What are Prepaid Expenses and Why Do They Matter?
In financial reporting, prepaid expenses represent a crucial aspect of a company’s assets. They are payments made in advance for goods or services that have not yet been received. To accurately reflect a company’s financial position, it is essential to understand prepaid expenses and how they differ from other types of assets and liabilities. Unlike accounts receivable or accounts payable, prepaid expenses are not directly related to a company’s daily operations. Instead, they represent a prepayment for a future benefit, such as rent, insurance, or subscription services. Accurately accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet is vital, as it ensures that a company’s financial reports are transparent, reliable, and compliant with accounting standards. By grasping the concept of prepaid expenses, businesses can better manage their finances, make informed decisions, and maintain a competitive edge in their respective markets.
How to Classify and Record Prepaid Expenses
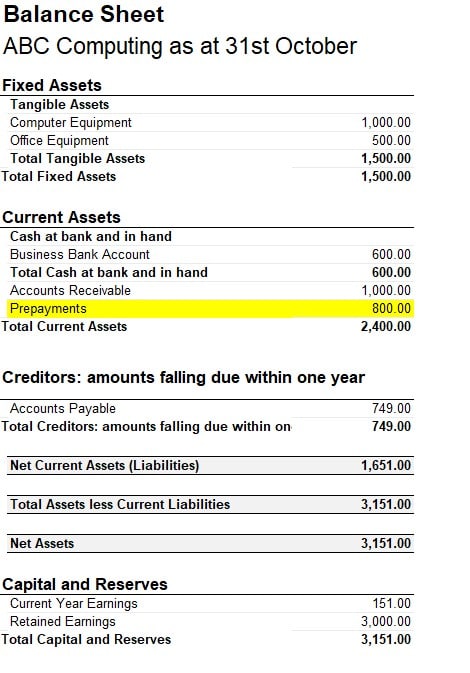
To accurately account for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet, it is essential to understand how to classify and record them. Prepaid expenses can be classified into different categories, such as rent, insurance, subscriptions, and inventory. When recording prepaid expenses, companies should follow a step-by-step approach. First, identify the prepaid expense and determine its value. Next, record the prepaid expense as an asset on the balance sheet, typically under the “Prepaid Expenses” or “Other Assets” category. Then, allocate the prepaid expense to the correct period, ensuring that it is matched with the corresponding revenue or expense. For example, if a company prepays for a year’s worth of insurance, the prepaid expense should be allocated to each month of the year, rather than being expensed entirely in the first month. By following this approach, companies can ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for on the balance sheet, providing a clear picture of their financial position.
The Impact of Prepaid Expenses on Financial Statements
Prepaid expenses have a significant impact on a company’s financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. On the balance sheet, prepaid expenses are recorded as an asset, typically under the “Prepaid Expenses” or “Other Assets” category. This is because prepaid expenses represent a future benefit that the company will receive, such as rent or insurance coverage. As the prepaid expense is used up or expires, it is gradually expensed on the income statement, reducing the asset value on the balance sheet. For example, if a company prepays for a year’s worth of rent, the prepaid rent asset will decrease each month as the rent is expensed on the income statement. On the cash flow statement, prepaid expenses affect the operating activities section, as they represent a cash outflow at the time of payment. Accurately accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet is crucial, as it ensures that a company’s financial reports accurately reflect its financial position and performance. Inaccurate accounting for prepaid expenses can lead to misstated financial statements, which can have serious consequences for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Accounting for Prepaid Expenses
When accounting for prepaid expenses, it is essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate financial reporting. One common error is misclassifying prepaid expenses as assets or liabilities. Prepaid expenses should be recorded as assets on the balance sheet, as they represent a future benefit that the company will receive. Misclassifying prepaid expenses can lead to an inaccurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance. Another mistake is failing to allocate prepaid expenses to the correct period. Prepaid expenses should be expensed over the period they relate to, rather than being expensed entirely in the period of payment. For example, if a company prepays for a year’s worth of insurance, the prepaid expense should be allocated to each month of the year, rather than being expensed entirely in the first month. To avoid these mistakes, companies should establish clear accounting policies and procedures for prepaid expenses, and regularly review and adjust their prepaid expense accounts to ensure accuracy. By avoiding these common mistakes, companies can ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for on the balance sheet, providing a clear picture of their financial position and performance.
Prepaid Expenses vs. Accrued Expenses: What’s the Difference?
Prepaid expenses and accrued expenses are two types of expenses that are often confused with each other. However, they have distinct differences in terms of their accounting treatment and impact on the balance sheet. Prepaid expenses, as discussed earlier, represent payments made in advance for goods or services that will be received in the future. They are recorded as assets on the balance sheet, as they represent a future benefit that the company will receive. On the other hand, accrued expenses represent expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid. They are recorded as liabilities on the balance sheet, as they represent a future payment that the company must make. A key difference between the two is the timing of payment and receipt of goods or services. Prepaid expenses involve payment before receipt of goods or services, while accrued expenses involve receipt of goods or services before payment. For example, a company may prepay for a year’s worth of insurance, which would be recorded as a prepaid expense asset on the balance sheet. On the other hand, a company may receive goods from a supplier but not yet pay for them, which would be recorded as an accrued expense liability on the balance sheet. Understanding the difference between prepaid expenses and accrued expenses is crucial for accurate financial reporting, as misclassifying them can lead to an inaccurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance. By properly accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet, companies can ensure that their financial reports accurately reflect their financial situation.
Real-World Examples of Prepaid Expenses in Action
Prepaid expenses are a common practice in various industries, and understanding how they work in real-world scenarios can help illustrate their importance. Let’s take a look at a few examples of companies that have prepaid expenses. A retail company, for instance, may prepay for inventory to ensure a steady supply of goods during peak seasons. This prepaid expense would be recorded as an asset on the balance sheet, as it represents a future benefit that the company will receive. Another example is a software company that prepays for subscription services, such as cloud storage or cybersecurity software. This prepaid expense would also be recorded as an asset on the balance sheet, as it represents a future benefit that the company will receive. In both cases, the prepaid expense is initially recorded as an asset on the balance sheet, and then gradually expensed over the period it relates to. By accurately accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet, these companies can ensure that their financial reports accurately reflect their financial situation. For instance, if the retail company fails to account for the prepaid inventory, it may overstate its expenses and understate its assets, leading to an inaccurate representation of its financial position. Similarly, if the software company fails to account for the prepaid subscription services, it may overstate its expenses and understate its assets, leading to an inaccurate representation of its financial position. By understanding how prepaid expenses work in real-world scenarios, companies can better appreciate the importance of accurately accounting for them on the balance sheet.
Best Practices for Managing Prepaid Expenses
Effective management of prepaid expenses is crucial for accurate financial reporting and to ensure that a company’s financial statements accurately reflect its financial position. Here are some best practices for managing prepaid expenses: Setting up a prepaid expense account is essential to track and record prepaid expenses. This account should be separate from other asset accounts to ensure that prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for on the balance sheet. Tracking prepaid expenses is also critical to ensure that they are properly expensed over the period they relate to. This can be done by setting up a schedule to track the amortization of prepaid expenses over time. Regularly reviewing and adjusting prepaid expense accounts is also important to ensure that they are accurate and up-to-date. This includes reviewing the prepaid expense account at the end of each period to ensure that it is properly expensed and adjusting the account as necessary. By following these best practices, companies can ensure that their prepaid expenses are accurately accounted for on the balance sheet, which is essential for accurate financial reporting. Accurate accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of a company’s financial position and performance, which is essential for making informed business decisions. In contrast, inaccurate accounting for prepaid expenses can lead to an inaccurate representation of a company’s financial position and performance, which can have serious consequences. By managing prepaid expenses effectively, companies can ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect their financial situation, which is essential for long-term success.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Prepaid Expense Accounting
In conclusion, accurately accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet is crucial for companies to ensure accurate financial reporting. Prepaid expenses on the balance sheet represent a significant aspect of a company’s financial position and performance, and inaccurate accounting can lead to misleading financial statements. By understanding the concept of prepaid expenses, classifying and recording them correctly, and managing them effectively, companies can ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect their financial situation. This, in turn, enables stakeholders to make informed business decisions and assess a company’s performance and position accurately. Furthermore, accurate accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet helps companies to avoid errors and misconceptions that can lead to financial misrepresentation. By following best practices for managing prepaid expenses, companies can ensure that their financial statements are accurate, reliable, and transparent. In today’s competitive business environment, accurate financial reporting is essential for long-term success, and prepaid expenses on the balance sheet play a critical role in achieving this goal. By prioritizing accurate accounting for prepaid expenses on the balance sheet, companies can build trust with stakeholders, enhance their reputation, and drive business growth.