What are Dividends? Unpacking the Basics
Dividends represent a portion of a company’s profits shared with its shareholders. Think of it like receiving a share of the earnings for owning a piece of the company. Companies distribute these payouts to reward investors for their investment. The amount and frequency of dividend payments vary greatly. Importantly, not all companies choose to pay dividends; some reinvest profits for growth instead. For example, imagine a successful technology company decides to share 20% of its yearly profit with its shareholders. This distribution is known as a dividend. Understanding dividends is crucial when considering what is forward dividend and yield, as it forms the basis of the calculation. This process allows investors to directly benefit from the company’s success. A key aspect to remember is that dividend payments are not guaranteed. Companies may adjust or suspend payments based on their financial performance and business needs. Therefore, investors should understand that what is forward dividend and yield is an estimation based on future projections.
Dividends provide a valuable income stream for investors seeking regular returns on their investments. This passive income can be a significant part of a diversified investment portfolio. It helps investors to participate in the success of a company. The decision to pay a dividend is at the discretion of the company’s board of directors. They assess the company’s financial health, future prospects, and overall business strategy before deciding whether or not to distribute dividends. The absence of dividends doesn’t necessarily indicate poor performance; it simply reflects a company’s decision to prioritize other avenues for growth, such as reinvesting profits in research and development or acquiring other companies. Understanding this dynamic is key to interpreting what is forward dividend and yield. Investors should evaluate each company individually to determine whether its dividend policy aligns with their investment goals. Analyzing dividend payment history can also help investors to understand the company’s dividend policy and predict future payments. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the dividend process is critical in building a successful investment strategy.
When considering what is forward dividend and yield, remember the importance of understanding the company’s financial health. This includes reviewing its profitability, debt levels, and cash flow. These factors significantly influence a company’s ability to sustain its dividend payments. A company’s history of dividend payments is another crucial factor. Consistent dividend payments over a long period can indicate a stable and reliable income stream for investors. Conversely, a history of erratic or missed dividend payments may signal higher risk. Investors should carefully examine a company’s financial statements, press releases, and investor presentations to assess the sustainability of its dividend policy. This due diligence is essential to making informed decisions when assessing what is forward dividend and yield. By considering a range of factors, investors can develop a better understanding of the company’s financial position and the likelihood of future dividend payments. It’s important to remember that past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Always diversify investments across different asset classes and companies to mitigate potential risks. A well-diversified portfolio is more resilient to market fluctuations. This balanced approach reduces reliance on any single company or asset and strengthens an investor’s overall financial position.
Forward Dividend: Looking Ahead at Company Payouts
What is forward dividend and yield? Understanding forward dividends is crucial for investors interested in dividend-paying stocks. A forward dividend represents the estimated total dividends a company expects to distribute to shareholders over the next twelve months. It’s a projection, not a guarantee. The actual dividend payments may differ from the forward dividend estimate due to various factors influencing company performance and profitability. It’s important to note that declared dividends, which are official announcements by a company about upcoming dividend payments, differ from the forward-looking nature of the forward dividend. What is forward dividend and yield, in essence, is a predictive tool for investors, and a thorough understanding of its predictive nature is essential.
Several sources contribute to forward dividend estimates. Financial analysts frequently predict future dividends based on their assessment of a company’s financial health, future earnings potential, and past dividend payment patterns. Company management itself might offer guidance on expected future dividend payouts. These projections, however, remain estimates, subject to revision based on unforeseen circumstances and changing market conditions. Therefore, investors should consider forward dividends as a projection, not a fixed commitment from the company. Always remember that the actual dividend payouts may differ significantly from these initial estimates. Understanding what is forward dividend and yield, and its limitations, is crucial for informed investment decisions.
The difference between declared dividends and forward dividends is significant for discerning investors. Declared dividends represent officially announced payments, usually following a company’s board of directors’ approval. These are concrete commitments, barring unforeseen events. In contrast, forward dividends remain projections, subject to change. Investors should utilize both declared and forward dividend figures cautiously. What is forward dividend and yield, when considered together with declared dividends, provides a more comprehensive view of a company’s dividend policy. This balanced perspective helps in making informed investment choices, mitigating risks associated with relying solely on projected figures.
How to Calculate Forward Dividend Yield: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding what is forward dividend and yield is crucial for investors. The forward dividend yield represents the expected annual dividend income relative to the current stock price. It’s a vital tool for assessing potential returns, but remember, it’s a projection, not a guarantee. To calculate it, one needs two key pieces of information: the forward dividend and the current market price of the stock. The formula is straightforward: Forward Dividend Yield = (Forward Annual Dividend / Current Market Price) x 100.
Let’s illustrate with a hypothetical example. Consider a company whose stock currently trades at $50 per share. Analysts predict the company will pay a total dividend of $2 per share over the next twelve months. To calculate the forward dividend yield, we substitute these values into our formula: Forward Dividend Yield = ($2 / $50) x 100 = 4%. This means that, based on current predictions, an investor can expect a 4% return on their investment from dividends alone. It’s important to reiterate that this is an *estimate* of what is forward dividend and yield; the actual yield may differ.
The calculation emphasizes the use of the *current* market price. Using the purchase price will not give you an accurate reflection of the current forward dividend yield. The market price fluctuates constantly, influencing the yield. A rising stock price will lower the yield, while a falling stock price will raise it. What is forward dividend and yield, in essence, is a snapshot of the predicted dividend return based on today’s market conditions. Investors should always use the most up-to-date market price for accurate calculations. Remember that a high forward dividend yield doesn’t automatically guarantee a profitable investment. Other factors, such as the company’s financial health and overall market trends, should also be carefully considered. Understanding what is forward dividend and yield is only one piece of the investment puzzle.
Understanding Dividend Yield: Return on Investment
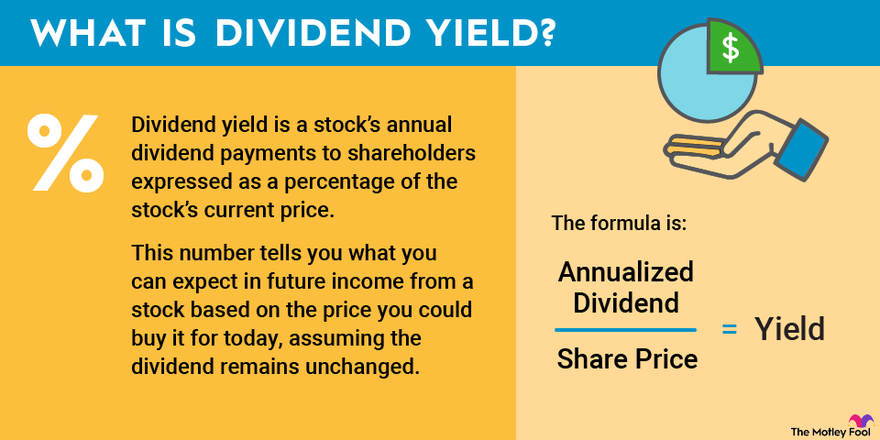
Dividend yield is a crucial metric that shows the annual dividend income relative to a stock’s price. It represents the return an investor receives from dividends, expressed as a percentage. The calculation is straightforward: annual dividend per share divided by the current market price per share, multiplied by 100 to express it as a percentage. Understanding what is forward dividend and yield is essential for assessing investment returns, particularly for income-oriented investors. A higher dividend yield suggests a greater return on investment from dividends, but it’s crucial to remember this is just one piece of the puzzle. Investors should always consider the overall financial health and future prospects of the company.
What is forward dividend and yield in the context of investment analysis? It’s important to differentiate between forward and trailing dividend yields. Trailing dividend yield reflects past dividend payments, while forward dividend yield projects future dividend payments. Forward dividend yield is based on analysts’ estimates or company guidance of the total dividends expected over the next twelve months. This projected yield helps investors anticipate their potential dividend income. The choice between focusing on forward or trailing yield depends on the investor’s time horizon. Long-term investors might prioritize forward yield to gauge the long-term income potential. Conversely, short-term traders may find trailing yield more relevant, as it reflects actual recent payments. Understanding what is forward dividend and yield is critical for informed decision-making.
The significance of dividend yield in investment decisions cannot be overstated. Investors seeking a steady income stream often favor stocks with higher dividend yields. However, a high yield doesn’t automatically signify a superior investment. It’s crucial to consider the company’s financial stability and growth prospects. A high yield might indicate financial distress, leading to a potential dividend cut. Conversely, a lower yield might signal a company reinvesting profits for future growth, potentially leading to higher capital appreciation. Therefore, what is forward dividend and yield should be considered alongside other financial metrics and factors before making any investment choices. A balanced approach, considering both dividend income and potential capital growth, is usually the most effective investment strategy.
Forward Dividend vs. Trailing Dividend: Key Differences Explained
Understanding the difference between forward and trailing dividend yields is crucial for informed investment decisions. What is forward dividend and yield? It’s a prediction of future dividend payments. Trailing dividend yield, on the other hand, reflects past dividend payments. Forward dividend yield looks ahead, estimating the total dividends a company expects to pay within the next twelve months, relative to the current stock price. This projection is based on analyst estimates and company guidance, and it’s important to remember that it’s not a guaranteed amount. In contrast, trailing dividend yield calculates the dividend payments made over the past year, divided by the current stock price. This provides a historical perspective on dividend payouts. Investors seeking to understand what is forward dividend and yield and its implications must consider this distinction.
The time horizon is the key differentiator. Forward dividend yield focuses on the future, providing a forward-looking perspective on potential dividend income. Trailing dividend yield, conversely, looks backward, reflecting past performance. This difference in timeframes means that each metric serves a different purpose in investment analysis. For long-term investors, the forward dividend yield might be more relevant. They are interested in the potential income stream over a longer period. Short-term traders, however, might find the trailing dividend yield more informative, as it reflects the recent dividend payout history. The choice between focusing on what is forward dividend and yield or trailing yield depends on the individual investor’s goals and time horizon.
Consider two hypothetical scenarios. Company A has a strong track record of dividend payments and consistently increases its dividends annually. Its trailing dividend yield might be attractive, but its forward dividend yield may be only slightly higher, reflecting investor confidence in continued growth. Company B, experiencing temporary financial difficulties, might show a high trailing dividend yield due to a high payout relative to the current low stock price. However, its forward dividend yield might be significantly lower, reflecting uncertainty about future payouts. Understanding both metrics provides a more comprehensive picture than relying on either alone. What is forward dividend and yield in relation to past performance should therefore be a part of any investment strategy. Analyzing both forward and trailing yields allows investors to make better informed decisions, considering both the company’s history and future expectations.
Factors Influencing Forward Dividend and Yield
Several key factors influence a company’s forward dividend and yield, impacting what is forward dividend and yield and investor expectations. Profitability is paramount. Companies with strong earnings and robust cash flows are better positioned to distribute higher dividends. Financial health also plays a critical role. High levels of debt or weak balance sheets may constrain a company’s ability to maintain or increase dividend payments. Understanding these aspects is crucial when considering what is forward dividend and yield. Industry trends significantly shape a company’s prospects and dividend policy. A thriving industry generally supports higher payouts, while sector downturns might lead to dividend reductions or suspensions. Management decisions regarding capital allocation directly affect dividend policies. Management might prioritize reinvesting profits in growth initiatives over dividend payouts, impacting what is forward dividend and yield. This decision reflects the company’s strategic priorities and long-term vision.
External economic conditions also influence forward dividend and yield. Economic growth or recessionary periods can affect company performance, influencing dividend decisions. Interest rates also play a part. Higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs, impacting a company’s ability to pay dividends. Investor sentiment and market conditions play a role in shaping what is forward dividend and yield. Positive investor sentiment and strong market performance often lead to higher dividend expectations. Conversely, negative sentiment and market volatility may result in lower expectations or even dividend cuts. Regulatory changes can also create uncertainty and impact dividend policies. Changes in tax laws or accounting standards might affect how companies approach dividend payments and what is forward dividend and yield.
The interplay of these factors creates a dynamic environment for forward dividend and yield. Analyzing these factors helps investors understand the potential risks and opportunities associated with a specific company’s dividend payments. What is forward dividend and yield is only one aspect of evaluating a stock’s overall value. Companies may choose to prioritize share repurchases or reinvestments over dividends, even with strong earnings. Therefore, investors should always consider the bigger picture and not solely rely on what is forward dividend and yield for investment decisions. A holistic approach, encompassing various financial metrics and qualitative factors, is crucial for informed decision-making.
Interpreting Forward Dividend and Yield: What the Numbers Mean
Understanding what is forward dividend and yield requires careful consideration of several factors. A high forward dividend yield might seem attractive, promising substantial income. However, this doesn’t automatically translate to a sound investment. Investors should remember that a high yield can sometimes signal underlying problems. For example, a company facing declining profits might maintain its dividend payout, artificially inflating the yield. This could be unsustainable in the long run, leading to a dividend cut and a significant drop in the stock price. Therefore, what is forward dividend and yield shouldn’t be the sole basis for investment decisions. Always investigate a company’s financial health, growth prospects, and overall market position before investing based solely on yield figures.
What is forward dividend and yield, in practice? It’s a crucial component of investment analysis, but it’s only one piece of the puzzle. Investors should examine the company’s dividend payout history. Consistent dividend increases demonstrate financial strength and management’s commitment to rewarding shareholders. Conversely, inconsistent or declining dividends raise red flags. Analyzing financial statements, such as the income statement and balance sheet, helps gauge the sustainability of the current dividend payout. Investors should also assess the company’s industry, considering broader economic trends and competitive pressures. Understanding the company’s business model and future prospects further enhances the analysis of what is forward dividend and yield in relation to the overall business. These factors paint a more complete picture, helping investors make informed decisions. Comparing the forward dividend yield with similar companies in the same industry provides valuable context. Is the yield significantly higher or lower? Why? Understanding this will further refine the assessment of what is forward dividend and yield.
In conclusion to this section on what is forward dividend and yield, remember that this metric is just one factor in a broader evaluation. While it provides valuable information about the potential income stream from a stock, investors should always consider the bigger picture. A comprehensive analysis that includes financial health, growth prospects, and industry dynamics is crucial for making sound investment decisions. Over-reliance on a single metric, like forward dividend yield, can be detrimental to long-term investment success. What is forward dividend and yield should be considered within a broader context of risk and reward to achieve a well-diversified portfolio aligned with individual goals.
Using Forward Dividend and Yield in Your Investment Strategy
Understanding what is forward dividend and yield is crucial for developing a robust investment strategy. Investors seeking a consistent income stream can utilize forward dividend yields to identify stocks likely to provide regular payouts. By comparing forward dividend yields across various sectors and companies, investors can construct a diversified portfolio tailored to their income goals. Remember, a high yield alone doesn’t guarantee a good investment; thorough due diligence remains essential. What is forward dividend and yield, and how to use it effectively requires careful consideration of a company’s financial health and future prospects.
Forward dividend and yield data can also aid in identifying potentially undervalued stocks. Companies with strong fundamentals but lower-than-average forward dividend yields might present opportunities for long-term growth. Investors should analyze a company’s earnings, debt levels, and growth potential alongside its forward dividend yield. This holistic approach helps determine if the current yield reflects a genuine undervaluation or other underlying factors. What is forward dividend and yield in the context of your overall portfolio? It’s a tool, not a crystal ball. Don’t rely solely on this metric; combine it with fundamental analysis and risk assessment.
Diversification is paramount when using forward dividend and yield information. Focusing solely on high-yielding stocks can expose your portfolio to unnecessary risk. A balanced approach, combining high-yield investments with growth-oriented stocks and other asset classes, is vital for mitigating risk and achieving a well-rounded investment strategy. Remember that what is forward dividend and yield is just one piece of the puzzle. Consider the broader market conditions, the company’s competitive landscape, and your own risk tolerance before making any investment decisions. Regular portfolio reviews and adjustments ensure your strategy remains aligned with your financial objectives.