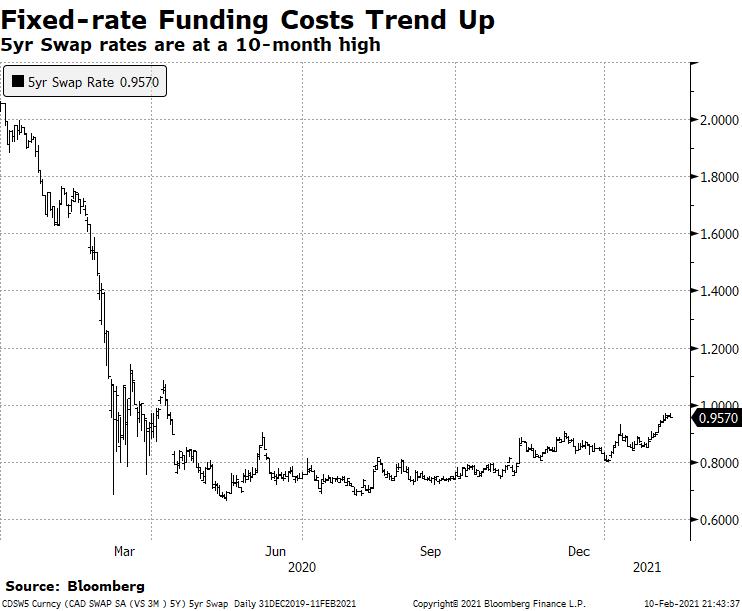
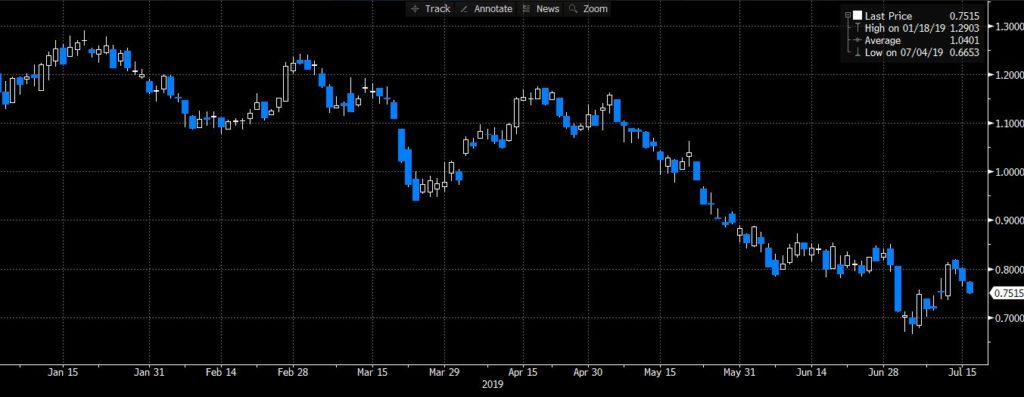
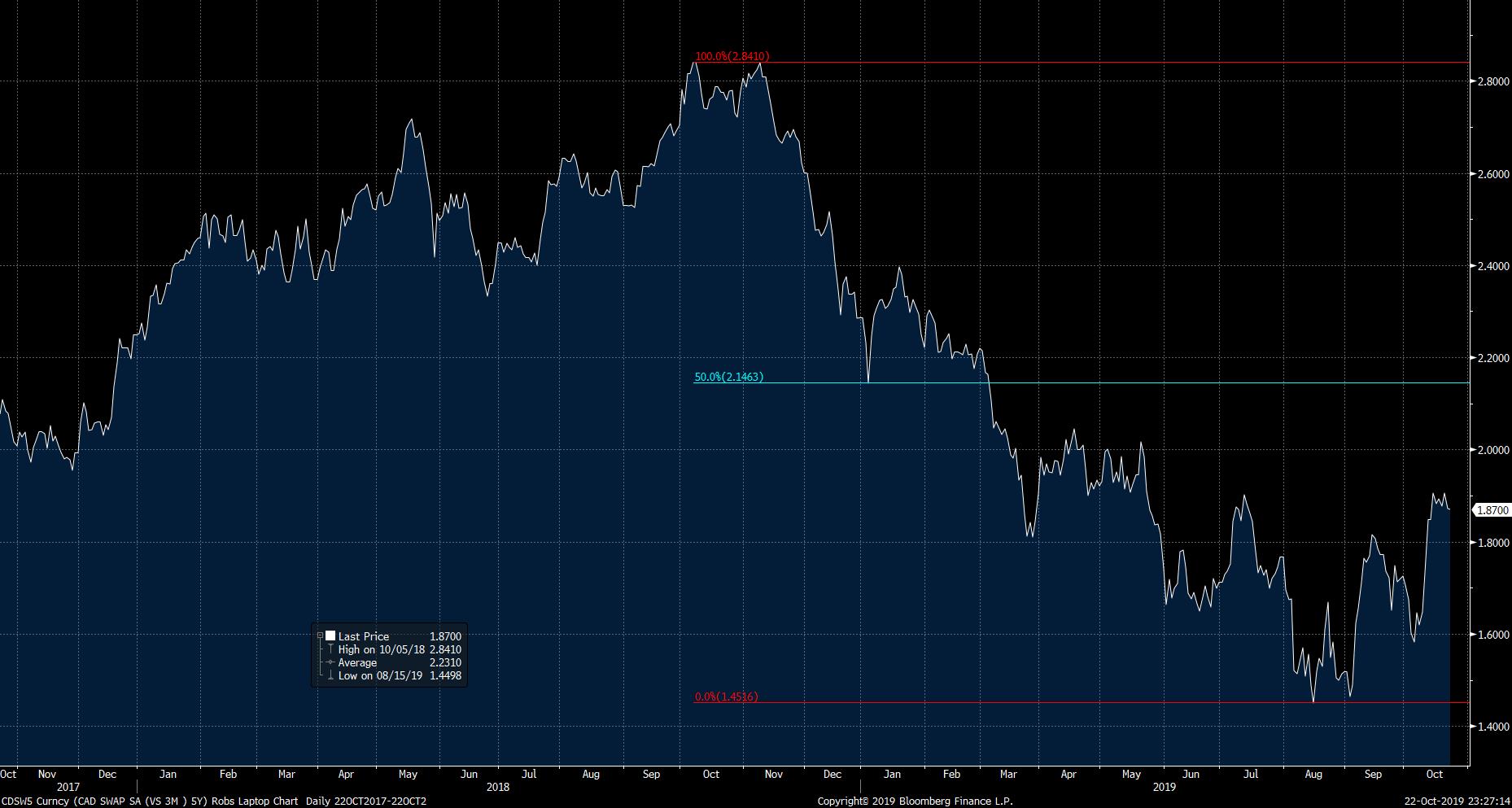
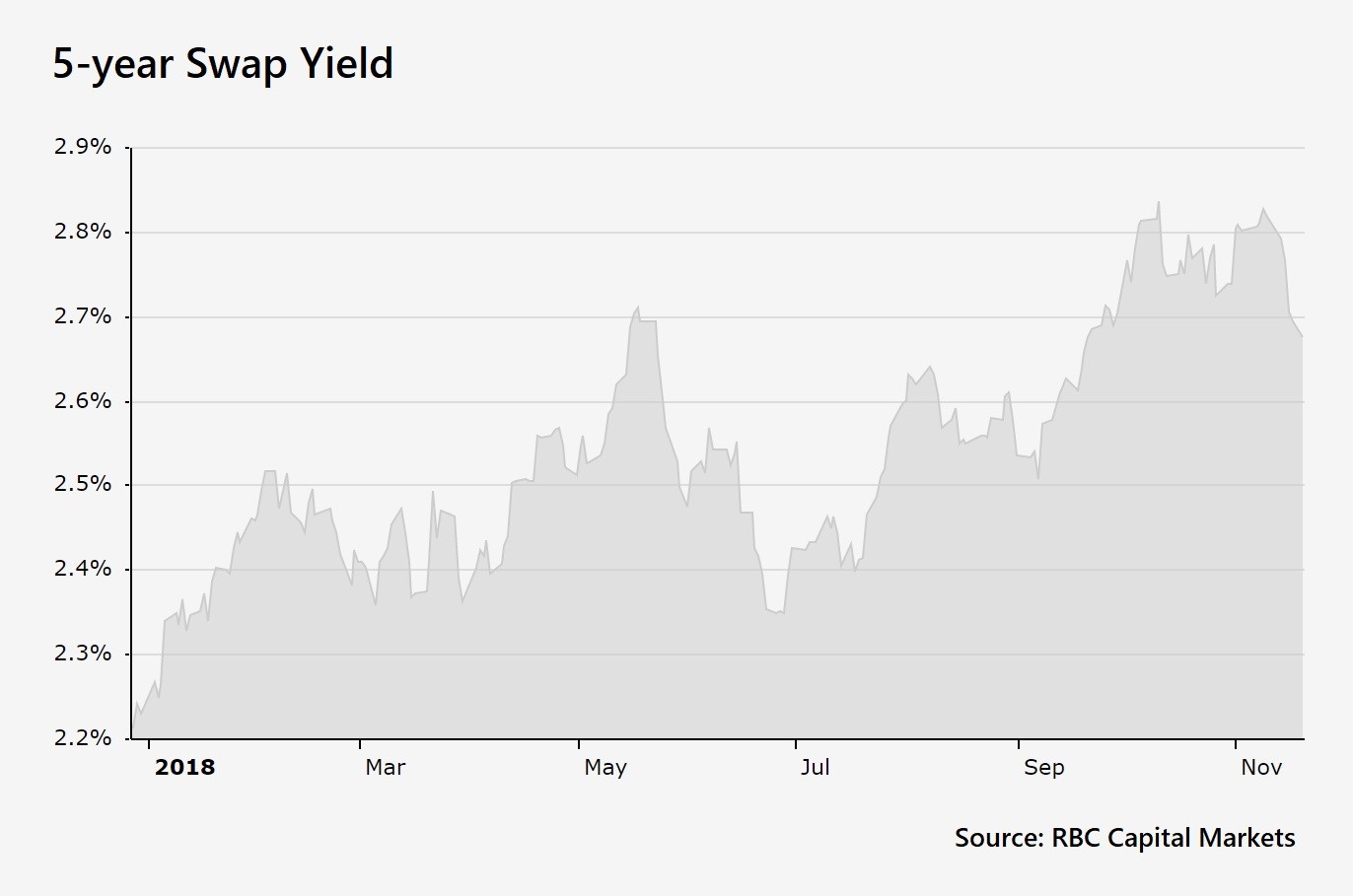
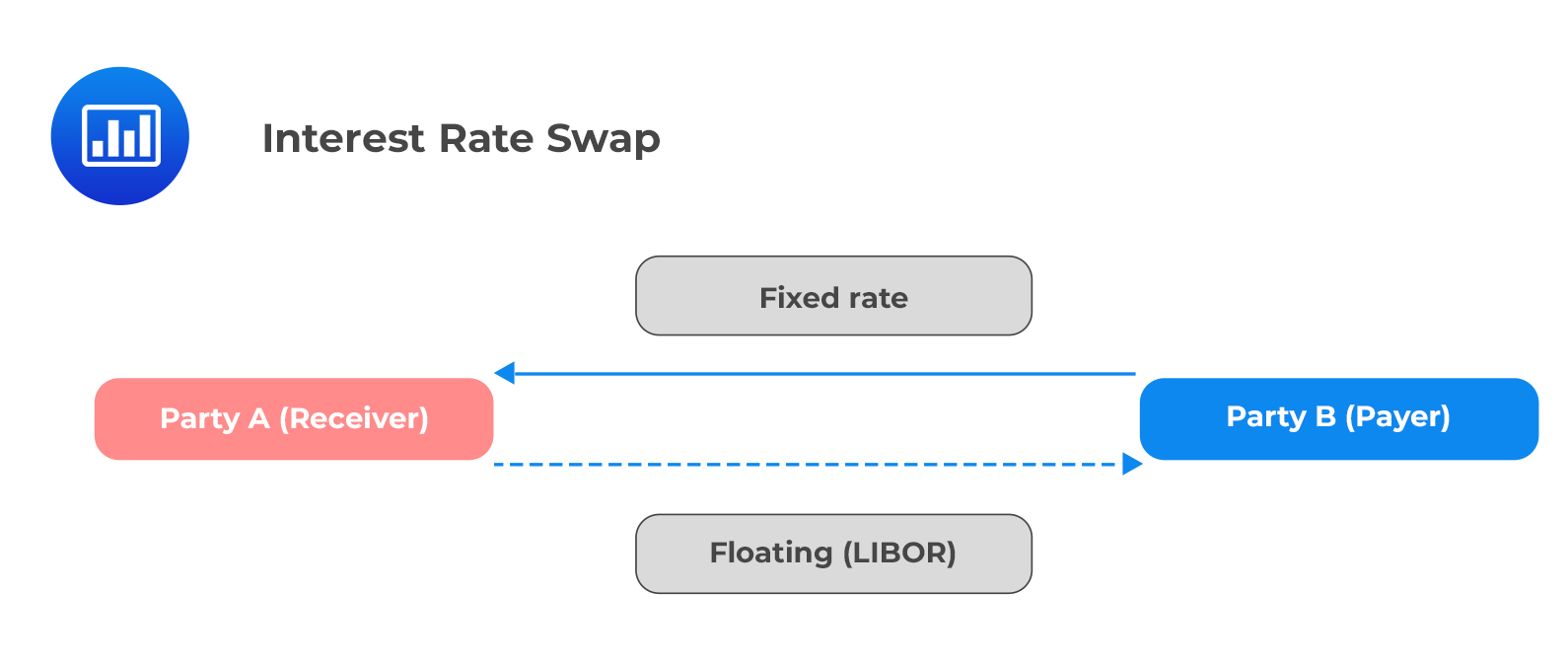
What is a 5-Year Swap Rate and Why Does it Matter?
In the world of finance, interest rate swaps are a crucial tool for managing risk and optimizing investment strategies. At the heart of this mechanism lies the 5-year swap rate, a key indicator that reflects the market’s expectations of future interest rates. But what exactly is a 5-year swap rate, and why does it matter to investors and businesses?
A 5-year swap rate represents the fixed interest rate that parties agree to exchange for a floating interest rate, typically based on a benchmark rate such as LIBOR, over a 5-year period. This rate serves as a benchmark for various financial instruments, including bonds, loans, and derivatives. As a result, the 5-year swap rate has a profound impact on the entire financial ecosystem, influencing borrowing costs, investment decisions, and risk management strategies.
The significance of the 5-year swap rate lies in its ability to provide insights into market sentiment and economic conditions. By analyzing the current 5-year swap rate, investors and businesses can gain a better understanding of the market’s expectations of future interest rate movements, inflation, and economic growth. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions, managing risk, and optimizing portfolio performance. The current 5-year swap rate, in particular, serves as a key indicator of the market’s expectations, making it an essential tool for investors and businesses seeking to navigate the complex world of finance.
How to Interpret the Current 5-Year Swap Rate
Understanding the current 5-year swap rate is crucial for investors and businesses seeking to navigate the complex world of finance. This key indicator provides valuable insights into market sentiment, economic conditions, and potential future interest rate movements. But how can one interpret the current 5-year swap rate, and what does it reveal about the market?
A high current 5-year swap rate may indicate a strong economy, with rising inflation expectations and a potential increase in interest rates. This could lead to higher borrowing costs, making it more expensive for businesses and individuals to access credit. On the other hand, a low current 5-year swap rate may suggest a slowing economy, with lower inflation expectations and a potential decrease in interest rates. This could lead to lower borrowing costs, making it cheaper for businesses and individuals to access credit.
The current 5-year swap rate can also provide insights into market sentiment, with a high rate indicating a more optimistic outlook and a low rate indicating a more pessimistic outlook. Additionally, the current 5-year swap rate can be used to gauge the effectiveness of central bank policies, with a high rate suggesting that monetary policy is having a positive impact on the economy and a low rate suggesting that it may be having a negative impact.
By analyzing the current 5-year swap rate in conjunction with other market indicators, such as the yield curve and inflation expectations, investors and businesses can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions. The current 5-year swap rate is a powerful tool that can help investors and businesses stay ahead of the curve and navigate the complex world of finance.
The Impact of Market Forces on the 5-Year Swap Rate
The 5-year swap rate is influenced by a complex array of market forces, each playing a crucial role in shaping its trajectory. Understanding these factors is essential for investors and businesses seeking to navigate the intricacies of the financial market. In this section, we’ll delve into the key market forces that impact the 5-year swap rate, including central bank policies, inflation expectations, and supply and demand imbalances.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, play a significant role in influencing the 5-year swap rate through their monetary policy decisions. By adjusting interest rates, central banks can impact the overall direction of the economy, which in turn affects the 5-year swap rate. For instance, a tightening of monetary policy can lead to a increase in the 5-year swap rate, while a loosening of policy can lead to a decrease.
Inflation expectations are another critical factor that influences the 5-year swap rate. When inflation expectations rise, investors demand higher returns to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power, leading to an increase in the 5-year swap rate. Conversely, when inflation expectations fall, investors are willing to accept lower returns, leading to a decrease in the 5-year swap rate.
Supply and demand imbalances in the market also have a significant impact on the 5-year swap rate. When there is a surplus of liquidity in the market, the 5-year swap rate tends to decrease, as investors are willing to accept lower returns. Conversely, when there is a shortage of liquidity, the 5-year swap rate tends to increase, as investors demand higher returns.
These market forces interact in complex ways, making it essential to monitor the 5-year swap rate in conjunction with other market indicators. By understanding the impact of these forces, investors and businesses can gain a deeper insight into the market and make more informed investment decisions. The current 5-year swap rate, in particular, provides a valuable snapshot of the market’s expectations and can be used to inform investment strategies and risk management approaches.
A Historical Perspective: Trends and Patterns in the 5-Year Swap Rate
Examining the historical trends and patterns of the 5-year swap rate provides valuable insights into its behavior and can inform investment decisions. By analyzing the swap rate’s response to different economic conditions and market events, investors and businesses can gain a deeper understanding of its significance and potential future movements.
Historical data reveals that the 5-year swap rate tends to increase during periods of economic growth and decrease during periods of economic downturn. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, the 5-year swap rate plummeted as investors sought safe-haven assets and central banks implemented quantitative easing policies. Conversely, during the post-crisis recovery period, the 5-year swap rate gradually increased as economic growth resumed and inflation expectations rose.
Another key trend observed in the 5-year swap rate is its correlation with central bank policies. When central banks implement hawkish policies, such as raising interest rates, the 5-year swap rate tends to increase. Conversely, when central banks implement dovish policies, such as lowering interest rates, the 5-year swap rate tends to decrease. This correlation highlights the significant impact of central bank policies on the swap rate and the broader economy.
The 5-year swap rate has also exhibited patterns in response to changes in inflation expectations. When inflation expectations rise, the 5-year swap rate tends to increase, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, when inflation expectations fall, the 5-year swap rate tends to decrease, as investors are willing to accept lower returns.
By analyzing these historical trends and patterns, investors and businesses can gain a better understanding of the current 5-year swap rate and its potential future movements. This knowledge can inform investment decisions, risk management strategies, and borrowing costs, ultimately helping to navigate the complex world of finance.
What the Current 5-Year Swap Rate Means for Investors and Businesses
The current 5-year swap rate has significant implications for investors, businesses, and the broader economy. As a key indicator of market sentiment and economic conditions, the swap rate can inform investment decisions, risk management strategies, and borrowing costs.
For investors, the current 5-year swap rate can influence the attractiveness of various asset classes. For instance, a high swap rate may make fixed-income investments more appealing, while a low swap rate may lead investors to seek higher-yielding assets. Additionally, the swap rate can impact the performance of hedging strategies, making it essential for investors to monitor its movements.
Businesses, particularly those with significant debt obligations, are also affected by the current 5-year swap rate. A rising swap rate can increase borrowing costs, making it more expensive to access capital. Conversely, a falling swap rate can reduce borrowing costs, making it more attractive to invest in growth initiatives. By understanding the implications of the swap rate, businesses can optimize their capital structures and make informed investment decisions.
The current 5-year swap rate also has broader implications for the economy. A high swap rate can indicate a strong economy with rising inflation expectations, while a low swap rate may suggest a slowing economy with decreased inflation expectations. By monitoring the swap rate, policymakers and economists can gain insights into the economy’s trajectory and make informed decisions about monetary policy.
Furthermore, the current 5-year swap rate can influence risk management strategies. A rising swap rate may indicate increased market volatility, prompting investors and businesses to adopt more conservative risk management approaches. Conversely, a falling swap rate may suggest a more stable market environment, allowing for more aggressive risk-taking. By understanding the implications of the swap rate, market participants can optimize their risk management strategies and navigate the complex world of finance.
In conclusion, the current 5-year swap rate is a critical indicator that can inform investment decisions, risk management strategies, and borrowing costs. By understanding its implications, investors, businesses, and policymakers can make more informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial market.
Comparing the 5-Year Swap Rate to Other Market Indicators
When analyzing the current 5-year swap rate, it’s essential to consider its relationship with other key market indicators. By comparing the swap rate to these indicators, investors and businesses can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the economy and financial markets.
One key indicator to compare with the 5-year swap rate is the yield curve. The yield curve represents the relationship between bond yields and maturities, providing insights into market expectations of future interest rates. A steepening yield curve, where long-term yields rise faster than short-term yields, may indicate a growing economy and increasing inflation expectations, which can lead to a higher 5-year swap rate. Conversely, a flattening yield curve may suggest a slowing economy and decreasing inflation expectations, leading to a lower 5-year swap rate.
Inflation expectations are another important indicator to consider when analyzing the 5-year swap rate. As inflation expectations rise, the 5-year swap rate tends to increase, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, when inflation expectations fall, the 5-year swap rate tends to decrease, as investors are willing to accept lower returns.
Credit spreads, which represent the difference in yields between high-quality and low-quality bonds, are also closely related to the 5-year swap rate. Widening credit spreads, indicating increased credit risk, may lead to a higher 5-year swap rate, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the increased risk. Conversely, narrowing credit spreads may suggest a lower 5-year swap rate, as investors are willing to accept lower returns.
By comparing the 5-year swap rate to these indicators, investors and businesses can gain a more nuanced understanding of the economy and financial markets. For instance, a rising 5-year swap rate accompanied by a steepening yield curve and increasing inflation expectations may indicate a growing economy with rising interest rates. Conversely, a falling 5-year swap rate accompanied by a flattening yield curve and decreasing inflation expectations may suggest a slowing economy with decreasing interest rates.
Ultimately, understanding the relationships between the 5-year swap rate and other market indicators is crucial for making informed investment decisions, managing risk, and navigating the complex world of finance.
Managing Risk with the 5-Year Swap Rate
Risk management is a crucial aspect of investing and business operations, and the 5-year swap rate can play a vital role in this process. By understanding how to use the current 5-year swap rate to manage risk, investors and businesses can better navigate the complexities of the financial market.
One key strategy for managing risk with the 5-year swap rate is hedging. By entering into a swap agreement, investors and businesses can lock in a fixed interest rate, protecting themselves from potential future interest rate movements. For example, a company with a floating-rate loan can use a 5-year swap to fix its interest rate, reducing the risk of rising borrowing costs.
Speculation is another strategy that can be employed using the 5-year swap rate. Investors can take a position on the direction of interest rates, betting on whether the current 5-year swap rate will rise or fall. This can be done through various financial instruments, such as futures contracts or options.
Portfolio optimization is another key application of the 5-year swap rate in risk management. By analyzing the current 5-year swap rate and other market indicators, investors can optimize their portfolios to minimize risk and maximize returns. This can involve adjusting the allocation of assets, such as bonds and stocks, to take advantage of market opportunities and mitigate potential losses.
Monitoring the 5-year swap rate is essential for effective risk management. By tracking changes in the swap rate, investors and businesses can stay ahead of market developments and adjust their strategies accordingly. This can involve setting up alerts and notifications, as well as incorporating the swap rate into a broader market monitoring strategy.
Ultimately, the current 5-year swap rate is a valuable tool for managing risk in the financial market. By understanding how to use the swap rate to hedge, speculate, and optimize portfolios, investors and businesses can better navigate the complexities of the market and achieve their financial goals.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Tracking Changes in the 5-Year Swap Rate
Staying up-to-date with changes in the current 5-year swap rate is crucial for investors, businesses, and financial professionals. By tracking the swap rate, market participants can gain valuable insights into market sentiment, economic conditions, and potential future interest rate movements.
To stay ahead of the curve, it’s essential to access reliable and timely data on the 5-year swap rate. This can be achieved through various sources, including financial news websites, central banks, and financial data providers. By setting up alerts and notifications, market participants can receive real-time updates on changes in the swap rate, enabling them to respond quickly to market developments.
Incorporating the 5-year swap rate into a broader market monitoring strategy is also critical. This can involve tracking other key market indicators, such as the yield curve, inflation expectations, and credit spreads, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market. By analyzing these indicators in conjunction with the swap rate, market participants can identify trends, patterns, and potential risks and opportunities.
Additionally, staying informed about market news and events can help investors and businesses anticipate potential changes in the 5-year swap rate. This can include monitoring central bank policies, economic indicators, and geopolitical developments, which can all impact the swap rate.
By tracking changes in the current 5-year swap rate and incorporating it into a broader market monitoring strategy, investors and businesses can make more informed investment decisions, manage risk more effectively, and stay ahead of the curve in the rapidly changing financial market.
Ultimately, staying up-to-date with changes in the 5-year swap rate is essential for navigating the complexities of the financial market. By accessing reliable data, setting up alerts, and incorporating the swap rate into a broader market monitoring strategy, market participants can gain a competitive edge and achieve their financial goals.