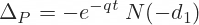Understanding the Black-Scholes Formula
The Black-Scholes formula is a cornerstone of option pricing. It provides a theoretical price for European-style options, based on several key variables. These variables are: the current stock price (S), the strike price (K), the time to expiration (T), the volatility of the underlying asset (σ), the risk-free interest rate (r), and the dividend yield (q). Understanding each variable is crucial for accurate option pricing using the black and scholes formula excel.
The stock price (S) represents the current market price of the underlying asset. The strike price (K) is the price at which the option can be exercised. Time to expiration (T) is the time remaining until the option expires. Volatility (σ) measures the fluctuation of the underlying asset’s price, a crucial factor influencing option value. The risk-free interest rate (r) reflects the return from a risk-free investment, such as a government bond. Finally, the dividend yield (q) accounts for any dividends paid on the underlying asset during the option’s life. The black and scholes formula excel implementation requires precise input of these variables. Incorrect inputs lead to inaccurate pricing.
The formula itself is a complex mathematical equation. While a visual representation is helpful, a simplified explanation is vital for understanding. The formula essentially calculates the present value of the expected payoff from the option, considering the probability of the stock price moving above or below the strike price. The higher the volatility, the higher the probability of significant price movements, thus affecting option pricing. Using the black and scholes formula excel enables efficient calculation of this complex formula. The ease of use and accessibility of Excel makes it a popular choice for option pricing calculations. The formula incorporates various mathematical functions like logarithms (ln), exponentials (exp), and the cumulative standard normal distribution (NORMSDIST), all readily available in Excel. Mastering these functions is crucial for accurate implementation of the black and scholes formula excel.
Why Use Excel for Black-Scholes Calculations?
Excel offers significant advantages for implementing the Black and Scholes formula excel. Its accessibility makes it an ideal tool for both beginners and experienced professionals. Users familiar with spreadsheet software can quickly grasp the process. The software’s intuitive interface simplifies complex calculations. Furthermore, Excel’s ability to handle large datasets efficiently streamlines the analysis of multiple scenarios. This is particularly valuable when testing different parameters within the black and scholes formula excel. The flexibility of Excel allows for easy modification of variables, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of their impact on option pricing.
Compared to programming languages like Python or R, Excel provides a more user-friendly environment for implementing the black and scholes formula excel. While programming languages offer greater power and flexibility, they require a steeper learning curve. Excel’s ease of use reduces the time and effort needed to perform the calculations. This allows for a quicker understanding of the model’s mechanics. Moreover, the visual representation of data in Excel aids comprehension. Users can easily track changes in variables and their corresponding effects on the final option price. This visual clarity is particularly beneficial for interpreting results and making informed decisions.
The black and scholes formula excel implementation in Excel also excels in its capacity for sensitivity analysis. Users can easily modify input variables to observe their impact on the option price. This feature is crucial for risk management and understanding the model’s limitations. Excel’s built-in charting capabilities further enhance its utility. Users can create graphs to visualize the relationship between variables and option prices. This visual representation improves understanding and facilitates communication of findings. In summary, Excel provides a powerful yet accessible platform for mastering the black and scholes formula excel, ideal for both introductory explorations and advanced applications.
How to Implement the Black-Scholes Model in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
Implementing the black and scholes formula excel is straightforward. First, gather your inputs: stock price (S), strike price (K), time to expiration (T, in years), volatility (σ, as a decimal), risk-free rate (r, as a decimal), and dividend yield (q, as a decimal). Organize these in separate cells within your Excel spreadsheet for easy reference. This structured approach enhances clarity and simplifies the application of the black and scholes formula excel.
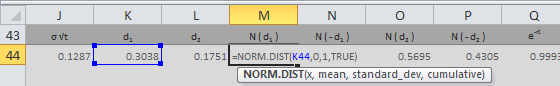
Next, utilize Excel’s built-in functions to calculate intermediate values. The cumulative standard normal distribution function, NORMSDIST, is crucial. Calculate d1 = [ln(S/K) + (r – q + σ^2/2) * T] / (σ * sqrt(T)) and d2 = d1 – σ * sqrt(T). Remember to use the correct cell references in your formulas. The EXP function calculates e^x, and LN calculates the natural logarithm. These functions are essential for accurate black and scholes formula excel implementation. Screenshots illustrating these steps would greatly benefit visual learners. Pay close attention to the order of operations; Excel follows standard mathematical precedence rules.
Finally, calculate the option price. For a call option, the black and scholes formula excel is: C = S * NORMSDIST(d1) – K * EXP(-r * T) * NORMSDIST(d2). For a put option, the formula is: P = K * EXP(-r * T) * NORMSDIST(-d2) – S * NORMSDIST(-d1). Input the calculated values of d1 and d2 into these formulas, ensuring correct cell referencing. The resulting values represent the theoretical price of the call and put options, respectively, based on the black and scholes formula excel. This step concludes the calculation process, providing the final option price based on the inputs and the black and scholes formula excel. Accurate data entry is paramount to obtain reliable results using the black and scholes formula excel.
Dealing with Volatility: Estimating and Interpreting Standard Deviation
Volatility is a crucial input in the Black-Scholes formula excel. It represents the standard deviation of the stock’s returns and measures the price’s fluctuation over time. Higher volatility implies greater uncertainty, leading to higher option prices. Accurately estimating volatility is vital for obtaining reliable option prices using the black and scholes formula excel. Several methods exist for estimating historical volatility, a common approach involves calculating the standard deviation of the stock’s logarithmic returns over a specific historical period. In Excel, this can be achieved using the STDEV function on a series of logarithmic returns. To calculate logarithmic returns, take the natural logarithm of the ratio of consecutive closing prices. The choice of historical period significantly impacts the volatility estimate. A longer period might smooth out short-term fluctuations, providing a more stable estimate. However, it may not reflect recent market changes. Conversely, a shorter period captures recent volatility more accurately, but it may be susceptible to noise and less reliable for longer-term option pricing.
Using Excel to estimate historical volatility for the black and scholes formula excel involves several steps. First, collect historical closing prices for the underlying asset. Then, calculate the daily logarithmic returns using the LN function in Excel. The formula would be =LN(Today’s Price/Yesterday’s Price). Next, apply the STDEV function to this series of logarithmic returns. The resulting value represents the historical volatility. Remember to annualize this figure by multiplying it by the square root of the number of trading days in a year (typically 252). Understanding the limitations of historical volatility is essential. It is a backward-looking measure and does not perfectly predict future volatility. External factors, unforeseen events, or market shifts can significantly alter the actual volatility. Consequently, the option prices derived from the black and scholes formula excel might deviate from the market prices. Option traders frequently adjust their volatility inputs based on market expectations and implied volatility derived from option market prices. This adds a layer of complexity and emphasizes the importance of understanding volatility’s significance in option pricing.
Interpreting the standard deviation, as an estimate of volatility, is critical in the context of the black and scholes formula excel. A higher standard deviation indicates greater price fluctuations, implying higher risk and, in turn, higher option premiums. Conversely, lower standard deviation suggests lower price fluctuations, resulting in lower risk and lower option premiums. The black and scholes formula excel directly incorporates this volatility estimate into the calculation, making it a pivotal factor in determining option value. The relationship between volatility and option price is not linear; it is more complex. Small changes in volatility can cause significant changes in option prices, particularly for options with longer times to expiration. Therefore, accurately estimating and interpreting volatility is paramount for effective option pricing using the black and scholes formula excel. Different volatility estimates significantly alter option prices derived from the black and scholes formula excel; hence, understanding these variations is vital for informed decision-making.
Interpreting the Results: Understanding Option Pricing Outputs
The Black-Scholes formula in Excel provides a calculated option price. This price represents the theoretical value of the option contract based on the inputs provided. Understanding this output is crucial for making informed investment decisions. The model’s output reflects the fair price for a given option, considering factors like the underlying asset’s price, volatility, time until expiration, and interest rates. Remember that this is a theoretical price; the actual market price might differ due to various market factors. Accurate application of the black and scholes formula excel is key to obtaining meaningful results. Using the black and scholes formula excel effectively requires careful consideration of all inputs.
Call options grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy the underlying asset at the strike price before expiration. A higher calculated call price using the black and scholes formula excel suggests the option is more valuable, reflecting a higher probability the underlying asset’s price will rise above the strike price before expiration. Conversely, a lower price suggests a lower probability. Put options grant the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. A higher calculated put price indicates a greater likelihood the asset’s price will fall below the strike price before the option expires. The black and scholes formula excel calculations are used to assess the value of both call and put options. The precision of the price prediction depends greatly on the accuracy of the input parameters in the black and scholes formula excel.
The calculated option price from the black and scholes formula excel serves as a benchmark for investment decisions. Investors compare this theoretical price to the market price to identify potential mispricings. A discrepancy between the theoretical and market price might indicate an arbitrage opportunity, though market inefficiencies and other factors can affect actual prices. Therefore, while the black and scholes formula excel is a powerful tool, investors should always use it in conjunction with other analytical methods and their own risk assessment. Remember that accurate interpretation of the black and scholes formula excel output depends on the reliability and precision of the input data. Using the black and scholes formula excel should be part of a broader strategy, not solely relied upon for investment decisions. The calculated price provides valuable insights, aiding informed decision making, but should not be the sole basis for investment choices.
Advanced Applications of the Black-Scholes Model in Excel
Beyond basic option pricing, the Black-Scholes formula in Excel enables sophisticated analyses. One powerful application is sensitivity analysis, often referred to as calculating the “Greeks.” These metrics quantify an option’s price sensitivity to changes in underlying variables. Delta measures the change in option price per one-unit change in the underlying asset’s price. Gamma reflects the rate of change in delta. Theta shows the daily time decay of the option’s value. Vega indicates sensitivity to volatility changes. Finally, Rho measures the impact of changes in the risk-free interest rate. Excel’s functionality allows for easy calculation of these Greeks, providing a comprehensive understanding of option risk and potential profit/loss. This deep dive into the black and scholes formula excel capabilities empowers users to make more informed trading decisions.
Another advanced application involves creating dynamic pricing models. Users can build Excel spreadsheets that automatically update option prices based on real-time market data. This requires linking the spreadsheet to external data feeds, a feature easily implemented in Excel. By incorporating functions that automatically fetch current stock prices, volatility measures, and time to expiry, users create a powerful tool for real-time option valuation. This enhances the black and scholes formula excel’s practicality and extends its utility beyond simple, static calculations. The ability to model various market scenarios and their impact on option pricing adds significant value to investment strategies.
Furthermore, the black and scholes formula excel can be extended to accommodate more complex option types beyond basic European calls and puts. While the core formula might need adjustments, Excel’s flexibility allows for the incorporation of factors like early exercise possibilities (for American options) or adjustments for dividends. This adaptability makes the black and scholes formula excel a versatile tool for a wide range of option pricing challenges. By combining the power of Excel’s computational capabilities with the core principles of the Black-Scholes model, users can achieve sophisticated analyses previously only accessible through dedicated financial software or programming.
Troubleshooting Common Errors in Excel Black-Scholes Implementations
Implementing the Black and Scholes formula in Excel can present several challenges. Incorrect input of variables is a frequent source of error. Double-check all data entries, ensuring accuracy in stock prices, strike prices, time to expiration (expressed in years), risk-free interest rate, volatility, and dividend yield. Units must be consistent throughout the calculation. Using the wrong cell references in formulas is another common mistake. Carefully review all formulas, paying close attention to cell referencing. Excel’s error-checking tools can help identify such issues. The Black and Scholes formula relies heavily on the NORMSDIST function. Ensure this function is used correctly and that the input argument is appropriately scaled. Incorrect interpretation of results is also possible. Understand that the Black-Scholes model provides a theoretical price; actual market prices may differ. The model’s assumptions—such as constant volatility and efficient markets—may not always hold true in real-world scenarios. Always consider the limitations of the model.
Another potential problem relates to volatility estimation. The accuracy of the Black and Scholes formula depends heavily on a precise volatility estimate. Using historical data, ensure the period used for volatility calculation is relevant to the option’s timeframe. An excessively short or long period can lead to inaccurate results. The method used for calculating volatility—standard deviation of logarithmic returns—must be correctly applied. Small errors in the calculation of standard deviation can significantly impact the final option price. Remember, volatility is an estimate, not a precise figure. Understand that different volatility estimates will produce different option prices. The model’s sensitivity to volatility changes underscores the need for careful estimation. Understanding the limitations of your volatility estimation method is crucial for interpreting the results effectively when using the black and scholes formula excel.
Formula errors are another frequent issue. The Black and Scholes formula involves several nested functions. Errors in the order of operations or incorrect function arguments can lead to incorrect results. Excel’s formula auditing tools help identify these errors. Pay close attention to parentheses and function arguments. Using the wrong functions—for example, using NORM.S.DIST instead of NORMSDIST in older Excel versions—can yield significant inaccuracies. Excel’s built-in help can clarify function usage and syntax. When working with the black and scholes formula excel, remember to double check your formula carefully. Test your implementation with known values to validate your formula’s accuracy before applying it to real-world data. Documenting each step of your calculations also helps catch mistakes and promotes understanding.
Practical Examples and Case Studies: Applying Black-Scholes to Real-World Scenarios
To solidify understanding of the black and scholes formula excel implementation, consider these practical examples. First, imagine pricing a European call option on a stock currently trading at $100. The strike price is $105, with 6 months until expiration. Assume a risk-free rate of 2% per annum and a volatility of 20%. Using the black and scholes formula excel functions detailed earlier, one can calculate the theoretical price of this option. This process demonstrates how the black and scholes formula excel model translates market inputs into a price prediction.
Next, let’s examine a scenario involving a put option. Suppose a company’s stock is priced at $50, and an investor wants to price a put option with a strike price of $45 and three months to expiry. The risk-free rate remains at 2%, but the volatility has decreased to 15%. The application of the black and scholes formula excel will yield a different price compared to the call option example due to the differing option type and volatility. This illustrates the sensitivity of option prices to these inputs. Remember, accurate volatility estimation is crucial for reliable pricing using the black and scholes formula excel.
Finally, consider a slightly more complex scenario, incorporating dividends. A stock trading at $75 pays an annual dividend yield of 3%. An investor needs to price a European call option with a strike price of $80 and nine months to expiration. The risk-free rate is still 2%, and volatility is estimated at 25%. This example showcases how the black and scholes formula excel handles dividends, a factor that affects option pricing. By adjusting the formula to account for the dividend yield, a more accurate option price is derived. These examples, coupled with a thorough understanding of the black and scholes formula excel, empower users to confidently price options under varying market conditions.