Recent Trends in 4-Week Treasury Bill Rates
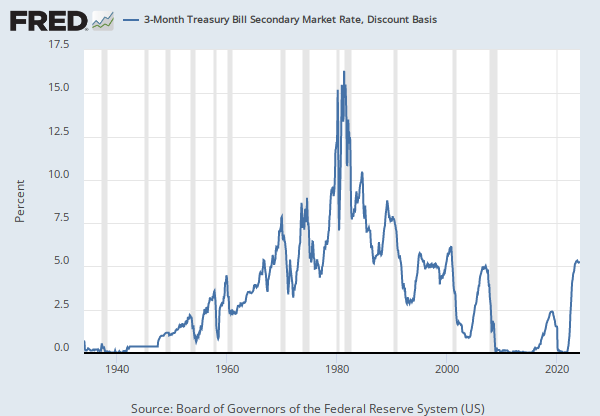
Current market trends for short-term treasury bills, specifically the 4-week variety, exhibit fluctuations. Recent changes in treasury bill rates, both increases and decreases, reflect the overall economic climate. Understanding these short-term treasury bill rate fluctuations requires analyzing the intricate interplay of economic factors.
The observed fluctuations in 4-week treasury bill rates are likely linked to various economic indicators. Economic indicators such as inflation figures, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies are major contributors to the ever-changing dynamics of treasury bill rates. Recent Federal Reserve policy decisions have a profound impact on short-term treasury bill rates. The interplay between these factors creates a complex yet dynamic market for treasury bill rates, making them an important area of study for investors.
Analyzing historical data on treasury bill rates and related economic indicators provides valuable insight into potential future trends. Tracking the correlations between these indicators and treasury bill rates 4 week can offer investors a better understanding of the potential direction of rates in the short term. Investors should consider consulting financial analysts for guidance.
Factors Influencing Treasury Bill Rates
Several key economic factors significantly impact short-term treasury bill rates, particularly the 4-week variety. Central bank policies, specifically the Federal Reserve’s actions, play a crucial role. Recent interest rate adjustments, quantitative easing or tightening programs, and announcements regarding future monetary policy targets all directly affect treasury bill rates 4 week. These adjustments influence investor expectations regarding the overall economic climate. Inflation figures provide another critical viewpoint. High inflation often compels the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates to control price increases, thus impacting treasury bill rates 4 week. Conversely, low inflation might lead to lower rates. Other relevant financial indicators, including GDP growth, employment reports, and consumer confidence, also play a substantial role. Strong economic signals frequently correlate with rising treasury bill rates 4 week, while weaker indicators often lead to lower rates. Understanding the interconnectedness of these factors is vital for comprehending the fluctuations observed in short-term treasury bill rates 4 week.
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions directly influence short-term treasury bill rates 4 week. For instance, if the Fed raises interest rates, the yield on treasury bills 4 week tends to increase as well. This is because higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive for the government, and investors will demand higher returns to compensate for the increased risk. Conversely, if the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, the yields on treasury bills 4 week tend to decrease, as borrowing becomes more attractive for the government, and investors require a lower return. Inflation figures, alongside monetary policy, strongly correlate with these trends. Increased inflation frequently results in higher treasury bill rates 4 week, as investors seek compensation for the eroding purchasing power of their investments. Economic growth and investor sentiment are connected as well. A positive economic outlook often encourages investors to seek higher yields, leading to potentially higher treasury bill rates 4 week. Conversely, uncertain economic periods frequently result in lower treasury bill rates 4 week.
Understanding the intricate interplay between these factors and short-term treasury bill rates 4 week is essential for interpreting market fluctuations. The Federal Reserve’s actions are a primary driver, impacting investor sentiment and influencing the demand for treasury bills 4 week. Inflation figures often dictate the direction of these rates, with rising inflation typically resulting in higher treasury bill rates 4 week. A careful analysis of these and other pertinent economic indicators allows for a better understanding of the trends in treasury bill rates 4 week and their potential implications for investors.
How to Interpret Treasury Bill Rate Changes
Understanding fluctuations in 4-week treasury bill rates is crucial for investors and those interested in the overall economic climate. Changes in these rates reflect shifting market sentiment and potential future economic projections. A rise in 4-week treasury bill rates typically indicates an increase in investor demand, often a sign of anticipated future interest rate hikes. Conversely, a decrease suggests a decrease in investor interest, potentially signaling a less optimistic economic outlook. This analysis is important to understand when navigating the complexities of the investment landscape.
An increase in 4-week treasury bill rates often signals increased investor confidence in the safety and liquidity of short-term investments. This can reflect growing concerns about potential inflation or an anticipated tightening of monetary policy by central banks, such as the Federal Reserve. Investors perceive these treasury bill rates as a safe haven and may seek to lock in returns at these higher rates. An example might be a rise in the 4-week treasury bill rate if investors anticipate the Federal Reserve will increase interest rates. Conversely, a decrease in 4-week treasury bill rates often indicates diminished investor interest. This might be due to reduced inflation expectations or a perception of less risk in the economy. For instance, if inflation falls unexpectedly, investors might reduce their demand for the safety of 4-week treasury bills. Declining treasury bill rates can also signal potential economic slowdown. Analyzing treasury bill rates, particularly the 4-week variety, allows investors to make informed decisions regarding the overall investment climate.
Interpreting changes in 4-week treasury bill rates requires careful consideration of various economic factors. Changes in these rates can also influence other investment instruments, including money market funds and certificates of deposit (CDs). Consideration of the wider economic picture and market sentiment is paramount when evaluating the significance of changes in 4-week treasury bill rates. This allows investors to make informed decisions aligning with their investment strategies and risk tolerance. A thorough analysis of 4-week treasury bill rates offers critical insights into market trends and future economic projections, enabling investors to adjust their portfolios accordingly.
Comparing 4-Week Treasury Bills to Other Treasury Instruments
Understanding the nuances of 4-week treasury bills requires a comparative analysis with other Treasury instruments. Treasury bills, particularly the 4-week variety, represent short-term debt obligations. In contrast, longer-term Treasury bonds represent a commitment for a more extended period. This fundamental difference in maturity profoundly influences the associated yield.
The shorter maturity of 4-week treasury bills typically results in lower yields compared to longer-term bonds. Investors seeking higher yields often opt for the longer-term instruments. This inverse relationship stems from the reduced risk investors perceive with the shorter-term investments. A significant factor is the potential for changes in interest rates during the longer bond term. Investors will have less exposure to rate fluctuation risks during the 4 week treasury bill rates tenure.
The choice between 4-week treasury bills and longer-term bonds depends significantly on an investor’s financial goals and risk tolerance. Investors with a need for immediate liquidity often favor the certainty of short-term treasury bill rates. Alternatively, investors seeking potentially higher returns over a longer period might choose longer-term instruments. Understanding this maturity-yield relationship is crucial for effectively managing a diversified investment portfolio. Investors should also understand the specific characteristics of a particular 4-week treasury bill rates offering before making an investment.
Impact on Short-Term Investments
Shifting 4-week treasury bill rates significantly impact short-term investments. These rates serve as a benchmark for numerous money market instruments. Understanding how these rates fluctuate is crucial for investors and financial institutions. Treasury bill rates directly influence money market funds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and other short-term investment vehicles. Changes in treasury bill rates affect the return on investment in these instruments. For example, if 4-week treasury bill rates rise, money market funds may adjust their yields to remain competitive. This consequently impacts the returns for investors in these funds. Conversely, if rates fall, returns may decrease for short-term investors.
Investors in certificates of deposit (CDs) experience similar impacts from changing 4-week treasury bill rates. These rates often determine the interest rates offered on CDs. An increase in treasury bill rates 4 week frequently leads to higher CD interest rates. Conversely, lower treasury bill rates lead to lower returns on CDs. The relationship between treasury bill rates and short-term investment vehicles illustrates the interconnectedness within the financial market. This interplay necessitates careful consideration by investors to align their investment strategies with current treasury bill rates.
The fluctuating nature of short-term treasury bill rates can also influence the pricing and yields of other short-term investment instruments. For example, short-term corporate bonds often adjust their yields in response to shifts in the prevailing treasury bill rates. Understanding these intricate relationships allows investors to anticipate likely adjustments and make informed decisions aligned with their financial goals. Investors seeking short-term income should closely monitor these treasury bill rates 4 week trends to maximize returns and mitigate potential risks.
Forecasting Future 4-Week Treasury Bill Rates
Predicting future treasury bill rates, particularly for the 4-week variety, is a complex undertaking. Several factors need consideration, and accurate forecasting remains challenging. Economic indicators, market sentiment, and government policies all play a significant role in shaping these rates. Market analysis, expert opinions, and available data provide a framework, but uncertainty is inherent.
Techniques for forecasting future 4-week treasury bill rates involve examining recent trends in the market. Analysis of past data reveals patterns, correlations, and potential indicators. Economic forecasts and projections from reputable institutions can offer valuable insights. Monitoring the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, especially interest rate adjustments, will have a significant impact on treasury bill rates. Changes in inflation rates and economic growth forecasts can also signal future shifts. Crucially, understanding the interplay of these elements is crucial for a well-rounded forecast.
It’s essential to recognize the inherent challenges in predicting 4-week treasury bill rates. Economic models and expert assessments offer potential trajectories, but unpredictable events can disrupt anticipated paths. External factors, such as geopolitical instability or unexpected shifts in market sentiment, can alter the predicted course of treasury bill rates. Therefore, while forecasting offers insights, it’s important to acknowledge inherent uncertainties and to approach projections with a healthy dose of realism. The goal is not absolute certainty, but rather a well-informed understanding of possible future trends regarding 4-week treasury bill rates.
Investment Strategies in Light of Treasury Bill Rates
Analyzing current 4-week treasury bill rates provides crucial insights for investors. Understanding the interplay between risk tolerance and investment potential is key when considering these short-term securities. Diversification strategies, especially when aligning with the current economic climate, become essential components of successful portfolios. Strategic adjustments may be necessary when facing fluctuating treasury bill rates. Assessing the expected return on investment and potential risks associated with different assets is crucial.
When evaluating investment strategies in the face of changing treasury bill rates, consider various portfolios. A portfolio heavily weighted toward short-term investments might yield lower returns compared to a diversified portfolio including both short-term and longer-term securities. Conversely, a portfolio emphasizing longer-term securities could be less responsive to short-term fluctuations in 4-week treasury bill rates. Analyzing individual risk tolerance and financial goals is vital. If a higher return is a priority, investors should cautiously assess risk tolerance. Carefully consider how different asset classes, including treasury bills and other instruments, respond to economic shifts. The optimal portfolio will vary based on individual circumstances.
Diversification is paramount when navigating fluctuating 4-week treasury bill rates. A well-diversified portfolio that includes a mix of assets, including stocks, bonds, and treasury bills, can help mitigate potential losses from adverse market conditions. Assessing current market conditions, along with individual risk tolerances, helps investors determine appropriate asset allocations. Thorough analysis of the specific needs and goals of each investor is crucial for crafting a tailored investment strategy. Carefully evaluating the current market environment, as well as assessing the overall health of the economy, helps to inform investment decisions.
The Role of Government Policy in Treasury Bill Rates
Government policy significantly influences 4-week treasury bill rates. Understanding this relationship is crucial for navigating the complexities of short-term investments. One key factor is the government’s budget deficit. When government spending exceeds revenue, the Treasury Department must borrow money to cover the shortfall. This increased borrowing creates higher demand for government debt, including 4-week treasury bills. This increased demand can push treasury bill rates 4 week upwards, as investors seek a higher return for lending to the government. Conversely, a shrinking deficit can decrease demand and potentially lower 4-week treasury bill rates.
Another impactful policy is government borrowing itself. The Treasury Department manages the national debt by issuing various debt instruments, including 4-week treasury bills. The frequency and size of these issuances directly impact the supply of treasury bills in the market. A large influx of new treasury bills can put downward pressure on treasury bill rates 4 week, as the increased supply can outpace demand. Conversely, a reduced issuance can lead to scarcity and potentially higher rates. Fiscal stimulus programs, often implemented during economic downturns, can also affect treasury bill rates 4 week. These programs typically involve increased government spending, leading to larger deficits and greater borrowing. This, in turn, can drive up demand for treasury bills and potentially increase their rates.
Furthermore, the interplay between fiscal and monetary policy adds another layer of complexity. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, such as setting the federal funds rate, can influence investor behavior and indirectly impact treasury bill rates 4 week. For instance, if the Fed raises interest rates, investors might shift funds from treasury bills to other higher-yielding investments, potentially putting downward pressure on treasury bill rates. Conversely, if the Fed lowers rates, treasury bills might become more attractive, increasing demand and potentially raising rates. Therefore, understanding the combined effects of government borrowing, fiscal stimulus, and monetary policy provides a comprehensive view of the forces shaping treasury bill rates 4 week.