as it reflects the collective expectations of investors and market participants. When interest rate expectations rise, bond yields tend to increase, and vice versa. By analyzing the bond market’s reaction to changes in interest rate expectations, investors and economists can gain insights into the likelihood of a rate hike. For instance, a flattening of the yield curve, where short-term yields approach long-term yields, can signal a higher probability of a rate hike. Conversely, a steepening of the yield curve can suggest a lower likelihood of a rate hike. Additionally, the bond market’s reaction to Fed communications and economic data releases can provide clues about the central bank’s future policy decisions. By monitoring the bond market’s behavior, investors can better assess the fed interest rate hike probability and make informed investment decisions.
Fed Speak: Decoding the Language of Central Bankers
Understanding the language and communication style of central bankers, including Fed Chair Jerome Powell, is crucial in deciphering the Fed’s next move and assessing the fed interest rate hike probability. Central bankers often use nuanced language to convey their policy intentions, and subtle changes in tone or phraseology can signal a shift in the Fed’s stance. For instance, a shift from “accommodative” to “neutral” language can indicate a higher likelihood of a rate hike. Similarly, the use of phrases like “data-dependent” or “patient” can suggest a more cautious approach to monetary policy. By carefully analyzing the language and communication style of central bankers, investors and economists can gain valuable insights into the Fed’s thinking and better assess the likelihood of a rate hike. This requires a deep understanding of the Fed’s communication strategy and the ability to decode the subtle signals embedded in their language.
Historical Context: Lessons from Past Rate Hike Cycles
Examining past instances of interest rate hikes can provide valuable insights into the current economic environment and the likelihood of a rate hike. By analyzing the historical context of previous rate hike cycles, investors and economists can identify patterns and trends that can inform their assessment of the fed interest rate hike probability. For example, the 2004-2006 rate hike cycle, which was characterized by a gradual increase in interest rates to combat inflation, can provide lessons for the current economic environment. Similarly, the 2015-2018 rate hike cycle, which was marked by a more cautious approach to monetary policy, can offer insights into the Fed’s decision-making process. By studying these past instances, investors can better understand the factors that influence the Fed’s decisions and make more informed predictions about the likelihood of a rate hike. This historical context can also help investors identify potential risks and opportunities associated with changes in interest rates, allowing them to make more informed investment decisions.
The Impact of Global Economic Trends on Rate Hike Probability
Global economic trends, such as trade tensions and currency fluctuations, can significantly influence the Fed’s decision-making process and the likelihood of a rate hike. For instance, a strengthening dollar can lead to higher import prices, which can fuel inflation and increase the fed interest rate hike probability. Similarly, trade tensions can impact economic growth and inflation expectations, leading the Fed to adjust its monetary policy stance. The Fed closely monitors global economic developments, and their impact on the US economy, to inform their interest rate decisions. By understanding the interplay between global economic trends and the Fed’s decision-making process, investors and economists can better assess the likelihood of a rate hike and make more informed investment decisions. This requires a nuanced understanding of the complex relationships between global economic variables and their impact on the US economy.
Putting it All Together: A Framework for Assessing Rate Hike Probability
To accurately assess the fed interest rate hike probability, it is essential to consider a range of factors, including key economic indicators, inflation expectations, bond market signals, and global economic trends. By incorporating these factors into a comprehensive framework, investors and economists can make more informed predictions about the likelihood of a rate hike. This framework should include an analysis of GDP growth, inflation rates, and labor market conditions, as well as an assessment of inflation expectations and their impact on the Fed’s decision-making process. Additionally, the framework should consider the bond market’s reaction to changes in interest rate expectations and the language and communication style of central bankers. By synthesizing these factors, investors and economists can develop a nuanced understanding of the fed interest rate hike probability and make more informed investment decisions. This framework can be used to monitor the evolving economic landscape and adjust predictions about the likelihood of a rate hike accordingly.