Understanding the Mechanics of 3-Month SOFR Contracts
The Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) is a benchmark interest rate. It reflects the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by Treasury securities. SOFR has become an important benchmark. It is used in place of LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate). 3-month cme 3 month sofr futures contracts are vital tools. They help manage interest rate risk in the short-term money market. These contracts serve two primary purposes: hedging and speculation.
A futures contract is an agreement. It obligates the holder to buy or sell an asset at a predetermined future date and price. In the context of cme 3 month sofr futures, the underlying asset is the 3-month SOFR rate. The contract allows participants to lock in a future interest rate. This protects them from potential adverse movements. Hedgers, such as banks and corporations, use cme 3 month sofr futures. They mitigate the risk associated with fluctuating interest rates. Speculators, on the other hand, aim to profit from correctly predicting the direction of interest rate changes. They use cme 3 month sofr futures to implement their strategies.
Understanding key terms is essential for trading cme 3 month sofr futures. The ‘underlying asset’ is the 3-month SOFR rate itself. ‘Contract size’ refers to the notional amount of the underlying asset covered by a single futures contract. For CME’s 3-month SOFR futures, the contract size is typically $1 million. ‘Tick size’ is the minimum price increment by which the contract price can fluctuate. It is usually a fraction of a basis point. These specifications are standardized. This ensures transparency and liquidity in the cme 3 month sofr futures market. Traders must understand these mechanics. It enables them to effectively utilize cme 3 month sofr futures for hedging or speculative purposes.
How to Trade Short-Term SOFR Futures: A Practical Guide
Trading cme 3 month sofr futures requires a strategic approach and understanding of market mechanics. This guide provides a step-by-step overview for beginners. First, open a brokerage account with a firm that offers access to futures trading. Funding the account is the next step, ensuring sufficient capital for margin requirements. Margin is the amount of money required to open and maintain a futures position. It is not a down payment, but rather a performance bond. Next, thoroughly research cme 3 month sofr futures contracts. The CME Group’s website offers detailed contract specifications, including the contract size, tick size, and settlement procedures. Understanding these details is crucial for informed trading decisions.
Placing buy and sell orders is done through the brokerage platform. A buy order initiates a long position, betting that the price of cme 3 month sofr futures will increase. Conversely, a sell order initiates a short position, betting that the price will decrease. Several order types exist, including market orders (executed immediately at the best available price) and limit orders (executed only at a specified price or better). After placing an order, carefully monitor your positions. Keep an eye on market movements and be prepared to adjust your strategy as needed. Understanding margin calls is vital. If the market moves against your position, your broker may issue a margin call, requiring you to deposit additional funds to maintain the position.
Trading cme 3 month sofr futures involves inherent risks. Futures markets can be highly volatile, and significant losses are possible. It is essential to understand leverage, which magnifies both potential gains and losses. Before trading, consider your risk tolerance and financial situation carefully. Employ risk management techniques such as stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Diversification is also crucial. Avoid allocating a disproportionate amount of capital to a single trade or asset class. Remember that past performance is not indicative of future results. Continuously educate yourself about market dynamics and trading strategies to improve your chances of success in the cme 3 month sofr futures market. Trading futures is not suitable for all investors. Consult with a financial advisor before engaging in futures trading to determine if it aligns with your investment goals and risk profile. Always be aware that the price of cme 3 month sofr futures are affected by factors that influence interest rates.
The Role of SOFR Futures in Interest Rate Risk Management
Financial institutions and corporations leverage cme 3 month sofr futures as a critical tool to mitigate risks associated with fluctuating short-term interest rates. These futures contracts enable entities to hedge against potential adverse movements in interest rates, thereby providing greater financial stability and predictability. The cme 3 month sofr futures market offers a transparent and liquid platform for managing interest rate exposure.
Consider a bank with a substantial portfolio of floating-rate loans. As interest rates rise, the bank’s borrowing costs increase, potentially squeezing profit margins. To hedge this risk, the bank can sell cme 3 month sofr futures contracts. If interest rates indeed rise, the value of these futures contracts will decline, generating a profit that offsets the increased borrowing costs. Conversely, a corporation planning to issue commercial paper in the near future faces the risk of rising interest rates, which would increase its funding expenses. To hedge this risk, the corporation can buy cme 3 month sofr futures contracts. Should interest rates rise, the value of the futures contracts will increase, offsetting the higher costs of issuing commercial paper. These are examples of how cme 3 month sofr futures contracts are used.
Compared to other hedging instruments, such as interest rate swaps, cme 3 month sofr futures offer several advantages, especially for specific hedging needs. Futures contracts are traded on exchanges, providing greater transparency and liquidity. This exchange trading helps ensure fair pricing and reduces counterparty risk. They also offer greater flexibility in terms of contract size and expiration dates, allowing institutions to tailor their hedging strategies to their specific needs. Cme 3 month sofr futures also have lower transaction costs than some other hedging instruments. Financial institutions use cme 3 month sofr futures as a dynamic way to manage interest rate risk effectively. The transition from LIBOR to SOFR has further solidified the importance of cme 3 month sofr futures in the financial landscape.
Analyzing Factors Influencing Short-Term Interest Rate Markets
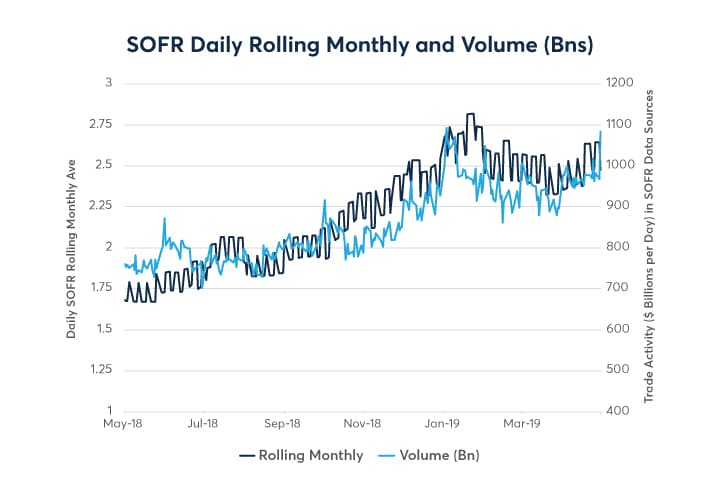
Understanding the forces that move short-term interest rates is crucial for successful trading in CME 3-month SOFR futures. Several key economic indicators and events exert significant influence on these markets. Central bank policy announcements, particularly those from the Federal Reserve, are paramount. Interest rate decisions made by the Fed directly impact the cost of borrowing and lending, creating ripples throughout the short-term interest rate landscape. Traders closely monitor these announcements and interpret the underlying economic rationale to anticipate future rate movements and their effect on CME 3-month SOFR futures.
Inflation data is another critical factor. Rising inflation typically prompts central banks to raise interest rates to curb spending and control price increases. Conversely, low inflation may lead to lower interest rates to stimulate economic activity. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth provides insights into the overall health of the economy. Strong GDP growth can lead to higher interest rates, while weak GDP growth may result in lower rates. Employment reports, including the monthly non-farm payrolls data, are also closely watched. A strong labor market can contribute to inflationary pressures, potentially leading to higher interest rates. Geopolitical events can also introduce volatility into short-term interest rate markets. Unexpected global events or political instability can create uncertainty and impact investor sentiment, causing fluctuations in CME 3-month SOFR futures prices. The CME 3-month SOFR futures market is very sensitive to all these factors, since it represents a consensus view of all market participants regarding the future level of short term rates.
Analyzing these factors requires a combination of fundamental and quantitative analysis. Traders use economic calendars to track upcoming data releases and policy announcements. They also employ quantitative tools, such as regression analysis and time series models, to identify patterns and predict future interest rate movements. These models often incorporate historical data on economic indicators and interest rate levels. Furthermore, analysis of the yield curve can offer insights into market expectations for future interest rate changes. An upward-sloping yield curve typically suggests that investors expect higher interest rates in the future, while a downward-sloping yield curve may indicate an anticipated economic slowdown and lower rates. By carefully monitoring these indicators, events, and using appropriate analytical tools, traders can make more informed trading decisions in the CME 3-month SOFR futures market and manage their interest rate risk more effectively.
Strategies for Trading CME 3-Month SOFR Futures Contracts
Several trading strategies can be employed when trading cme 3 month sofr futures. These strategies cater to different risk appetites and market views. Understanding these strategies is vital for success in the short-term interest rate market. Spread trading, trend following, and mean reversion represent a few popular approaches. Each offers unique opportunities and challenges for traders navigating the world of cme 3 month sofr futures.
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related cme 3 month sofr futures contracts. A common example is a calendar spread. This strategy capitalizes on expected changes in the yield curve. For instance, a trader might buy a contract expiring in June and sell one expiring in September. The expectation is that the price difference between the two contracts will widen or narrow. The rationale is based on anticipating shifts in the yield curve’s shape. These shifts reflect changing expectations for future interest rate movements. Calendar spreads can help reduce overall portfolio risk compared to outright directional bets. The trader is betting on the relationship between two contracts rather than the absolute level of interest rates. This strategy requires careful analysis of the yield curve and an understanding of how various factors can influence it. Sophisticated traders also make use of intermarket spreads, comparing sofr futures to other interest rate instruments.
Trend following is another popular approach. This strategy aims to identify and capitalize on established trends in cme 3 month sofr futures prices. Traders using this method often rely on technical indicators. These indicators might include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and MACD. When the price of cme 3 month sofr futures breaks above a key resistance level, a trend follower might buy the contract. The expectation is that the price will continue to rise. Conversely, if the price breaks below a support level, the trader might sell. Stop-loss orders are crucial for managing risk in trend-following strategies. These orders limit potential losses if the trend reverses. Mean reversion strategies operate on the assumption that prices will eventually revert to their average level. Traders identify overbought or oversold conditions using indicators like Bollinger Bands. When the price of cme 3 month sofr futures deviates significantly from its average, a mean reversion trader might take a position. The expectation is the price will return to the mean. These strategies require patience and disciplined risk management.
Comparing CME SOFR Futures to Alternative Interest Rate Products
CME 3-month SOFR futures offer a distinct avenue for managing short-term interest rate risk, but understanding their position relative to other instruments is crucial. Products such as Eurodollar futures, Treasury bill futures, and interest rate swaps serve similar, yet different, purposes. Eurodollar futures, once a dominant tool, have seen their prominence wane with the transition away from LIBOR. CME 3-month SOFR futures have emerged as a primary alternative, reflecting the market’s shift toward SOFR as a benchmark.
Treasury bill futures represent another option for managing short-term interest rate exposure. Unlike CME 3-month SOFR futures, which are based on a specific rate, Treasury bill futures are linked to the price of Treasury bills. This difference makes them sensitive to factors affecting the broader Treasury market, including government debt supply and demand. Interest rate swaps, on the other hand, are customized agreements between two parties to exchange interest rate cash flows. While swaps offer flexibility in terms of maturity and notional amount, they lack the transparency and liquidity of exchange-traded futures like the CME 3-month SOFR futures. The liquidity of CME 3-month SOFR futures is generally high, offering ease of entry and exit for market participants. Transparency is enhanced through exchange-based trading and readily available price data.
The transition from LIBOR to SOFR has significantly impacted the landscape of interest rate derivatives. Regulatory changes and concerns about LIBOR’s reliability spurred the adoption of SOFR. This shift has led to increased focus and liquidity in CME 3-month SOFR futures. Each product carries its own risk profile. CME 3-month SOFR futures are subject to market risk, basis risk (the risk that the futures price does not perfectly track the underlying SOFR rate), and counterparty risk (though this is mitigated by exchange clearing). The regulatory environment also plays a crucial role. Regulations governing margin requirements, position limits, and reporting obligations can affect the attractiveness and usability of these instruments. Weighing these factors is essential when selecting the most appropriate tool for managing interest rate risk. The cme 3 month sofr futures are becoming increasingly important.
Understanding Contract Specifications and Market Conventions for CME 3-Month SOFR Futures
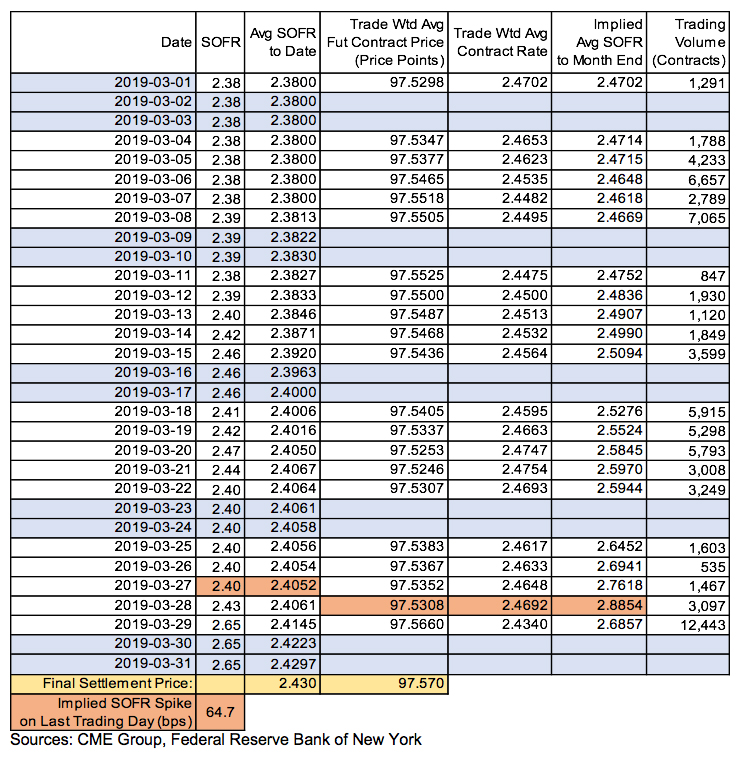
A detailed understanding of contract specifications is crucial for anyone trading CME 3-month SOFR futures. The Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) provides comprehensive details on its website regarding these contracts. Key specifications include the contract size, which represents the notional amount of the underlying instrument. The tick size defines the minimum price fluctuation. For CME 3-month SOFR futures, this is a fraction of a percentage point. Understanding these specifications is essential for calculating potential profits and losses. The delivery method and settlement procedures are also important. CME 3-month SOFR futures are cash-settled, meaning no physical delivery of an underlying asset occurs. Instead, the final settlement price is based on the prevailing SOFR rate at the contract’s expiration.
Market conventions dictate how CME 3-month SOFR futures are traded. Trading hours align with global financial markets. These hours allow participation from various time zones. Awareness of these hours helps traders plan their strategies. Open interest and volume are key indicators of contract liquidity. Open interest reflects the total number of outstanding contracts. Volume represents the number of contracts traded in a given period. High open interest and volume suggest a liquid market, facilitating easier order execution for cme 3 month sofr futures. Real-time updates and contract information are available on the CME’s official website and through their API. Traders can access this data to stay informed about market conditions and make timely decisions. Understanding the order book dynamics, including bid and ask prices, is also critical for successful trading. Understanding these market indicators allows the trader to have better knowledge when trading cme 3 month sofr futures.
Furthermore, familiarity with market conventions extends to understanding the implied yield curve and how it impacts cme 3 month sofr futures pricing. Changes in the yield curve can signal shifts in market expectations for future interest rate movements. These movements affect the value of SOFR futures contracts. Traders often employ strategies based on anticipated shifts in the yield curve. These strategies use tools such as calendar spreads, which involve simultaneously buying and selling contracts with different expiration dates. Understanding the regulatory environment is also crucial. Regulations can impact trading activity and market behavior. Monitoring regulatory announcements and changes ensures compliance and informed decision-making. These features are critical when understanding the full product of cme 3 month sofr futures.
The Future of Short-Term Interest Rate Benchmarks
The landscape of short-term interest rate benchmarks is constantly evolving. Innovation in SOFR-based derivatives continues to emerge. The market may see further advancements in the future. These advancements could include the introduction of new contract expirations for CME 3-month SOFR futures. Algorithmic trading strategies may also become more prevalent for CME 3-month SOFR futures.
Several factors influence the direction of short-term interest rate benchmarks. Alternative benchmarks to SOFR are also under development. Regulatory changes could influence these benchmarks. The current regulatory landscape plays a vital role in shaping the future of these rates. Traders should monitor regulatory updates to understand the implications for trading strategies in CME 3-month SOFR futures. The adoption of SOFR is still unfolding. Its global integration faces challenges and opportunities. Further prospects involve broader international acceptance and standardization of SOFR. This includes increased liquidity and participation in CME 3-month SOFR futures from global investors.
Trading CME 3-month SOFR futures offers significant benefits, but it also poses challenges. Participants in the global financial system must understand these elements. CME 3-month SOFR futures play a crucial role in managing interest rate risk. They also facilitate price discovery in short-term money markets. As the transition from LIBOR progresses, SOFR’s importance will likely increase. Ongoing innovation and adaptation are required to navigate the complexities of the interest rate market. Participants should stay informed on market developments and regulatory changes for CME 3-month SOFR futures.