What are Money Market Deposit Accounts?
Money market deposit accounts are a type of savings account that offers a unique combination of liquidity, low risk, and competitive interest rates. These accounts are designed to provide individuals and businesses with a safe and flexible way to manage their short-term financial needs. Unlike traditional savings accounts, money market deposit accounts often come with debit cards, checks, and online banking capabilities, making it easy to access funds when needed. Additionally, they typically offer higher interest rates than traditional savings accounts, making them an attractive option for those seeking to earn a return on their deposits. With their low-risk profile and competitive yields, money market deposit accounts have become a popular choice for individuals and businesses alike. In fact, money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, which are monetary aggregates that play a crucial role in the economy. Understanding the differences between these aggregates and how money market deposit accounts fit into them can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
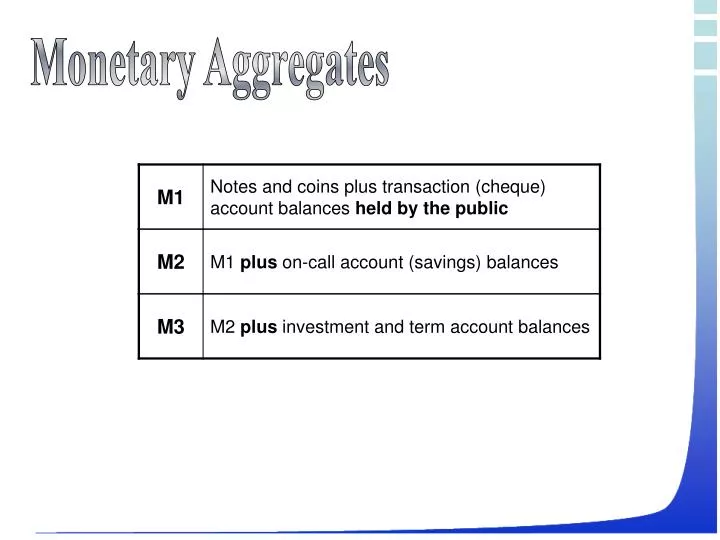
Understanding the Monetary Aggregates: M1 and M2
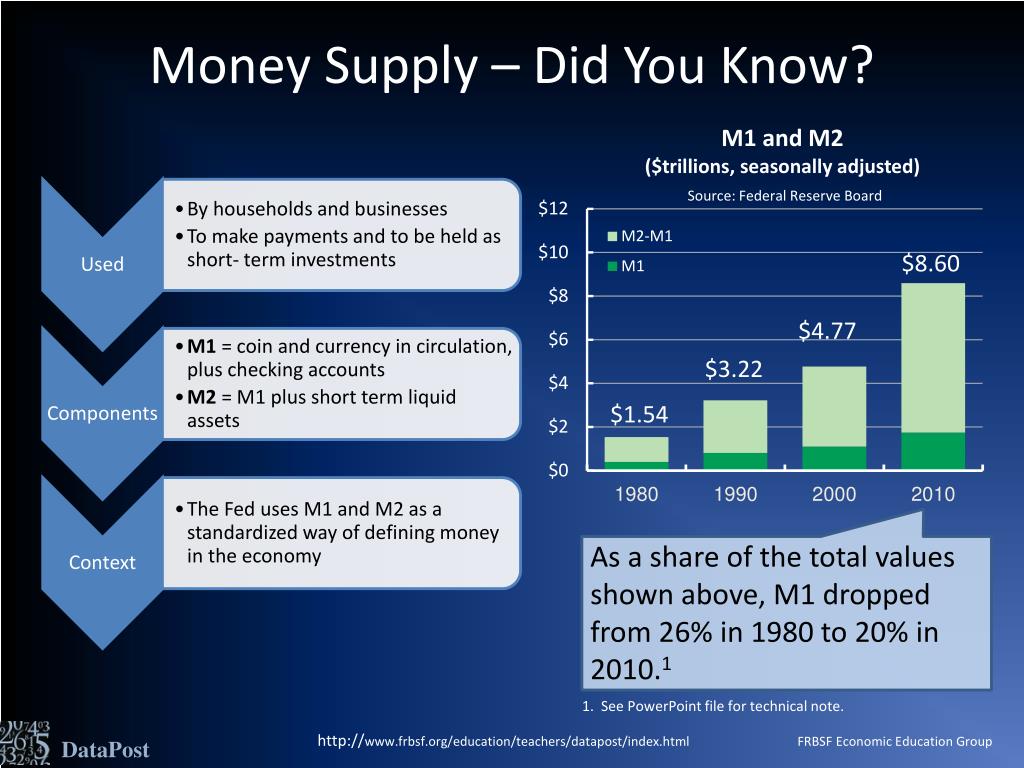
Monetary aggregates, specifically M1 and M2, play a vital role in the economy by measuring the money supply and influencing monetary policy decisions. M1, also known as the narrow money aggregate, consists of physical currency, demand deposits, and other liquid assets that can be easily converted into cash. On the other hand, M2, or the broad money aggregate, includes M1 plus savings deposits, time deposits, and money market funds. Understanding the components of each aggregate is crucial in grasping their significance in the economy. Central banks use these aggregates to set monetary policy, regulate the money supply, and maintain economic stability. In the context of money market deposit accounts, understanding M1 and M2 is essential, as these accounts can be included in either aggregate, depending on their characteristics. Money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, and their classification has implications for the overall economy and monetary policy.
How to Determine if Your Deposit Account is Part of M1 or M2
To determine whether a money market deposit account is included in M1 or M2, it’s essential to understand the criteria used by central banks to classify deposits into these aggregates. The key factors to consider are the account’s liquidity, accessibility, and interest rate structure. Accounts with high liquidity, easy accessibility, and competitive interest rates are more likely to be included in M1, while those with lower liquidity and more restrictive access may be classified as M2. Additionally, central banks consider the account’s purpose, such as whether it’s used for transactional or savings purposes. Money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2 based on their characteristics, and understanding these criteria can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their financial strategies. By examining the account’s features and purpose, it’s possible to determine whether it’s part of M1 or M2, and how it contributes to the overall money supply and economy.
The Role of Money Market Deposit Accounts in M1 and M2
Money market deposit accounts play a significant role in the composition of M1 and M2, as they contribute to the overall money supply and influence the economy. These accounts, which are included in M1 or M2, provide liquidity to the financial system, enabling individuals and businesses to access funds when needed. The inclusion of money market deposit accounts in M1 or M2 also affects the monetary policy decisions of central banks, as they consider the aggregate money supply when setting interest rates and regulating the economy. Furthermore, money market deposit accounts help to stabilize the financial system by providing a safe and liquid place for individuals and businesses to park their funds. As a result, they play a crucial role in maintaining economic stability and promoting growth. By understanding the role of money market deposit accounts in M1 and M2, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their financial strategies and optimize their use of these accounts.
Benefits of Money Market Deposit Accounts in M1 and M2
Having a money market deposit account included in M1 or M2 offers several benefits to individuals and businesses. One of the primary advantages is increased liquidity, as these accounts provide easy access to funds when needed. Additionally, money market deposit accounts are generally considered low-risk, making them an attractive option for those seeking to minimize risk. Furthermore, accounts included in M1 or M2 often offer competitive interest rates, providing the potential for higher returns on deposits. Another benefit is the flexibility to write checks, use debit cards, or make online transfers, making it easy to manage daily financial transactions. Moreover, money market deposit accounts are typically insured, providing an additional layer of security for depositors. By understanding the benefits of having a money market deposit account included in M1 or M2, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their financial strategies and optimize their use of these accounts. As money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, they play a crucial role in the overall economy, and their benefits can have a significant impact on financial stability and growth.
Comparing Money Market Deposit Accounts: M1 vs M2
When it comes to money market deposit accounts, understanding the differences between those included in M1 and M2 is crucial. Money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2 based on their characteristics and features. Accounts included in M1 are typically more liquid and have lower minimum balance requirements, making them more accessible to individuals and businesses. In contrast, accounts included in M2 may have higher minimum balance requirements and may offer higher interest rates, but may also come with more restrictions on withdrawals. In terms of risk profiles, accounts included in M1 are generally considered lower-risk, while those in M2 may carry slightly higher risk due to the potential for fluctuations in interest rates. Furthermore, money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2 based on the level of transactional activity, with M1 accounts allowing for more frequent transactions. By understanding the differences between money market deposit accounts included in M1 and M2, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their financial strategies and optimize their use of these accounts. As money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, they play a crucial role in the overall economy, and their differences can have a significant impact on financial stability and growth.
Impact of Monetary Policy on Money Market Deposit Accounts
Monetary policy decisions, such as changes in interest rates, have a significant impact on money market deposit accounts and their inclusion in M1 or M2. When central banks adjust interest rates, it affects the entire economy, including the money market deposit accounts. For instance, a decrease in interest rates can make borrowing cheaper, leading to an increase in money supply and, consequently, an expansion of M2. On the other hand, an increase in interest rates can reduce borrowing, leading to a decrease in money supply and a contraction of M2. Money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2 based on their characteristics, and changes in interest rates can influence the classification of these accounts. For example, a decrease in interest rates may lead to a shift of deposits from M2 to M1, as individuals and businesses seek more liquid and lower-risk options. Conversely, an increase in interest rates may lead to a shift of deposits from M1 to M2, as individuals and businesses seek higher returns. Understanding the impact of monetary policy on money market deposit accounts is crucial for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their financial strategies and optimize their use of these accounts. As money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, they play a vital role in the overall economy, and their response to monetary policy decisions can have a significant impact on financial stability and growth.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of Money Market Deposit Accounts
In conclusion, understanding money market deposit accounts and their role in M1 and M2 is crucial for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their financial strategies. By grasping the unique features of money market deposit accounts, such as liquidity, low risk, and competitive interest rates, individuals and businesses can optimize their use of these accounts and navigate the complex world of monetary aggregates. Money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2 based on their characteristics, and understanding the differences between these aggregates can help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their financial strategies. As money market deposit accounts are included in M1 or M2, they play a vital role in the overall economy, and their response to monetary policy decisions can have a significant impact on financial stability and growth. By recognizing the significance of money market deposit accounts in M1 and M2, individuals and businesses can unlock the secrets of these accounts and make the most of their financial opportunities.