Understanding the Basics of CDs: A Safe Haven for Your Savings
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) are a type of savings account offered by banks and credit unions that provide a low-risk investment option for individuals seeking a stable return on their deposits. CDs are time deposits, meaning that the deposited funds are locked in the account for a specified period, ranging from a few months to several years. In exchange for this commitment, CD holders receive a fixed interest rate, which is typically higher than that of a traditional savings account.
One of the primary benefits of CDs is their FDIC insurance, which protects deposits up to $250,000 per account owner, per insured bank. This insurance provides an added layer of security, making CDs an attractive option for risk-averse investors. Additionally, CDs tend to be less volatile than other investment products, such as stocks or mutual funds, making them a suitable choice for those seeking a more predictable return.
When considering a CD, it’s essential to understand the different types available, including traditional CDs, jumbo CDs, and no-penalty CDs. Each type has its unique features, such as varying interest rates, term lengths, and withdrawal penalties. By selecting the right CD for their financial goals and risk tolerance, investors can create a stable source of income and achieve long-term financial security. Furthermore, understanding whether a CD is classified as M1 or M2 can help investors make informed decisions about their savings strategy, as it affects the liquidity and interest rates of the CD. Is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? This question will be answered in the following sections.
What is M1 and M2 Money: A Brief Overview
M1 and M2 are two monetary aggregates that play a crucial role in the economy. Understanding the difference between these two aggregates is essential for investors, as it affects the classification of Certificates of Deposit (CDs) and other financial instruments.
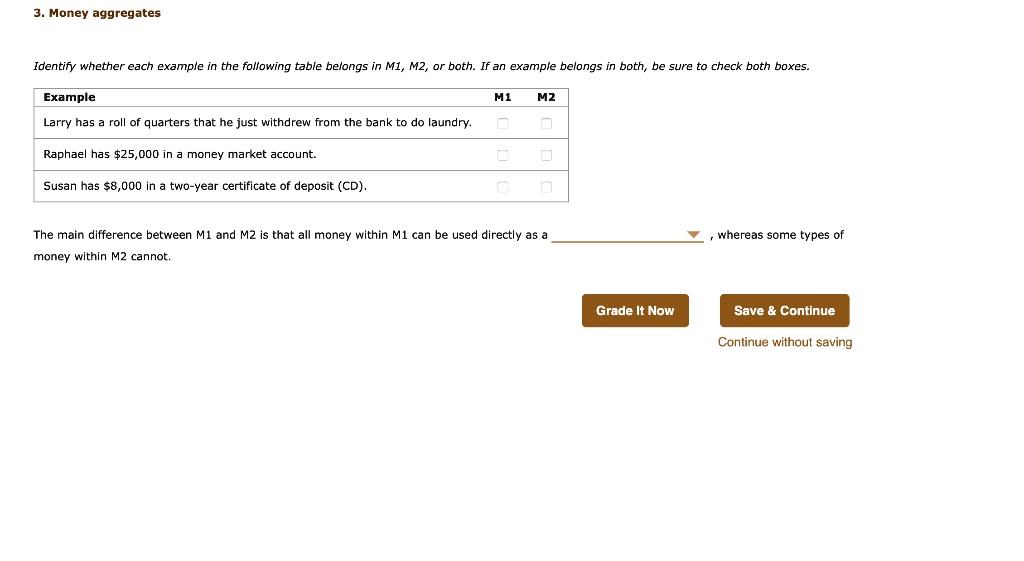
M1, also known as narrow money, refers to the most liquid forms of money, including physical currency, checking accounts, and other checkable deposits. M1 is the most widely used measure of the money supply and is considered the most liquid form of money. It is the money that is readily available for spending and investing.
M2, on the other hand, is a broader measure of the money supply, including M1, savings deposits, money market funds, and other less liquid forms of money. M2 is a more comprehensive measure of the money supply, as it includes money that is not as readily available for spending and investing.
The history of M1 and M2 dates back to the 1950s, when the Federal Reserve began tracking these monetary aggregates. Over time, the definitions and components of M1 and M2 have evolved, but their importance in understanding the economy and financial markets remains unchanged.
In the context of CDs, understanding the difference between M1 and M2 is crucial, as it affects the classification of CDs and their interest rates and liquidity. Is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? This question will be answered in the following sections, as we explore how to determine the classification of a CD and the implications for investors.
How to Determine if a CD is M1 or M2: A Step-by-Step Guide
Determining whether a Certificate of Deposit (CD) is classified as M1 or M2 is crucial for investors, as it affects the CD’s interest rates, liquidity, and overall investment strategy. So, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? To answer this question, follow these steps:
Step 1: Check the CD’s term length. M1 CDs typically have shorter term lengths, ranging from a few months to a year, while M2 CDs have longer term lengths, often exceeding a year.
Step 2: Evaluate the CD’s liquidity. M1 CDs are generally more liquid, allowing investors to access their funds quickly, whereas M2 CDs are less liquid, with penalties for early withdrawal.
Step 3: Consider the CD’s interest rate. M1 CDs tend to offer lower interest rates due to their shorter term lengths and higher liquidity, while M2 CDs offer higher interest rates to compensate for their lower liquidity.
Step 4: Review the CD’s underlying assets. M1 CDs are often backed by short-term commercial paper, treasury bills, and other liquid assets, whereas M2 CDs are backed by longer-term assets, such as mortgage-backed securities and corporate bonds.
By following these steps, investors can determine whether a CD is classified as M1 or M2, making informed investment decisions and optimizing their savings strategy. Remember, understanding the differences between M1 and M2 CDs is essential for achieving long-term financial goals.
The Impact of M1 and M2 on CD Interest Rates and Liquidity
The classification of a Certificate of Deposit (CD) as M1 or M2 has a significant impact on its interest rates and liquidity. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors to make informed decisions and optimize their savings strategy.
M1 CDs, with their shorter term lengths and higher liquidity, typically offer lower interest rates. This is because investors can access their funds quickly, reducing the need for high returns. In contrast, M2 CDs, with their longer term lengths and lower liquidity, offer higher interest rates to compensate for the reduced access to funds.
The interest rates of M1 and M2 CDs are also influenced by the monetary policy of central banks. During times of economic growth, central banks may increase interest rates to curb inflation, benefiting M2 CDs with their longer term lengths. Conversely, during economic downturns, central banks may lower interest rates to stimulate growth, benefiting M1 CDs with their shorter term lengths.
In addition to interest rates, the M1 and M2 classification affects the liquidity of CDs. M1 CDs are generally more liquid, allowing investors to access their funds quickly, whereas M2 CDs are less liquid, with penalties for early withdrawal. This liquidity difference is critical for investors who may need to access their funds unexpectedly.
Ultimately, the impact of M1 and M2 on CD interest rates and liquidity has significant implications for investors and the overall economy. By understanding these differences, investors can make informed decisions, optimize their savings strategy, and achieve their long-term financial goals. Remember, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? The answer to this question can have a lasting impact on your investment portfolio.
CDs as a Tool for Managing M1 and M2: Strategies for Savers
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) can be a valuable tool for savers looking to manage their M1 and M2 money effectively. By understanding the differences between M1 and M2 CDs, investors can develop strategies to optimize their savings and achieve their long-term financial goals.
One effective strategy is laddering, which involves dividing investments into multiple CDs with staggered term lengths. This approach allows investors to take advantage of higher interest rates offered by longer-term M2 CDs while maintaining access to their funds through shorter-term M1 CDs.
Diversification is another key strategy for managing M1 and M2 money. By spreading investments across multiple CDs with different term lengths and interest rates, investors can reduce risk and increase potential returns. This approach can be particularly effective for investors with a mix of short-term and long-term financial goals.
Risk management is also crucial when using CDs to manage M1 and M2 money. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance and adjust their CD portfolio accordingly. For example, investors with a low risk tolerance may prefer shorter-term M1 CDs with lower returns, while those with a higher risk tolerance may opt for longer-term M2 CDs with higher returns.
Ultimately, the key to successfully managing M1 and M2 money with CDs is to understand the differences between these two types of certificates and develop a strategy that aligns with individual financial goals. By doing so, investors can optimize their savings, reduce risk, and achieve long-term financial success. Remember, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? The answer to this question can have a significant impact on your investment strategy.
The Role of CDs in a Diversified Investment Portfolio: M1 and M2 Considerations
In a diversified investment portfolio, Certificates of Deposit (CDs) can play a crucial role in balancing M1 and M2 assets to achieve long-term financial goals. By understanding the differences between M1 and M2 CDs, investors can strategically allocate their investments to maximize returns and minimize risk.
A well-diversified portfolio typically includes a mix of low-risk, liquid investments (M1) and higher-return, less-liquid investments (M2). CDs can be used to balance these two types of assets, providing a stable source of income and reducing overall portfolio risk. For example, investors may allocate a portion of their portfolio to short-term M1 CDs for liquidity and another portion to longer-term M2 CDs for higher returns.
When incorporating CDs into a diversified portfolio, it’s essential to consider the M1 and M2 classifications. M1 CDs, with their shorter term lengths and higher liquidity, are ideal for investors seeking quick access to their funds. In contrast, M2 CDs, with their longer term lengths and lower liquidity, are better suited for investors with a longer investment horizon.
By balancing M1 and M2 CDs in a diversified portfolio, investors can achieve a range of benefits, including reduced risk, increased returns, and improved liquidity. This approach can be particularly effective for investors seeking to manage their cash flow, reduce volatility, and achieve long-term financial goals. Remember, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? Understanding the answer to this question can have a significant impact on your investment strategy and overall portfolio performance.
Common Misconceptions about M1 and M2 CDs: Setting the Record Straight
When it comes to Certificates of Deposit (CDs), there are several common misconceptions that can lead to confusion and misinformed investment decisions. In this section, we’ll address some of the most prevalent myths about M1 and M2 CDs, providing clarity and insight to help investors make informed choices.
Myth #1: M1 CDs are always low-risk and low-return. Reality: While M1 CDs are generally considered low-risk, they can offer competitive interest rates, especially for shorter term lengths. In fact, some M1 CDs may offer higher returns than traditional savings accounts.
Myth #2: M2 CDs are always high-risk and high-return. Reality: While M2 CDs may offer higher returns than M1 CDs, they are not necessarily high-risk. In fact, M2 CDs are still insured by the FDIC, providing a level of protection for investors.
Myth #3: CDs are illiquid investments. Reality: While CDs do come with penalties for early withdrawal, they are not entirely illiquid. In fact, many CDs offer flexible terms and conditions that allow investors to access their funds when needed.
Myth #4: M1 and M2 CDs are only for conservative investors. Reality: CDs can be a valuable addition to any investment portfolio, regardless of risk tolerance. By understanding the differences between M1 and M2 CDs, investors can strategically allocate their investments to achieve their financial goals.
By understanding the facts and dispelling these common misconceptions, investors can make informed decisions about whether a CD is M1 or M2 and how to incorporate these investments into their overall portfolio. Remember, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? Knowing the answer to this question can help you avoid common pitfalls and achieve long-term financial success.
Conclusion: Navigating the World of M1 and M2 CDs with Confidence
In conclusion, understanding the differences between M1 and M2 Certificates of Deposit (CDs) is crucial for making informed investment decisions. By grasping the concepts of M1 and M2 money, investors can strategically allocate their investments to achieve their financial goals. Whether you’re a conservative saver or an aggressive investor, CDs can play a vital role in your portfolio.
Remember, is a certificate of deposit M1 or M2? Knowing the answer to this question can help you navigate the world of CDs with confidence. By avoiding common misconceptions and understanding the impact of M1 and M2 on CD interest rates and liquidity, investors can make informed decisions about their investments.
In today’s complex financial landscape, it’s essential to stay informed and adapt to changing market conditions. By incorporating CDs into your investment strategy, you can achieve a balanced portfolio that meets your unique needs and goals. So, take the first step towards financial confidence – understand the world of M1 and M2 CDs and start making informed investment decisions today.