Understanding the Foundations of Economics
Economics, as a social science, is built upon a few fundamental principles. At its core, economics is concerned with the allocation of scarce resources to meet unlimited wants and needs. This inherent scarcity gives rise to the concept of opportunity cost, which refers to the value of the next best alternative forgone when choosing to allocate resources in a particular way. The behavior of individuals, businesses, and governments in making decisions about resource allocation is a crucial aspect of economics, as it influences the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. By grasping these foundational concepts, one can better appreciate the significance of understanding the difference between economics and financial economics, and how they intersect in shaping our understanding of the economy.
The Emergence of Financial Economics: A Subset of Economics
Financial economics, as a subfield of economics, has evolved to focus on the study of financial markets, instruments, and institutions, and their impact on the economy. This branch of economics emerged as a response to the growing complexity of financial systems and the need to understand the intricate relationships between financial variables and the broader economy. Financial economics draws on the principles of economics, incorporating theories and concepts from microeconomics and macroeconomics to analyze the behavior of financial markets and institutions. By examining the interactions between financial variables, such as asset prices, interest rates, and risk, financial economics provides valuable insights into the workings of the economy, shedding light on the difference between economics and financial economics.
How to Distinguish Between Economics and Financial Economics
To fully appreciate the difference between economics and financial economics, it is essential to understand their distinct objectives, methodologies, and applications. Economics, as a broader field, focuses on the study of scarcity, resource allocation, and the behavior of individuals, businesses, and governments. In contrast, financial economics is a subfield that concentrates on the study of financial markets, instruments, and institutions, and their impact on the economy. While economics provides a framework for understanding the economy as a whole, financial economics delves deeper into the intricacies of financial systems, examining the interactions between financial variables and the broader economy. By recognizing the difference between economics and financial economics, researchers and practitioners can better navigate the complexities of the economy, informing policy decisions, business strategy, and individual financial planning.
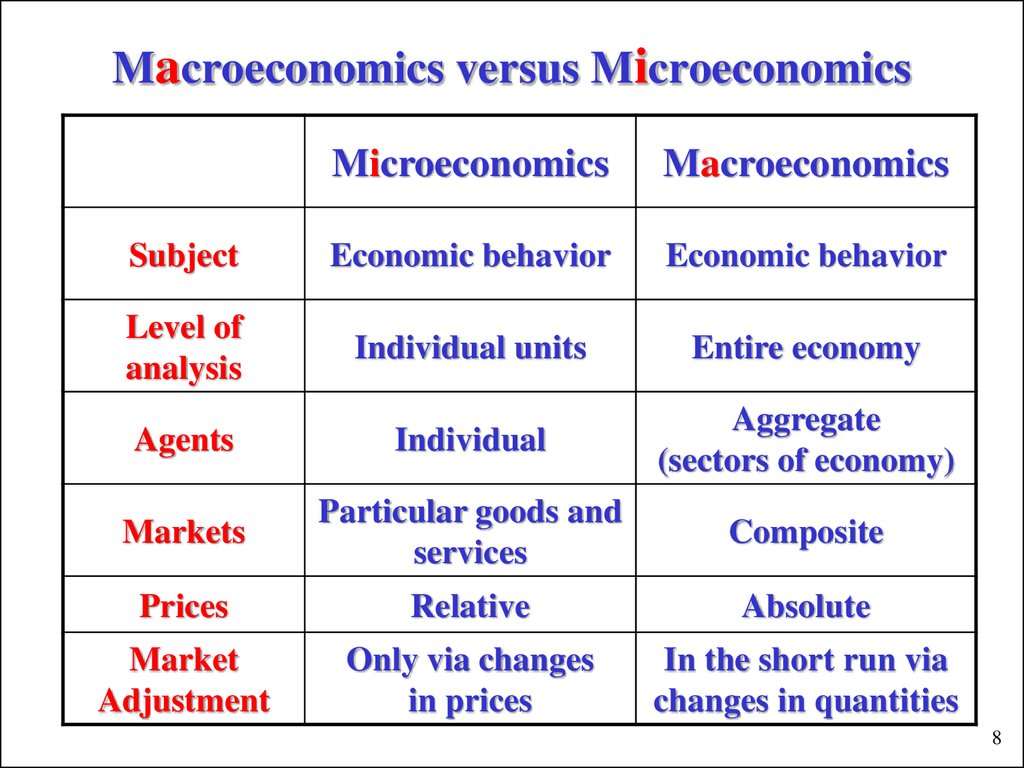
The Scope of Economics: Micro and Macro Perspectives
Economics, as a discipline, encompasses a broad range of topics and subfields, including microeconomics and macroeconomics. Microeconomics focuses on individual markets and consumer behavior, examining the interactions between supply and demand, and the allocation of resources within specific markets. Macroeconomics, on the other hand, takes a more aggregated approach, studying the economy as a whole, including issues such as economic growth, inflation, and unemployment. Financial economics, as a subfield of economics, fits into this framework by examining the financial aspects of microeconomic and macroeconomic phenomena. For instance, financial economics might analyze the impact of monetary policy on financial markets, or the role of financial institutions in facilitating economic growth. Understanding the scope of economics, including its micro and macro perspectives, is essential for recognizing the difference between economics and financial economics, and for appreciating the unique contributions of financial economics to our understanding of the economy.
Financial Economics in Action: Applications and Case Studies
Financial economics has numerous practical applications in various areas, including investment, risk management, and financial regulation. For instance, financial economists use models such as the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and the Arbitrage Pricing Theory (APT) to estimate the expected returns on investments and to manage risk. In the realm of financial regulation, financial economists play a crucial role in designing and implementing policies aimed at promoting financial stability and preventing crises. The 2008 global financial crisis, for example, highlighted the importance of financial economics in understanding the complex interactions between financial markets, institutions, and the broader economy. By recognizing the difference between economics and financial economics, researchers and practitioners can better appreciate the unique contributions of financial economics to our understanding of the economy and its applications in real-world scenarios. Case studies of successful companies, such as Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway, also demonstrate the power of financial economics in informing investment decisions and driving business growth.
The Interplay Between Economics and Financial Economics: A Two-Way Street
The relationship between economics and financial economics is one of mutual influence and interdependence. Economics provides the foundation for understanding the behavior of individuals, businesses, and governments, which in turn informs the study of financial markets, instruments, and institutions in financial economics. Conversely, financial economics sheds light on the role of financial factors in shaping economic outcomes, such as the impact of monetary policy on economic growth. The difference between economics and financial economics is not a rigid boundary, but rather a nuanced distinction that recognizes the complementary nature of these two fields. For instance, the concept of risk, which is central to financial economics, is also relevant in economics, where it is used to understand the behavior of consumers and firms under uncertainty. By acknowledging the interplay between economics and financial economics, researchers and practitioners can leverage the insights and tools of both fields to better understand the complex dynamics of the economy and make more informed decisions.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters: Implications for Policy and Practice
Recognizing the difference between economics and financial economics is crucial for informed decision-making in various areas, including policy, business, and individual financial planning. By understanding the distinct objectives, methodologies, and applications of these two fields, policymakers can design more effective economic policies that take into account the complex interactions between financial markets and the broader economy. For instance, a clear understanding of the difference between economics and financial economics can help policymakers navigate the trade-offs between monetary policy and fiscal policy, leading to more sustainable economic growth. In the business world, companies can benefit from recognizing the difference between economics and financial economics by developing more nuanced strategies that account for the interplay between financial markets and the economy. Furthermore, individual investors can make more informed investment decisions by understanding the role of financial economics in shaping market outcomes. The difference between economics and financial economics is not just an academic distinction; it has real-world implications for policy, practice, and individual decision-making.
Navigating the Boundaries: Future Directions for Economics and Financial Economics
As the global economy continues to evolve, the boundaries between economics and financial economics are likely to shift and blur. The ongoing integration of financial markets, the rise of new financial instruments, and the increasing importance of financial regulation will continue to blur the lines between these two fields. To stay ahead of the curve, researchers and practitioners must navigate these boundaries, exploring new areas of inquiry and collaboration. One promising area of research is the study of behavioral finance, which combines insights from psychology and economics to understand how cognitive biases shape financial decision-making. Another area of focus is the development of more sophisticated models of financial markets, which can better capture the complex interactions between financial institutions and the broader economy. By pushing the boundaries of what we know about the difference between economics and financial economics, we can unlock new insights and opportunities for growth, stability, and prosperity. As we move forward, it is essential to recognize the interdependencies between economics and financial economics, and to foster a spirit of collaboration and innovation that can help us navigate the complexities of the global economy.