Understanding the Difference between Real Assets and Financial Assets
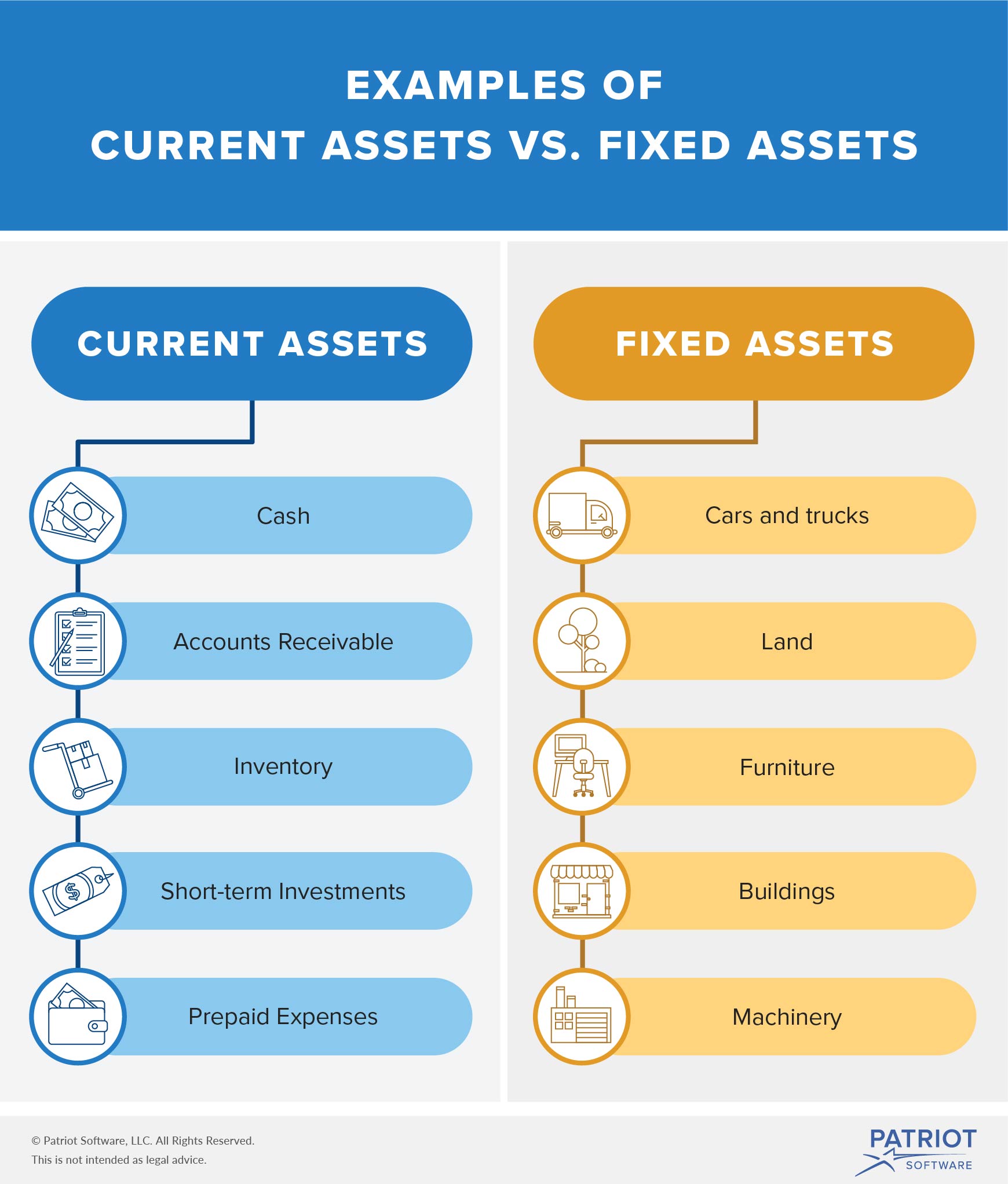
When it comes to building a strong investment portfolio, it’s essential to understand the distinction between real assets and financial assets. Real assets, such as real estate, commodities, and precious metals, have physical value and are often used to hedge against inflation or market volatility. On the other hand, financial assets, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, represent a claim on future cash flows and are valued based on their expected future income.
The key difference between real assets and financial assets lies in their underlying value drivers. Real assets are valued based on their physical properties, such as the value of the land or the rarity of a precious metal. In contrast, financial assets are valued based on their expected future cash flows, such as dividend payments or interest income. This fundamental difference has significant implications for investors, as it affects the risk profile, return potential, and diversification benefits of each asset class.
A well-diversified portfolio should include a mix of both real assets and financial assets. By allocating assets across both classes, investors can create a balanced portfolio that minimizes risk and maximizes returns. Real assets can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility, while financial assets can offer growth and income generation. By understanding the difference between real assets and financial assets, investors can make informed investment decisions and achieve their long-term financial goals.
Why Diversification Matters: Spreading Risk across Asset Classes
Diversification is a crucial aspect of building a strong investment portfolio. By allocating assets across different classes, investors can minimize risk and maximize returns. This is particularly important when it comes to combining real assets and financial assets, as each class has its unique characteristics and risk profiles.
A diversified portfolio can help reduce risk by spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions. This approach can also increase potential returns by capturing growth opportunities in various markets. For instance, real assets such as real estate and commodities can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility, while financial assets like stocks and bonds can offer growth and income generation.
One of the primary benefits of diversification is that it can help investors ride out market fluctuations. By allocating assets across different classes, investors can reduce their exposure to any one particular market or sector. This can help mitigate losses during economic downturns and capture growth opportunities during upswings.
Moreover, diversification can also help investors achieve their long-term financial goals. By spreading risk across different asset classes, investors can create a portfolio that is tailored to their individual goals and risk tolerance. This approach can help investors achieve a more consistent return over the long term, rather than relying on a single asset class or investment.
In conclusion, diversification is a critical component of building a strong investment portfolio. By allocating assets across different classes, investors can minimize risk, maximize returns, and achieve their long-term financial goals. Whether it’s combining real assets and financial assets or spreading investments across different sectors and geographic regions, diversification is a key strategy for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios.
How to Invest in Real Assets for Long-Term Growth
Real assets, such as real estate, commodities, and precious metals, offer a unique set of benefits for investors seeking long-term growth and diversification. These tangible assets have physical value and can provide a hedge against inflation, market volatility, and currency fluctuations. When investing in real assets, it’s essential to understand the different options available and how to get started.
Real estate is a popular real asset class, offering investors the potential for rental income, capital appreciation, and tax benefits. Investors can invest directly in physical properties or through real estate investment trusts (REITs). Commodities, such as gold, oil, and agricultural products, can also provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility. Precious metals, like gold and silver, are often used as a store of value and can provide a safe-haven asset during times of economic uncertainty.
When investing in real assets, it’s crucial to avoid common pitfalls, such as lack of diversification, inadequate research, and emotional decision-making. Investors should conduct thorough research, set clear investment objectives, and develop a long-term strategy. It’s also essential to consider the costs and fees associated with investing in real assets, as well as the potential tax implications.
In addition to direct investment, investors can also access real assets through various financial instruments, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, and index funds. These instruments offer a convenient and cost-effective way to invest in real assets, while also providing diversification benefits.
By incorporating real assets into a diversified portfolio, investors can potentially enhance returns, reduce risk, and achieve their long-term financial goals. Whether it’s through direct investment or financial instruments, real assets offer a unique set of benefits that can help investors build a strong and resilient investment portfolio.
The Role of Financial Assets in a Balanced Portfolio
Financial assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, play a crucial role in a diversified investment portfolio. These intangible assets represent a claim on future cash flows and offer investors the potential for growth, income generation, and diversification. When combined with real assets, financial assets can help create a balanced portfolio that minimizes risk and maximizes returns.
Stocks, for instance, offer investors the potential for long-term growth and capital appreciation. By investing in a diversified portfolio of stocks, investors can benefit from the performance of various companies and industries. Bonds, on the other hand, provide a fixed income stream and relatively lower risk, making them an attractive option for investors seeking predictable returns.
Mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) offer investors a convenient way to access a diversified portfolio of financial assets. These funds allow investors to benefit from the expertise of professional managers and diversify their portfolio with a single investment. Additionally, financial assets can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility, helping to protect investors’ wealth over the long term.
When incorporating financial assets into a portfolio, it’s essential to consider the investor’s risk tolerance, investment objectives, and time horizon. A balanced portfolio should allocate assets across different classes, sectors, and geographic regions to minimize risk and maximize returns. By combining financial assets with real assets, investors can create a diversified portfolio that is tailored to their individual needs and goals.
In a portfolio that includes both real assets and financial assets, investors can benefit from the unique characteristics of each asset class. Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, offer a hedge against inflation and market volatility, while financial assets provide the potential for growth and income generation. By combining these asset classes, investors can create a balanced portfolio that is well-positioned to achieve their long-term financial goals.
Managing Risk: Strategies for Protecting Your Wealth
Risk management is a crucial aspect of building a strong investment portfolio with real assets and financial assets. Investors must be prepared to navigate market volatility, economic downturns, and other uncertainties that can impact their wealth. By implementing effective risk management strategies, investors can protect their wealth and achieve their long-term financial goals.
One key strategy for managing risk is diversification. By allocating assets across different classes, sectors, and geographic regions, investors can minimize their exposure to any one particular market or sector. This approach can help reduce the overall risk of the portfolio and increase the potential for long-term growth.
Hedging is another important strategy for managing risk. This involves investing in assets that are negatively correlated with the overall portfolio, such as gold or other precious metals. By doing so, investors can reduce their exposure to market volatility and protect their wealth during times of economic uncertainty.
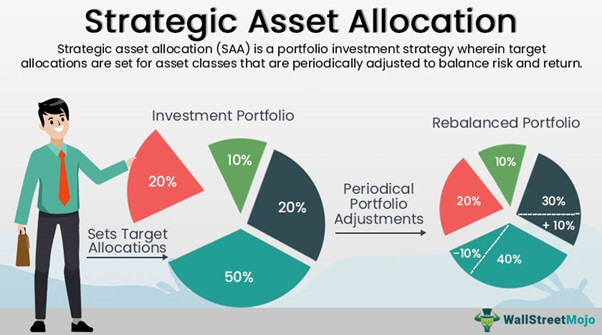
Regular portfolio rebalancing is also essential for managing risk. This involves periodically reviewing the portfolio and making adjustments to ensure that it remains aligned with the investor’s goals and risk tolerance. By rebalancing the portfolio, investors can prevent any one asset class from becoming too dominant and reduce the overall risk of the portfolio.
In addition to these strategies, investors should also consider implementing a stop-loss strategy. This involves setting a predetermined price level at which to sell a security if it falls below a certain threshold. By doing so, investors can limit their losses and protect their wealth during times of market volatility.
Finally, investors should consider working with a financial advisor or investment manager to develop a customized risk management strategy. These professionals can provide expert guidance and help investors navigate the complexities of risk management.
By implementing these risk management strategies, investors can protect their wealth and achieve their long-term financial goals. Whether investing in real assets, financial assets, or a combination of both, effective risk management is essential for building a strong and resilient investment portfolio.
The Benefits of Combining Real and Financial Assets
Combining real assets and financial assets in a portfolio can provide investors with a powerful strategy for achieving their long-term financial goals. By allocating assets across both tangible and intangible asset classes, investors can benefit from the unique characteristics of each, ultimately enhancing returns and reducing risk.
Real assets, such as real estate, commodities, and precious metals, offer a hedge against inflation and market volatility, providing a stable source of returns. Financial assets, including stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, offer the potential for growth and income generation, as well as diversification benefits. By combining these asset classes, investors can create a balanced portfolio that is better equipped to navigate changing market conditions.
One of the primary benefits of combining real and financial assets is the potential for enhanced returns. By allocating assets across different classes, investors can take advantage of growth opportunities in various sectors and markets, ultimately increasing the potential for long-term returns. Additionally, the diversification benefits of combining real and financial assets can help reduce risk, as the performance of one asset class can help offset the performance of another.
Another advantage of combining real and financial assets is the ability to tailor a portfolio to individual goals and risk tolerance. By allocating assets across different classes, investors can create a customized portfolio that aligns with their specific needs and objectives. For example, investors seeking income generation may allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to financial assets, while those seeking long-term growth may allocate more to real assets.
Furthermore, combining real and financial assets can provide investors with a more stable source of returns. Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, tend to perform well during periods of inflation, while financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, tend to perform well during periods of economic growth. By combining these asset classes, investors can create a portfolio that is better equipped to navigate changing market conditions and provide a more stable source of returns.
In conclusion, combining real assets and financial assets in a portfolio can provide investors with a powerful strategy for achieving their long-term financial goals. By allocating assets across both tangible and intangible asset classes, investors can benefit from the unique characteristics of each, ultimately enhancing returns and reducing risk.
Creating a Customized Investment Strategy for Your Goals
Creating a customized investment strategy is crucial for achieving long-term financial goals. A tailored approach takes into account an individual’s unique objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon, ensuring that their investment portfolio is aligned with their needs. By considering these factors, investors can create a strategy that balances risk and return, ultimately leading to greater financial success.
Assessing investment objectives is the first step in creating a customized strategy. This involves identifying specific goals, such as retirement savings, wealth accumulation, or income generation. Investors should also consider their time horizon, as this will impact the type of investments they choose and the level of risk they are willing to take.
Risk tolerance is another critical factor in creating a customized investment strategy. Investors who are risk-averse may prefer a more conservative approach, allocating a larger portion of their portfolio to financial assets such as bonds and money market funds. Those who are willing to take on more risk may opt for a more aggressive approach, allocating a larger portion to real assets such as real estate and commodities.
Once investment objectives and risk tolerance have been assessed, investors can begin allocating assets accordingly. This may involve combining real assets and financial assets in a portfolio, as each asset class offers unique benefits and characteristics. Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility, while financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, can offer growth and income generation.
A customized investment strategy should also consider an investor’s tax situation and overall financial circumstances. For example, investors in high tax brackets may benefit from tax-efficient investing strategies, such as allocating assets to tax-deferred accounts. Those with limited financial resources may need to prioritize cost minimization and seek out low-cost investment options.
Regular portfolio rebalancing is also essential for maintaining a customized investment strategy. As market conditions and investor objectives change, the portfolio may become misaligned with its original goals. By regularly reviewing and rebalancing the portfolio, investors can ensure that their strategy remains on track and that their goals are being met.
In conclusion, creating a customized investment strategy is critical for achieving long-term financial success. By assessing investment objectives, risk tolerance, and overall financial circumstances, investors can create a tailored approach that balances risk and return, ultimately leading to greater financial success.
Maximizing Returns: Tips for Optimizing Your Investment Portfolio
Optimizing an investment portfolio is crucial for maximizing returns and achieving long-term financial goals. By implementing effective strategies, investors can enhance their portfolio’s performance, minimize costs, and reduce risk. Here are some expert tips for optimizing an investment portfolio:
Tax-Efficient Investing: A key strategy for maximizing returns is tax-efficient investing. This involves allocating assets to tax-deferred accounts, such as 401(k)s or IRAs, to minimize tax liabilities. Additionally, investors can consider holding tax-efficient investments, such as index funds or municipal bonds, in non-registered accounts.
Cost Minimization: Minimizing costs is essential for maximizing returns. Investors should seek out low-cost investment options, such as exchange-traded funds (ETFs) or index funds, which offer similar performance to actively managed funds at a lower cost. Additionally, investors should avoid unnecessary fees, such as management fees or trading commissions.
Regular Portfolio Rebalancing: Regular portfolio rebalancing is critical for maintaining an optimal asset allocation. As market conditions change, the portfolio may become misaligned with its original goals. By regularly reviewing and rebalancing the portfolio, investors can ensure that their strategy remains on track and that their goals are being met.
Diversification: Diversification is a key principle of investing, and it’s essential for maximizing returns. By allocating assets across different classes, such as real assets and financial assets, investors can reduce risk and increase potential returns. A diversified portfolio can also help investors navigate changing market conditions and protect their wealth during economic downturns.
Real Assets and Financial Assets: Combining real assets and financial assets in a portfolio can provide investors with a powerful strategy for maximizing returns. Real assets, such as real estate and commodities, can provide a hedge against inflation and market volatility, while financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, can offer growth and income generation. By allocating assets across both classes, investors can create a balanced portfolio that is better equipped to navigate changing market conditions.
Active Portfolio Management: Active portfolio management involves regularly monitoring and adjusting the portfolio to ensure that it remains aligned with its original goals. This can involve rebalancing the portfolio, adjusting asset allocations, and making tactical investment decisions. By actively managing their portfolio, investors can maximize returns and achieve their long-term financial goals.
In conclusion, optimizing an investment portfolio requires a combination of effective strategies, including tax-efficient investing, cost minimization, regular portfolio rebalancing, diversification, and active portfolio management. By implementing these strategies, investors can maximize returns, reduce risk, and achieve their long-term financial goals.