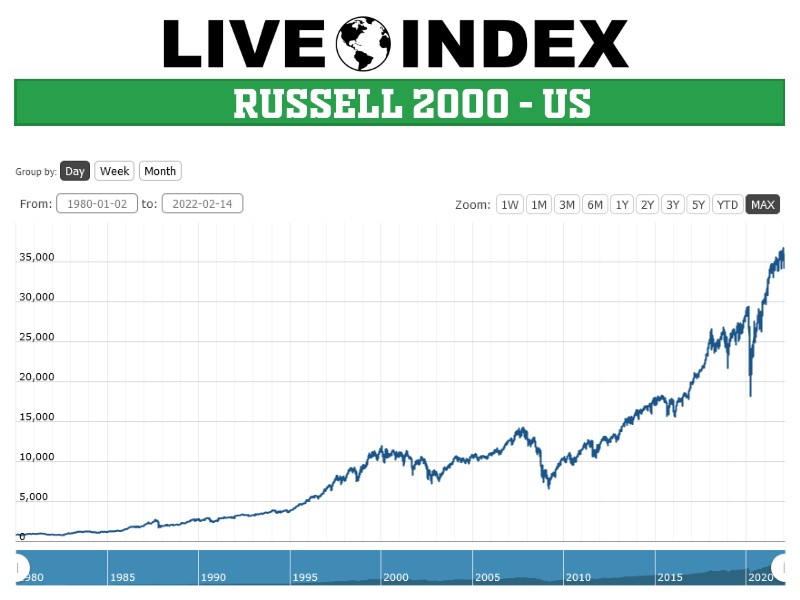
What is the Russell 2000 Index and Why Does it Matter?
The Russell 2000 Index is a widely followed stock market index that tracks the performance of small-cap stocks in the United States. It is a subset of the Russell 3000 Index, which represents approximately 98% of the investable US equity market. The Russell 2000 Index is designed to provide investors with a comprehensive view of the small-cap segment, which is often characterized by higher growth potential and greater volatility compared to large-cap stocks.
With a history dating back to 1984, the Russell 2000 Index has become a benchmark for small-cap investment strategies. It is calculated and maintained by FTSE Russell, a leading provider of index solutions. The index is market-capitalization weighted, meaning that the companies with the largest market capitalization have a greater influence on the index’s performance.
The Russell 2000 Index is important for investors because it provides a way to diversify a portfolio by allocating a portion of assets to small-cap stocks. This can help to increase potential returns and reduce overall portfolio risk. Many investment products, such as index funds and ETFs, are designed to track the performance of the Russell 2000 Index, making it easy for investors to gain exposure to this segment of the market.
In addition, the Russell 2000 Index serves as a valuable tool for investors seeking to understand the performance of small-cap companies. By analyzing the index’s components and their weightings, investors can gain insights into the trends and patterns shaping the small-cap market. This information can be used to inform investment decisions and identify opportunities for growth.
For example, investors may be interested in understanding which industries and sectors are currently dominating the Russell 2000 Index. By examining the index’s sector breakdown, investors can identify areas of strength and weakness, and adjust their portfolios accordingly. Similarly, investors may want to know which companies are currently leading the index in terms of market capitalization, and how these companies are performing relative to their peers.
Overall, the Russell 2000 Index is a critical component of the investment landscape, providing investors with a valuable tool for understanding and navigating the small-cap market. By understanding the index’s composition, performance, and trends, investors can make more informed decisions and achieve their investment goals.
How to Navigate the Russell 2000 Index: Understanding Market Capitalization Weighting
The Russell 2000 Index is a market-capitalization weighted index, meaning that the companies with the largest market capitalization have a greater influence on the index’s performance. This weighting method is commonly used in index construction, as it provides a more accurate representation of the market’s performance. However, it’s essential to understand the implications of market capitalization weighting on the Russell 2000 Index and its constituents.
The advantages of market capitalization weighting include:
-
Greater representation of the market’s largest companies, which tend to have a more significant impact on the overall market performance.
-
Easier to calculate and maintain, as it’s based on publicly available market data.
However, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
-
Larger companies may dominate the index, potentially masking the performance of smaller companies.
-
The index may be more susceptible to the performance of a few large companies, rather than the broader market trends.
In the context of the Russell 2000 Index, market capitalization weighting means that the top Russell 2000 companies by weight have a significant impact on the index’s performance. For example, the top 10 companies by weight in the Russell 2000 Index account for approximately 20% of the index’s total market capitalization. This concentration of weight can have a profound impact on investment decisions, as it may lead to a greater emphasis on these companies in a portfolio.
Investors should be aware of the implications of market capitalization weighting when investing in the Russell 2000 Index. By understanding the weightings of the top companies in the index, investors can make more informed decisions about their investment strategies. For instance, investors may choose to overweight or underweight certain sectors or industries based on their weightings in the index. Additionally, investors may want to consider the potential risks and opportunities associated with the top Russell 2000 companies by weight, and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Top Russell 2000 Companies by Weight: A Closer Look
The Russell 2000 Index is comprised of over 2,000 small-cap stocks, but a closer examination of the top Russell 2000 companies by weight reveals some interesting trends and patterns. The top 10 companies by weight in the Russell 2000 Index account for approximately 20% of the index’s total market capitalization, highlighting the significant impact these companies have on the index’s performance.
Here is a list of the top 10 Russell 2000 companies by weight, including their market capitalization, industry, and sector:
| Company | Market Capitalization (USD billion) | Industry | Sector |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTC Inc. | 14.3 | Software | Technology |
| Twitter Inc. | 13.4 | Internet Information Providers | Communication Services |
| Take-Two Interactive Software Inc. | 12.9 | Home Entertainment Software | Communication Services |
| Liberty Broadband Corp. | 12.5 | Cable Television | Communication Services |
| News Corp. | 12.3 | Publishing | Communication Services |
| Discovery Inc. | 11.9 | Cable Networks | Communication Services |
| ViacomCBS Inc. | 11.7 | Cable Networks | Communication Services |
| Live Nation Entertainment Inc. | 11.5 | Concert and Event Production | Communication Services |
| Wendy’s Co. | 11.3 | Restaurants | Consumer Discretionary |
| Domino’s Pizza Inc. | 11.2 | Restaurants | Consumer Discretionary |
An analysis of the top Russell 2000 companies by weight reveals a few key trends:
-
The technology sector is well-represented, with companies like PTC Inc. and Twitter Inc. featuring prominently.
-
The communication services sector is also heavily represented, with companies like Take-Two Interactive Software Inc. and Liberty Broadband Corp. making the list.
-
Consumer discretionary companies, such as Wendy’s Co. and Domino’s Pizza Inc., also feature in the top 10.
These trends and patterns provide valuable insights into the current market and can inform investment decisions. By understanding the top Russell 2000 companies by weight, investors can gain a better understanding of the index’s performance and make more informed investment decisions.
Industry Insights: Which Sectors Dominate the Russell 2000 Index?
The Russell 2000 Index is a diverse index comprising over 2,000 small-cap stocks, but a closer examination of the sector breakdown reveals some interesting trends and patterns. Understanding the dominant industries and their weightage in the index can provide valuable insights for investors and inform their investment decisions.
The Russell 2000 Index is heavily weighted towards the following sectors:
-
Healthcare: Accounting for approximately 23% of the index, the healthcare sector is the largest contributor to the Russell 2000 Index. This is due to the presence of numerous biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies, as well as healthcare services providers.
-
Technology: The technology sector accounts for around 20% of the index, with companies involved in software, IT services, and electronic components featuring prominently.
-
Financials: The financials sector, including banks, insurance companies, and real estate investment trusts (REITs), accounts for around 18% of the index.
-
Consumer Discretionary: The consumer discretionary sector, including companies involved in retail, restaurants, and leisure, accounts for around 12% of the index.
The dominance of these sectors is not surprising, given the nature of small-cap stocks. Many small-cap companies are focused on niche markets or emerging industries, which can lead to higher growth potential but also increased volatility.
The implications of this sector distribution on investment strategies are significant. Investors seeking to diversify their portfolios may want to consider allocating a larger proportion of their assets to the Russell 2000 Index, given its exposure to a broad range of sectors. Additionally, investors may want to focus on specific sectors within the index, such as healthcare or technology, to capitalize on growth opportunities.
It is also worth noting that the sector breakdown of the Russell 2000 Index can change over time, reflecting shifts in the market and the economy. As such, investors should regularly monitor the index’s composition and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
What Drives the Performance of Russell 2000 Companies?
Understanding the factors that influence the performance of Russell 2000 companies is crucial for investors seeking to capitalize on the growth potential of small-cap stocks. The performance of these companies is driven by a complex interplay of economic indicators, industry trends, and company-specific factors.
Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and interest rates, have a significant impact on the performance of Russell 2000 companies. For example, a strong economy with low unemployment and rising consumer spending can boost the performance of companies in the consumer discretionary sector. On the other hand, a slowing economy can lead to underperformance in the same sector.
Industry trends also play a critical role in shaping the performance of Russell 2000 companies. For instance, the growing demand for cloud computing and cybersecurity has driven the performance of technology companies in the index. Similarly, the increasing focus on healthcare and biotechnology has led to outperformance in the healthcare sector.
Company-specific factors, such as management teams, product pipelines, and competitive advantages, are also essential in driving the performance of Russell 2000 companies. A company with a strong management team, a robust product pipeline, and a competitive advantage in its industry is more likely to outperform the index.
Examples of Russell 2000 companies that have outperformed the index include:
-
Boot Barn Holdings, a retailer of western and work-related footwear and apparel, which has benefited from the growing demand for outdoor recreation and workwear.
-
ShockWave Medical, a medical device company focused on treating calcified cardiovascular disease, which has seen its stock price surge on the back of strong clinical trial results.
On the other hand, companies that have underperformed the index include:
-
GameStop, a video game retailer, which has struggled to adapt to the shift towards digital game downloads and online sales.
-
Ascena Retail Group, a retailer of women’s clothing, which has faced intense competition from online retailers and changing consumer preferences.
By understanding the key factors that drive the performance of Russell 2000 companies, investors can make more informed investment decisions and capitalize on the growth potential of small-cap stocks.
Investing in the Russell 2000 Index: Strategies and Considerations
Investing in the Russell 2000 Index can be an attractive option for investors seeking to tap into the growth potential of small-cap stocks. There are several ways to invest in the Russell 2000 Index, each with its own benefits and risks. In this section, we will discuss the various strategies and considerations for investing in the Russell 2000 Index.
Index Funds: One of the most popular ways to invest in the Russell 2000 Index is through index funds. These funds track the performance of the index by holding a basket of securities that replicate the index’s composition. Index funds offer broad diversification, low costs, and the potential for long-term growth. However, they may not offer the same level of customization as other investment options.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): ETFs are another popular option for investing in the Russell 2000 Index. They offer the flexibility of trading on an exchange like stocks, while providing the diversification benefits of a mutual fund. ETFs often have lower costs than actively managed funds and can be used to implement a variety of investment strategies.
Individual Stocks: Investors can also invest in individual Russell 2000 companies by weight, selecting stocks that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance. This approach requires a deeper understanding of the companies and their underlying fundamentals, as well as the ability to manage risk through diversification and portfolio rebalancing.
Actively Managed Funds: Actively managed funds offer a more hands-on approach to investing in the Russell 2000 Index. These funds are managed by experienced investment professionals who seek to beat the index’s performance through stock selection and market timing. While actively managed funds can offer the potential for outperformance, they often come with higher costs and may not always deliver on their promises.
Considerations: When investing in the Russell 2000 Index, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
-
Risk tolerance: Small-cap stocks can be more volatile than larger-cap stocks, so investors need to be comfortable with the potential for higher returns and higher risks.
-
Time horizon: The Russell 2000 Index is a long-term investment, so investors should have a time horizon of at least five years to ride out market fluctuations.
-
Costs: Investors should carefully consider the costs associated with each investment option, as they can eat into returns over time.
-
Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes and sectors can help reduce risk and increase the potential for long-term growth.
By understanding the various strategies and considerations for investing in the Russell 2000 Index, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Russell 2000 Index vs. Other Small-Cap Indices: A Comparison
When it comes to small-cap investing, the Russell 2000 Index is one of the most widely followed benchmarks. However, it’s not the only small-cap index available. In this section, we’ll compare the Russell 2000 Index with other popular small-cap indices, including the S&P SmallCap 600 and the CRSP US Small Cap Index.
Methodology: One of the key differences between these indices is their methodology. The Russell 2000 Index uses a market capitalization-weighted approach, where the largest companies by market cap have a greater influence on the index’s performance. In contrast, the S&P SmallCap 600 uses a float-adjusted market capitalization-weighted approach, which takes into account the publicly available shares of each company. The CRSP US Small Cap Index, on the other hand, uses a market capitalization-weighted approach with a twist: it includes a liquidity factor to ensure that the index is investable.
Constituents: Another key difference is the number of constituents in each index. The Russell 2000 Index has approximately 2,000 constituents, while the S&P SmallCap 600 has 600 constituents, and the CRSP US Small Cap Index has around 1,500 constituents. The Russell 2000 Index is generally considered to be a more comprehensive benchmark, while the S&P SmallCap 600 is seen as a more selective index.
Performance: In terms of performance, the Russell 2000 Index has historically been more volatile than the S&P SmallCap 600 and the CRSP US Small Cap Index. This is due to its broader constituent base and market capitalization-weighted approach. However, the Russell 2000 Index has also provided higher returns over the long term, making it a popular choice for investors seeking to tap into the growth potential of small-cap stocks.
Industry Exposure: The sector breakdown of each index also differs. The Russell 2000 Index has a higher weighting in the healthcare and technology sectors, while the S&P SmallCap 600 has a higher weighting in the financials and industrials sectors. The CRSP US Small Cap Index has a more balanced sector breakdown, with no single sector dominating the index.
Investment Implications: So, what does this mean for investors? The choice of small-cap index will depend on an investor’s specific investment objectives and risk tolerance. The Russell 2000 Index is a good choice for investors seeking broad exposure to the small-cap universe, while the S&P SmallCap 600 may be more suitable for investors seeking a more selective approach. The CRSP US Small Cap Index, on the other hand, may be a good choice for investors seeking a balanced sector exposure.
In conclusion, while the Russell 2000 Index is a widely followed benchmark, it’s not the only small-cap index available. By understanding the differences between these indices, investors can make informed decisions about which index best aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Monitoring Russell 2000 Index Changes
As a small-cap investor, it’s essential to stay informed about changes to the Russell 2000 Index. The index is rebalanced quarterly, and changes can have a significant impact on investment decisions. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of monitoring Russell 2000 Index changes and provide tips on how to stay ahead of the curve.
Additions and Deletions: One of the most significant changes to the Russell 2000 Index is the addition or deletion of companies. This can occur due to mergers and acquisitions, IPOs, or changes in market capitalization. Investors should closely monitor these changes, as they can affect the overall performance of the index and individual portfolios.
Weightage Adjustments: In addition to additions and deletions, the Russell 2000 Index also undergoes weightage adjustments. This involves rebalancing the index to ensure that the market capitalization of each company is accurately reflected. Weightage adjustments can have a significant impact on the performance of individual stocks and the overall index.
Why Monitoring Changes Matters: Monitoring changes to the Russell 2000 Index is crucial for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios. By staying informed about additions, deletions, and weightage adjustments, investors can make informed decisions about which stocks to buy or sell. This can help to minimize risk and maximize returns.
Tips for Staying Informed: So, how can investors stay informed about changes to the Russell 2000 Index? One approach is to follow reputable financial news sources and websites that provide updates on the index. Investors can also set up alerts for specific stocks or industries to stay informed about changes as they occur. Additionally, investors can consult with financial advisors or investment professionals who have expertise in small-cap investing.
Impact on Investment Decisions: Changes to the Russell 2000 Index can have a significant impact on investment decisions. For example, if a company is added to the index, it may experience an increase in demand, driving up its stock price. Conversely, if a company is deleted from the index, its stock price may decline. By staying informed about these changes, investors can make informed decisions about which stocks to buy or sell.
In conclusion, monitoring changes to the Russell 2000 Index is essential for small-cap investors seeking to optimize their portfolios. By staying informed about additions, deletions, and weightage adjustments, investors can make informed decisions about which stocks to buy or sell, minimizing risk and maximizing returns.