Understanding the True Cost of Borrowing
In the world of finance, making informed decisions is crucial to achieving success. One essential aspect of this is understanding the true cost of borrowing, which involves calculating the pretax cost of debt. This metric is vital for businesses and individuals alike, as it helps them evaluate the feasibility of various debt financing options and make informed decisions about their financial strategies. The pretax cost of debt differs significantly from the post-tax cost of debt, which takes into account the tax benefits of borrowing. By grasping the pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can better navigate the complex landscape of debt financing and optimize their financial performance. To calculate pretax cost of debt effectively, it’s essential to understand the underlying concepts and variables involved, which will be discussed in the following sections.
How to Calculate the Pretax Cost of Debt: A Step-by-Step Approach
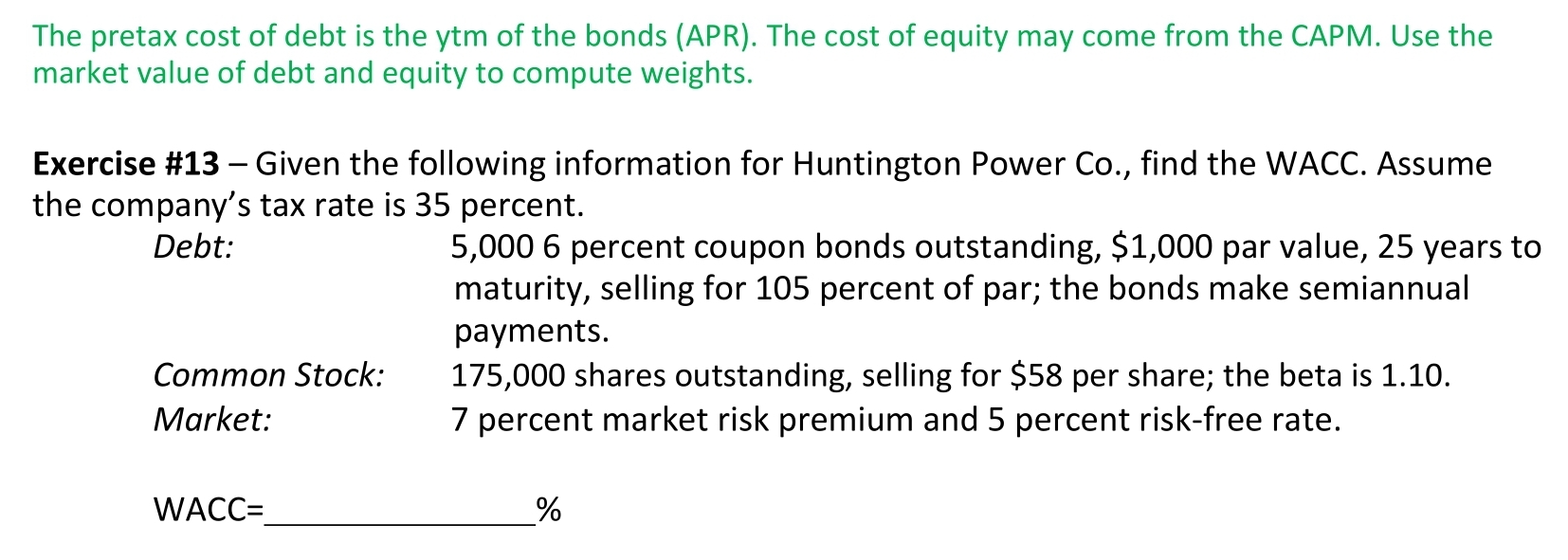
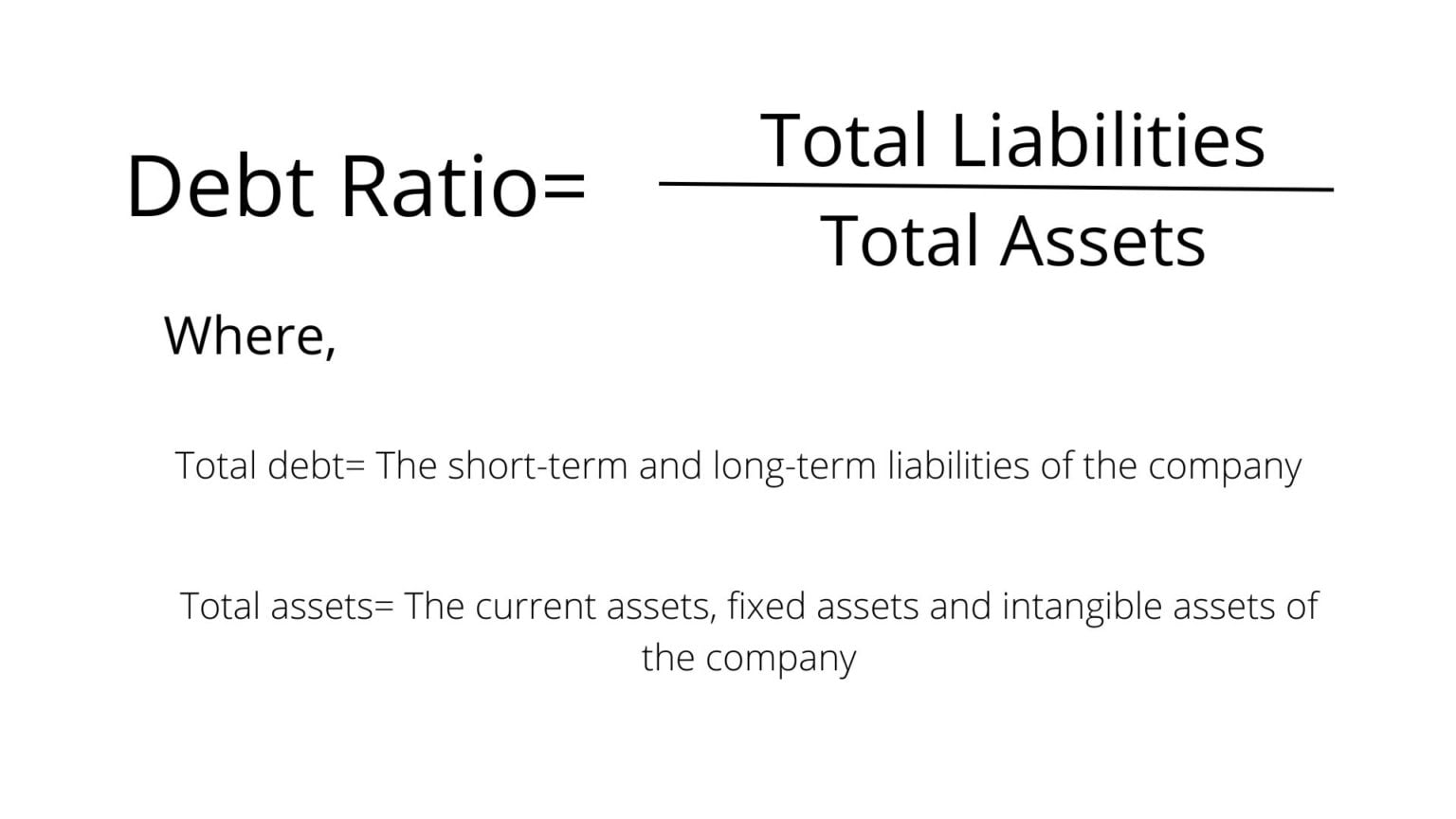
Calculating the pretax cost of debt is a crucial step in making informed financial decisions. To calculate pretax cost of debt, you need to understand the underlying formulas and variables involved. The pretax cost of debt is typically calculated using the following formula: Pretax Cost of Debt = (Interest Expense / Total Debt) x (1 – Tax Rate). In this formula, interest expense represents the total interest paid on the debt, total debt is the outstanding principal amount, and tax rate is the applicable tax rate. For instance, if a company has an interest expense of $10,000, total debt of $100,000, and a tax rate of 25%, the pretax cost of debt would be 10%. This means that for every dollar borrowed, the company is paying 10 cents in interest before taxes. By understanding how to calculate pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can better evaluate the feasibility of various debt financing options and make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
The Impact of Interest Rates on Pretax Cost of Debt
Interest rates play a crucial role in determining the pretax cost of debt. When interest rates rise, the pretax cost of debt increases, making borrowing more expensive. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the pretax cost of debt decreases, making borrowing more affordable. For instance, if a company borrows $100,000 at an interest rate of 8%, the pretax cost of debt would be 8%. However, if interest rates rise to 10%, the pretax cost of debt would increase to 10%, resulting in higher borrowing costs. To illustrate the impact of interest rates on pretax cost of debt, consider a real-world example. During the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to stimulate economic growth. As a result, the pretax cost of debt decreased, making it easier for businesses and individuals to borrow money. In contrast, during periods of high inflation, interest rates tend to rise, increasing the pretax cost of debt and making borrowing more expensive. By understanding the relationship between interest rates and pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can better navigate the complex landscape of debt financing and make informed decisions about their financial strategies. To calculate pretax cost of debt effectively, it’s essential to consider the impact of interest rates on borrowing costs.
Debt Financing Options: Weighing the Pros and Cons
When it comes to debt financing, individuals and businesses have various options to choose from, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding the pros and cons of each option is crucial in making informed financial decisions. One of the key factors to consider is the pretax cost of debt, which varies across different debt financing options. For instance, loans typically offer a fixed interest rate and a set repayment period, making it easier to calculate the pretax cost of debt. On the other hand, credit cards often come with variable interest rates and fees, making it more challenging to determine the pretax cost of debt. Bonds, another popular debt financing option, offer a fixed interest rate and a longer repayment period, resulting in a lower pretax cost of debt. To calculate pretax cost of debt effectively, it’s essential to understand the characteristics of each debt financing option and how they impact borrowing costs. By weighing the pros and cons of each option, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their debt financing strategies and optimize their financial performance. For example, a company may choose to issue bonds to finance a large-scale project, taking advantage of the lower pretax cost of debt. On the other hand, an individual may opt for a personal loan to consolidate debt, reducing the overall pretax cost of debt. By considering the pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their debt financing options and achieve their financial goals.
The Role of Credit Ratings in Determining Pretax Cost of Debt
Credit ratings play a significant role in determining the pretax cost of debt for individuals and businesses alike. A good credit score can lead to lower borrowing costs, while a poor credit score can result in higher interest rates and increased pretax cost of debt. This is because lenders view borrowers with good credit scores as less risky, and therefore, offer more favorable loan terms. On the other hand, borrowers with poor credit scores are considered riskier, and lenders charge higher interest rates to compensate for the increased risk. For instance, a company with a high credit rating may be able to borrow at an interest rate of 5%, resulting in a lower pretax cost of debt. In contrast, a company with a low credit rating may be forced to borrow at an interest rate of 10%, resulting in a higher pretax cost of debt. To calculate pretax cost of debt effectively, it’s essential to consider the impact of credit ratings on borrowing costs. By maintaining a good credit score, individuals and businesses can reduce their pretax cost of debt and achieve their financial goals. For example, a business may focus on improving its credit score by paying its debts on time and reducing its debt-to-equity ratio, resulting in lower borrowing costs and a reduced pretax cost of debt. By understanding the role of credit ratings in determining pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their debt financing strategies and optimize their financial performance.
Managing Debt Effectively: Strategies for Reducing Pretax Cost
Effective debt management is crucial for reducing the pretax cost of debt and achieving financial goals. By implementing the right strategies, individuals and businesses can minimize their borrowing costs and optimize their financial performance. One effective strategy for reducing pretax cost of debt is debt consolidation, which involves combining multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This can simplify the repayment process and reduce the overall cost of borrowing. Another strategy is refinancing, which involves replacing an existing loan with a new loan at a lower interest rate. This can be particularly effective in a low-interest-rate environment, where borrowers can take advantage of lower borrowing costs. Negotiating with lenders is also an effective strategy for reducing pretax cost of debt. By building a strong relationship with lenders and demonstrating a good credit history, borrowers can negotiate more favorable loan terms, including lower interest rates and fees. Additionally, borrowers can consider debt restructuring, which involves modifying the terms of an existing loan to reduce the pretax cost of debt. This can include extending the repayment period, reducing the interest rate, or waiving certain fees. By understanding how to calculate pretax cost of debt and implementing these strategies, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions about their debt financing options and achieve their financial goals. For instance, a company may use debt consolidation to reduce its pretax cost of debt and free up capital for investment opportunities. By managing debt effectively, individuals and businesses can reduce their pretax cost of debt and achieve long-term financial success.
Real-World Applications of Pretax Cost of Debt Calculation
In the real world, calculating the pretax cost of debt is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Many businesses and individuals have used pretax cost of debt calculations to evaluate investment opportunities, optimize capital structure, and achieve their financial goals. For instance, a company like Amazon may calculate the pretax cost of debt to determine the feasibility of a new project. By calculating the pretax cost of debt, Amazon can determine whether the project’s expected returns justify the borrowing costs. Similarly, an individual may calculate the pretax cost of debt to decide whether to take out a mortgage to purchase a new home. By understanding the pretax cost of debt, the individual can determine whether the benefits of homeownership outweigh the borrowing costs. Another example is a startup company that needs to calculate the pretax cost of debt to determine the best financing option for its business. By calculating the pretax cost of debt, the startup can compare the costs of different debt financing options, such as loans and bonds, and choose the option that best aligns with its financial goals. In each of these cases, calculating the pretax cost of debt is essential for making informed financial decisions and achieving long-term financial success. By understanding how to calculate pretax cost of debt, businesses and individuals can make informed decisions about their debt financing options and achieve their financial goals.
Conclusion: Mastering the Pretax Cost of Debt for Financial Success
In conclusion, understanding and calculating the pretax cost of debt is crucial for achieving financial goals and making informed decisions. By grasping the concepts outlined in this guide, businesses and individuals can unlock the secrets of debt financing and make informed decisions about their debt financing options. Whether it’s evaluating investment opportunities, optimizing capital structure, or managing debt effectively, calculating the pretax cost of debt is essential for financial success. By following the step-by-step approach to calculating the pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can gain a deeper understanding of the true cost of borrowing and make informed decisions that drive long-term financial success. Remember, calculating the pretax cost of debt is not a one-time task, but an ongoing process that requires regular monitoring and adjustment. By mastering the pretax cost of debt, individuals and businesses can navigate the complex world of debt financing with confidence and achieve their financial goals.