Understanding the Federal Funds Rate and its Significance
The federal funds rate is the target rate that the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) sets for overnight lending between banks. This rate significantly influences borrowing costs across the economy. A higher federal funds rate increases borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing economic growth and curbing inflation. Conversely, a lower federal funds rate makes borrowing cheaper, stimulating economic activity but potentially fueling inflation. Understanding this rate’s influence is crucial for navigating financial markets effectively, and the fed funds rate forward curve offers insights into future rate expectations. The FOMC’s decisions regarding the federal funds rate are pivotal in managing the overall economic health of the nation. Its impact ripples through various sectors, affecting everything from mortgage rates to corporate investment decisions. Therefore, accurately forecasting future federal funds rate movements is paramount for investors and businesses alike. The fed funds rate forward curve provides a valuable tool for this forecasting.
Predicting the federal funds rate is complex because it reacts to numerous economic factors. Inflation, employment levels, and economic growth projections all play significant roles. The FOMC closely monitors these indicators to determine appropriate adjustments to the federal funds rate. Its decisions are often communicated through press releases and speeches, offering clues about its future policy direction. However, unexpected events, both domestic and global, can significantly impact rate adjustments, creating uncertainty. Analyzing the fed funds rate forward curve offers a way to gauge market sentiment toward future rates and understand what the market anticipates from the FOMC’s future decisions. Effective use of the fed funds rate forward curve requires careful analysis of various economic indicators and a solid understanding of the FOMC’s policy goals.
The importance of understanding the federal funds rate cannot be overstated. It’s the cornerstone of monetary policy, directly impacting borrowing costs and influencing inflation and economic growth. While the FOMC sets the target rate, market participants form their own expectations about future movements, reflected in the fed funds rate forward curve. This curve, derived from interest rate futures contracts, provides a valuable tool for assessing market sentiment and informing investment strategies. By understanding how the curve is constructed and how its shape reflects market expectations, investors can make more informed decisions regarding their portfolios and overall risk management strategies. The fed funds rate forward curve is not a crystal ball, but it is a powerful tool for understanding the market’s view on the future of interest rates and the potential impact on investment decisions. Understanding and interpreting its nuances is critical in today’s dynamic financial environment.
Deciphering the Forward Curve: A Visual Representation of Future Rates
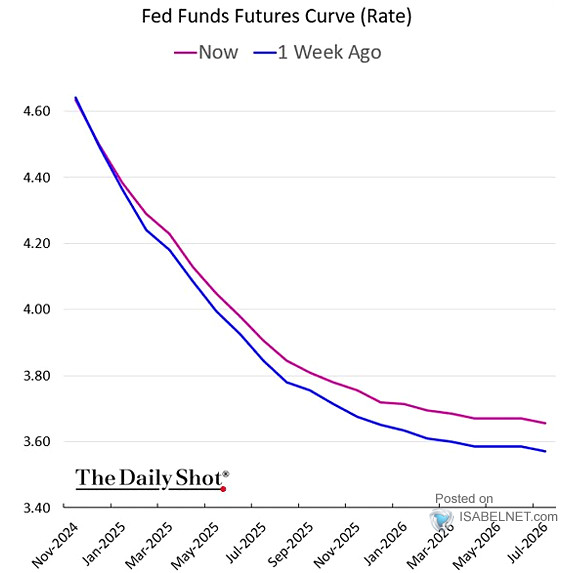
The fed funds rate forward curve provides a visual depiction of market expectations regarding future federal funds rates. It’s essentially a graph plotting the implied interest rates for different maturity dates. These implied rates are derived from the prices of interest rate futures contracts. These contracts allow investors to agree on a specific interest rate for a future period. The fed funds rate forward curve is built by connecting these implied rates across various maturities, creating a curve that illustrates the market’s collective outlook. Understanding the fed funds rate forward curve is crucial for navigating the complexities of interest rate markets.
A typical fed funds rate forward curve might show a gradual upward slope. This suggests that the market anticipates higher interest rates in the future. Conversely, a downward-sloping curve indicates expectations of decreasing rates. A relatively flat curve implies that the market anticipates little change in the federal funds rate over the forecast period. The shape of the fed funds rate forward curve is dynamic, constantly shifting to reflect new information and changing market sentiment. Investors use this curve to gauge market expectations and make informed decisions about their investments. The curve provides valuable insights into the collective wisdom of the market regarding future monetary policy.
Constructing the fed funds rate forward curve involves analyzing interest rate futures contracts traded on exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Each contract specifies a future period and a corresponding interest rate. The prices of these contracts reflect market expectations about the future federal funds rate. By analyzing these prices, financial professionals create the fed funds rate forward curve. This curve isn’t a prediction of the future; instead, it’s a representation of current market sentiment. The fed funds rate forward curve is a key tool for understanding the market’s view on future interest rates and assessing potential risks and opportunities.
Interpreting the Shape of the Curve: Clues about Future Monetary Policy
The shape of the fed funds rate forward curve offers valuable insights into market sentiment and expectations regarding future interest rate adjustments. An upward-sloping curve suggests that market participants anticipate higher interest rates in the future. This typically reflects expectations of robust economic growth, potentially leading to increased inflationary pressures. The Federal Reserve might respond by tightening monetary policy to curb inflation. Conversely, a downward-sloping curve indicates that the market anticipates lower interest rates down the line. This could be a signal of concerns about economic slowdown or deflationary risks, prompting the Federal Reserve to adopt a more accommodative monetary policy stance. A flat fed funds rate forward curve suggests relative stability in rate expectations, implying a relatively balanced outlook on future economic conditions. Investors closely monitor these shifts to anticipate potential changes in monetary policy.
Several factors influence the shape of the fed funds rate forward curve. Inflation expectations play a crucial role. High inflation projections usually lead to an upward-sloping curve, as markets anticipate the central bank raising rates to combat inflation. Economic growth forecasts are another key driver. Strong growth projections tend to support an upward-sloping curve, reflecting anticipation of tighter monetary policy. Conversely, weak growth expectations can lead to a downward or flatter curve. The perceived stance of the Federal Reserve itself significantly impacts the curve. Statements made by Federal Reserve officials, their communication strategies, and any hints about future policy actions can directly influence market expectations and the shape of the fed funds rate forward curve. The interaction of these factors creates a dynamic and ever-evolving curve, making its interpretation a crucial skill for investors and financial professionals.
Analyzing the fed funds rate forward curve requires a nuanced understanding of these underlying factors. It’s essential to consider the broader economic context. For example, a steep upward-sloping curve might reflect healthy growth, but it could also signal overheating, depending on inflation levels and other economic indicators. Conversely, a downward-sloping curve doesn’t necessarily guarantee a recession; it could simply indicate that the market expects a pause or a moderation in the pace of rate hikes. Careful examination of the curve, along with a holistic view of the economic landscape, provides a more complete picture of future interest rate prospects. The fed funds rate forward curve serves as an important tool, but it’s vital to remember that it represents market *expectations*, not certainties.
How to Use the Fed Funds Rate Forward Curve for Investment Strategies
The fed funds rate forward curve offers valuable insights for strategic investment decisions. Investors can utilize the curve to anticipate future interest rate movements and adjust their portfolios accordingly. For example, an upward-sloping curve, suggesting rising rates, might prompt adjustments to a bond portfolio. Reducing the duration of the portfolio, by shifting towards shorter-term bonds, mitigates potential capital losses from rising yields. Conversely, a downward-sloping curve might signal an opportunity to extend bond portfolio duration, potentially capturing higher returns from longer-term bonds. Understanding the fed funds rate forward curve is crucial for effective bond portfolio management.
Beyond bond portfolios, the fed funds rate forward curve informs decisions about debt financing. Businesses considering borrowing can use the curve to assess the potential trajectory of interest rates. An upward-sloping curve suggests increasing borrowing costs in the future. This might encourage businesses to lock in current, potentially lower, fixed interest rates through longer-term debt instruments. Conversely, a flat or downward-sloping curve may make floating-rate debt more attractive, allowing for potential cost savings as rates decrease. Careful analysis of the fed funds rate forward curve is essential for making informed decisions regarding debt maturity and type.
The implications of the fed funds rate forward curve extend beyond fixed income. The curve’s shape provides a glimpse into the market’s overall expectations for future economic growth and inflation. A steeply upward-sloping curve, for example, often reflects expectations of robust economic growth and rising inflation. This might lead investors to favor asset classes that typically perform well under such conditions, such as equities or commodities. Conversely, a flat or downward-sloping curve, which suggests slower economic growth or even deflation, might lead investors towards safer assets like government bonds or precious metals. In conclusion, mastering the interpretation and application of the fed funds rate forward curve allows investors to make more informed and strategic decisions across a range of asset classes. By understanding the market’s expectations for future interest rates, investors gain a significant edge in navigating the complexities of the financial markets.
Key Factors Influencing the Fed Funds Rate Forward Curve’s Movement
The fed funds rate forward curve, a visual representation of market expectations for future interest rates, is highly sensitive to various economic indicators and events. Inflation data, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, significantly influence the curve. High inflation readings typically push the curve upward, reflecting expectations of future rate hikes by the Federal Reserve to combat rising prices. Conversely, lower-than-expected inflation readings can flatten or even invert the curve, suggesting a potential for rate cuts.
Employment reports, particularly the non-farm payrolls figure, also play a crucial role. Strong employment growth, indicating a robust economy, often leads to upward pressure on the fed funds rate forward curve as the market anticipates tighter monetary policy. Conversely, weak employment data can signal economic slowdown, potentially leading to a downward sloping or flatter curve, as rate cuts become more likely. GDP growth figures provide another key indicator. Strong GDP growth reinforces expectations of higher interest rates, while weak GDP growth can flatten or invert the curve. The Federal Reserve’s own statements and actions, including press conferences and FOMC announcements, significantly impact market sentiment and the shape of the fed funds rate forward curve. Unexpected shifts in the Fed’s stance on monetary policy can immediately cause dramatic changes in the curve.
Other factors contributing to the fed funds rate forward curve’s movement include geopolitical events, commodity price fluctuations, and changes in global economic conditions. These events can introduce uncertainty into the market, making it challenging to accurately predict future rate changes. Understanding these influences is crucial for interpreting the curve and making informed investment decisions. The fed funds rate forward curve provides valuable insights into market expectations, but careful consideration of these influencing factors is essential for a nuanced understanding of its implications. Unexpected economic shocks can significantly impact the curve’s shape, demonstrating the inherent limitations of relying solely on it for forecasting future interest rates. Analyzing the curve in conjunction with other economic indicators provides a more complete picture.
Limitations and Considerations When Using the Fed Funds Rate Forward Curve
While the fed funds rate forward curve offers valuable insights into market expectations, it’s crucial to acknowledge its inherent limitations. The curve reflects probabilities, not certainties. Unexpected economic shocks, such as geopolitical events or unforeseen changes in consumer behavior, can dramatically alter the trajectory of interest rates. The fed funds rate forward curve, therefore, should not be interpreted as a precise predictor of future rates. Instead, it provides a dynamic snapshot of current market sentiment. Investors should recognize this inherent uncertainty and incorporate it into their investment strategies.
Furthermore, the fed funds rate forward curve represents market consensus. This consensus can sometimes be inaccurate or overly influenced by short-term market fluctuations. It may not fully capture the complexities of the economy or the potential impact of future policy decisions by the Federal Reserve. Over-reliance on the fed funds rate forward curve without considering other relevant economic indicators can lead to flawed investment decisions. A comprehensive analysis requires considering a broad range of data points and expert opinions. Diversification remains a vital strategy to mitigate risks associated with relying solely on the curve’s predictions.
Another important consideration is the potential for biases in the data used to construct the fed funds rate forward curve. Different data providers may employ varying methodologies, leading to discrepancies in the resulting curves. It is essential to compare data from multiple reputable sources and critically evaluate the underlying assumptions and methodologies. Understanding these limitations and employing a diversified approach to investment management is crucial for successful navigation of the complex landscape of interest rate forecasting. The fed funds rate forward curve provides valuable information, but it’s only one piece of a much larger puzzle.
Comparing Different Sources for Fed Funds Rate Forecasts
Investors can access fed funds rate forward curve data from various sources. Bloomberg Terminal and Refinitiv Eikon are prominent commercial platforms offering comprehensive financial data, including detailed fed funds rate forward curves. These platforms provide sophisticated analytical tools and historical data, allowing for in-depth analysis of the curve’s behavior. However, access to these platforms typically requires subscriptions, which can be expensive. The Federal Reserve itself publishes data related to interest rates and monetary policy. While not directly providing a graphical fed funds rate forward curve in the same way as commercial providers, the Federal Reserve’s data serves as a crucial foundation for understanding the context behind market expectations reflected in the curve. Analyzing this data alongside information from commercial sources offers a more complete picture.
The choice of data provider depends on individual needs and resources. For professional traders and analysts who require real-time data and advanced analytical capabilities, Bloomberg Terminal and Refinitiv Eikon are likely preferable. However, the Federal Reserve’s data provides a valuable, publicly accessible resource for anyone wanting to understand the underlying economic factors influencing the fed funds rate forward curve. It’s important to remember that even the most sophisticated sources only provide estimations of market sentiment and expectations. The fed funds rate forward curve itself is a dynamic representation of constantly evolving market forecasts, subject to change as new economic information becomes available. Understanding the limitations of any data source is critical for responsible use of the fed funds rate forward curve in investment decisions.
Different data providers may present the fed funds rate forward curve with slight variations in methodology or data frequency. These differences can influence the precise shape and interpretation of the curve. Careful consideration of these variations is necessary to avoid misinterpretations. Comparing data across multiple sources can provide a more robust understanding of market expectations and help refine investment strategies based on the fed funds rate forward curve. Understanding the nuances of different data providers allows investors to make more informed choices. Access to diverse data sources enhances the overall effectiveness of using the fed funds rate forward curve in decision-making.
The Role of the Forward Curve in Risk Management
The fed funds rate forward curve serves as a crucial tool for managing interest rate risk, particularly for entities with substantial exposure to interest rate fluctuations. Understanding the shape and implied expectations embedded within the curve allows institutions to proactively mitigate potential losses. For example, a steeply upward-sloping fed funds rate forward curve suggests rising interest rates in the future. This information enables investors to adjust their bond portfolio durations accordingly, reducing the impact of rising rates on portfolio value. Similarly, businesses can use the fed funds rate forward curve to make informed decisions regarding floating-rate versus fixed-rate debt, choosing the option that best aligns with their predicted interest rate environment.
Effective risk management often involves the strategic use of derivatives. The fed funds rate forward curve provides valuable insights into the potential for future rate changes, informing hedging strategies. For instance, if the curve anticipates a significant increase in rates, an institution could use interest rate swaps to lock in a fixed rate on future borrowings, effectively mitigating the risk of higher borrowing costs. This proactive approach protects against unexpected shifts in the market. The fed funds rate forward curve also aids in stress testing portfolios. By inputting different rate scenarios derived from the curve’s various possible shapes, institutions can assess the resilience of their investments under different economic conditions. This allows for a more comprehensive understanding of potential vulnerabilities and the development of robust contingency plans.
By analyzing the fed funds rate forward curve, financial institutions can adjust their overall investment strategies to minimize interest rate risk. This might involve shifting allocations between fixed-income and equity assets, or employing strategies like duration matching to offset the impact of rate changes on portfolio value. The curve facilitates more informed decision-making, promoting greater financial stability. Careful monitoring of the fed funds rate forward curve, combined with a thorough understanding of its implications, provides a strong foundation for effective interest rate risk management, enabling institutions to navigate volatile markets with greater confidence and resilience.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/UnderstandingTreasuryYieldAndInterestRates2-81d89039418c4d7cae30984087af4aff.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/FederalFundsRate-8064baabc82d47bf81b735e57a5c4557.jpg)