Understanding the Auction: How Buyers and Sellers Meet
The order book serves as a central hub, a digital ledger meticulously recording all outstanding buy and sell orders for a specific asset. Think of it as a virtual auction house, where buyers submit their bids (the price they’re willing to pay) and sellers post their asks (the price they’re willing to accept). This continuous interaction between buyers and sellers shapes the market’s price discovery process. Within this framework, orders are categorized primarily as market orders or limit orders, each playing a distinct role in how trades are executed.
Market orders are designed for immediate execution at the best available price. A buyer submitting a market order aims to purchase the asset instantly at the lowest ask price currently available. Conversely, a seller using a market order seeks to sell the asset immediately at the highest bid price. The speed and certainty of execution are the main advantages of market orders. On the other hand, limit orders offer more control over the price at which a trade is executed. A limit order to buy will only be executed if the price reaches or falls below the specified limit price. A limit order to sell will only be executed if the price reaches or exceeds the limit price. Understanding the nuances of market orders versus limit orders is crucial for navigating the order book effectively. The relationship between ask size vs bid size, alongside order types, defines potential trading opportunities.
The order book’s dynamic nature reflects the ever-changing balance between supply and demand. Analyzing the ask size vs bid size provides valuable insights into the prevailing market sentiment. A larger ask size vs bid size might indicate increased selling pressure, while a stronger bid size compared to the ask size could signal growing buying interest. Traders leverage this information to anticipate potential price movements and make informed trading decisions. Examining the depth of the order book, or the volume of orders at different price levels, further enhances a trader’s ability to assess market liquidity and potential price impact. The interplay between ask size vs bid size is a fundamental aspect of understanding order book dynamics and executing successful trades.
What are Bids and Asks? Key Components of Market Depth
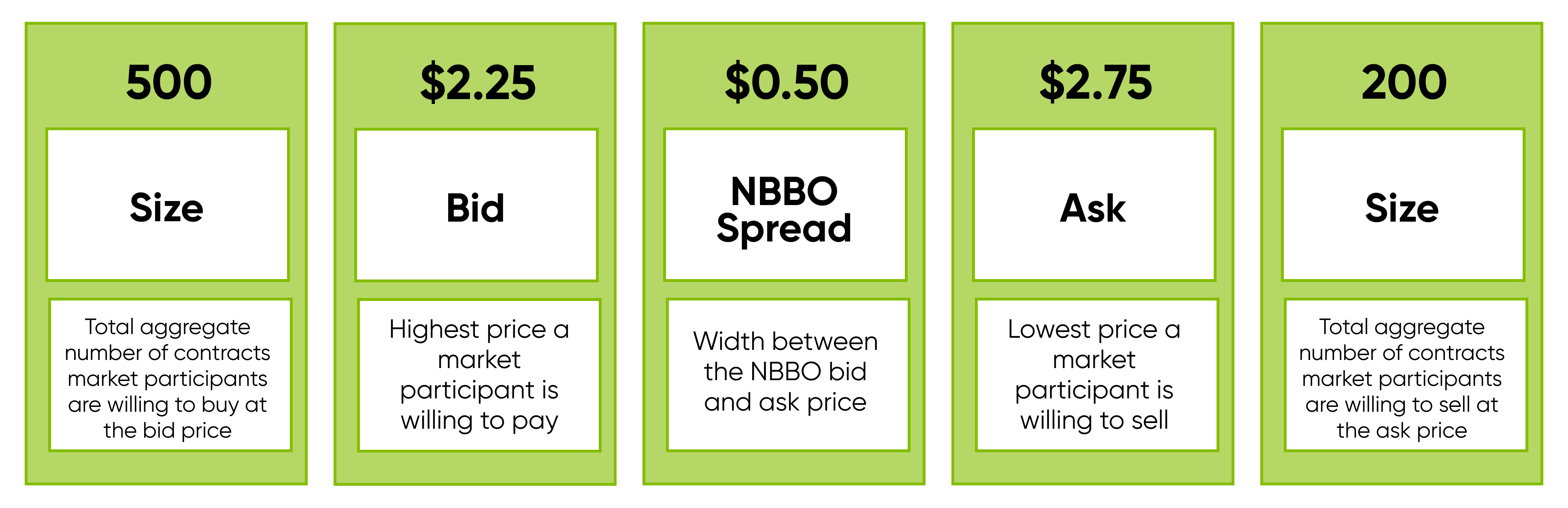
In the financial markets, understanding bids and asks is crucial for grasping market depth and potential trading opportunities. A ‘bid’ represents the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for an asset at a specific point in time. Conversely, the ‘ask’ or ‘offer’ signifies the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for that same asset. The difference between the bid and the ask is known as the spread. A narrow spread usually indicates high liquidity, while a wider spread can suggest lower liquidity or higher volatility. The ask size vs bid size provides insight into the immediate buying and selling pressure.
The size of the bid and ask reflects the current supply and demand dynamics in the market. A large bid size suggests there are many buyers interested in purchasing the asset at that price level. This can act as a support level, potentially preventing the price from falling further. On the other hand, a large ask size indicates strong selling pressure at a particular price. This can function as a resistance level, making it difficult for the price to increase beyond that point. Traders analyze the ask size vs bid size to determine the strength of these potential support and resistance levels. The relative ask size vs bid size also provides hints about potential short-term price movements.
It is important to note that larger sizes at certain price points can indeed act as significant support or resistance. For example, if a stock has a large number of shares being bid for at $50, that $50 level could act as a price floor. Conversely, if there is a substantial ask size at $55, it may be challenging for the stock to break through that price. However, these levels are not absolute. They can shift as orders are filled, canceled, or new orders are placed. Monitoring the fluctuations in ask size vs bid size is key to understanding the evolving market sentiment. Observing changes in the ask size vs bid size ratio can give traders an edge in anticipating price fluctuations and making informed decisions.
Unveiling Liquidity: What Bid and Ask Size Represents
The size of the bid and ask queues is a crucial indicator of liquidity for a particular asset. Understanding what bid and ask size represents provides valuable insights into the market’s depth and potential price movements. A large bid size suggests significant buying interest at that specific price point. This means many buyers are willing to purchase the asset at that price. Conversely, a large ask size indicates strong selling pressure. Many sellers are eager to offload their assets at the specified price. These sizes directly reflect the immediate supply and demand dynamics.
The relationship between bid size vs ask size profoundly influences trade execution, especially for larger orders. When substantial liquidity exists, indicated by large bid and ask sizes, traders can execute orders with minimal price slippage. Slippage occurs when a large order depletes the available liquidity at the best price, forcing the trader to accept less favorable prices to complete the order. For instance, if a trader wants to buy a large number of shares and the ask size is small, the order will consume all available shares at the lowest ask price and then move to higher ask prices. This results in the trader paying a higher average price than initially anticipated. Conversely, a large bid size can absorb significant selling pressure, preventing a drastic price decrease when a large sell order is executed.
Analyzing the bid size vs ask size is essential for managing risk and optimizing trade execution strategies. Traders often look for imbalances in the bid and ask sizes to identify potential trading opportunities. A significantly larger bid size compared to the ask size might signal an impending price increase, encouraging traders to buy. However, it’s crucial to remember that these indicators are not always definitive. Algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading can rapidly alter the bid and ask sizes, creating fleeting opportunities and potential false signals. Therefore, combining order book analysis with other technical indicators and fundamental analysis is vital for making informed trading decisions. Monitoring the bid size vs ask size provides a real-time snapshot of market sentiment and liquidity, empowering traders to navigate the complexities of the market more effectively.
How to Interpret Order Book Imbalances for Potential Trades
Traders can gain valuable insights into market sentiment by carefully analyzing the relative sizes of the bid and ask queues. A key aspect of order book analysis involves understanding the dynamics between ask size vs bid size. A significant disparity between the ask size vs bid size can signal potential trading opportunities. The ask size vs bid size is a direct reflection of the buying and selling pressure present at any given moment.
For example, consider a scenario where the bid size is substantially larger than the ask size. This suggests that there are significantly more buyers willing to purchase the asset at the current bid price than sellers willing to sell at the current ask price. This imbalance, with a larger bid size relative to the ask size, typically indicates bullish sentiment. Traders might interpret this as a potential signal that the price is likely to increase, as the buying pressure overwhelms the selling pressure. Conversely, if the ask size is considerably larger than the bid size, it suggests a surplus of sellers compared to buyers. This scenario usually points towards bearish sentiment, with the price potentially poised to decline due to increased selling pressure. Analyzing ask size vs bid size provides a quick way to gauge the overall mood of the market and anticipate potential price movements.
However, it’s crucial to remember that order book imbalances are not foolproof indicators. They represent a snapshot of the current market conditions and can change rapidly as new orders are placed and existing orders are filled or canceled. Skilled traders combine the analysis of ask size vs bid size with other technical indicators, news events, and overall market analysis to make more informed trading decisions. Furthermore, the interpretation of these imbalances can vary depending on the specific asset, the overall market context, and the time frame being considered. For instance, a large ask size vs bid size imbalance in a highly volatile stock might be interpreted differently than the same imbalance in a stable, low-volatility asset. Therefore, while the relationship between ask size vs bid size provides valuable clues, it should always be used in conjunction with a comprehensive trading strategy.
Spotting Support and Resistance Levels Using Order Book Data
The order book provides valuable insights into potential support and resistance levels by revealing areas of concentrated buying or selling interest. Significant clusters of large bid sizes can often act as support levels, preventing the price from declining further. These levels represent a price floor where buyers are likely to step in and purchase the asset, absorbing selling pressure and stabilizing the price. Analyzing the ask size vs bid size at different price points can help identify these support zones. Conversely, large ask sizes can function as resistance levels, hindering upward price movements. A substantial ask size vs bid size imbalance at a particular price suggests strong selling pressure, making it difficult for buyers to push the price higher.
It’s crucial to understand that these support and resistance levels derived from order book data are not static. They can shift as orders are filled, cancelled, or new orders are placed. As buy orders within a support zone are executed, the support weakens, potentially allowing the price to fall through. Similarly, as sell orders at a resistance level are filled, the resistance diminishes, potentially paving the way for a price breakout. The constant flux of the order book means traders must continuously monitor the ask size vs bid size and adjust their strategies accordingly. The dynamic nature of algorithmic trading further contributes to the fluidity of these levels.
Traders can use this information to inform their trading decisions. For example, a trader might consider placing a buy order slightly above a perceived support level, anticipating a price bounce. Conversely, a trader might consider placing a sell order slightly below a resistance level, anticipating a price rejection. Observing the ask size vs bid size surrounding these levels is critical for validating their strength. However, it’s important to remember that order book data provides only one piece of the puzzle, and should be used in conjunction with other forms of technical analysis and fundamental analysis to make well-informed trading decisions. Always consider the broader market context and be prepared for unexpected price movements, as even seemingly strong support and resistance levels can be broken.
Trade Execution Strategies: Considering Size and Price Impact
When executing trades, especially large orders, traders must carefully consider the ask size vs bid size. Failing to do so can lead to unfavorable outcomes due to price impact. Price impact occurs when a large market order consumes all available liquidity at the current best bid or ask, forcing the trader to execute at less favorable prices further down the order book. This effectively moves the price against the trader.
The ask size vs bid size directly influences the magnitude of price impact. A thin order book, characterized by small bid and ask sizes, is more susceptible to significant price fluctuations from even moderately sized market orders. Conversely, a deep order book with substantial liquidity at multiple price levels can absorb larger orders with less price disruption. Traders should analyze the ask size vs bid size to estimate the potential price impact of their intended trade. This involves assessing the available volume at the best prices and projecting how much the price might move as the order is filled. Understanding the ask size vs bid size is key to minimizing slippage and maximizing profitability.
To mitigate price impact, traders can employ various strategies. One common technique is to use limit orders, which guarantee a specific price or better. However, limit orders may not be filled entirely if the market moves away from the specified price. Another approach is to break up large orders into smaller chunks and execute them over time. This allows the trader to gradually participate in the market without overwhelming the available liquidity. Iceberg orders are another sophisticated tool, where a large order is displayed as a series of smaller, visible orders, with the remaining size hidden. This helps to prevent other market participants from front-running the order and reduces the overall price impact. By carefully considering the ask size vs bid size and employing appropriate execution strategies, traders can significantly improve their trading outcomes and minimize the adverse effects of price impact. Understanding the dynamics of ask size vs bid size enables smarter, more efficient trade execution.
Advanced Order Book Analysis: Beyond Simple Size Comparison
Analyzing the order book transcends simply comparing ask size vs bid size. Sophisticated techniques provide a deeper understanding of market dynamics. Heatmap visualizations offer an intuitive way to interpret order book depth. These maps display the concentration of buy and sell orders at various price levels. Colors represent order size, allowing traders to quickly identify significant support and resistance areas. Examining order flow is another advanced method. This involves tracking the sequence and size of executed trades to infer the intentions of market participants. Large trades executed at the ask may signal aggressive buying, while large trades at the bid may indicate aggressive selling. Analyzing ask size vs bid size in relation to order flow can provide valuable insights into potential price movements.
Level 2 data feeds provide a more granular view of the order book. Unlike Level 1 data, which only shows the best bid and ask, Level 2 data displays all visible orders at different price levels. This allows traders to see the entire depth of the market and identify potential hidden orders or iceberg orders. Analyzing the changes in ask size vs bid size at different price levels can reveal patterns and potential trading opportunities. For example, a sudden increase in ask size at a specific price point may indicate strong selling pressure and a potential reversal. These advanced techniques require specialized tools and platforms.
Several platforms cater to advanced order book analysis. These platforms often provide features such as real-time order book data, customizable heatmaps, and order flow analysis tools. Some platforms also offer algorithmic trading capabilities, allowing traders to automate their strategies based on order book data. The effective use of these tools, coupled with a deep understanding of ask size vs bid size dynamics, can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to identify and capitalize on market opportunities. Mastering these techniques enables a more informed and strategic approach to trading, moving beyond basic comparisons of ask size vs bid size to uncover more subtle market signals.
The Impact of Algorithmic Trading on Bid and Ask Dynamics
Algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading (HFT) have reshaped the dynamics of the order book. These automated systems execute orders based on pre-programmed instructions. Their speed and volume have significantly impacted both bid and ask size. Understanding this influence is now vital for traders. These algorithms can rapidly place and cancel orders. This action creates a dynamic, and often fleeting, sense of liquidity. The constant flux can make it challenging to interpret the true market sentiment. It also affects how traders analyze ask size vs bid size.
One key impact is the reduction of the bid-ask spread. HFT firms compete to provide liquidity. This competition often leads to tighter spreads, benefiting smaller traders. However, this liquidity can disappear quickly. Algorithms react to market events in milliseconds. This can result in “flash crashes” or sudden price swings. Traders must be aware of this potential volatility. Analyzing ask size vs bid size requires considering the presence of these algorithms. Identifying genuine buying or selling interest becomes more difficult. Strategies must adapt to this environment. Algorithmic behavior can also create artificial support and resistance levels. These levels may not reflect actual investor sentiment.
For human traders, these changes present both challenges and opportunities. The increased speed and complexity require sophisticated tools. Access to real-time data and advanced analytics is essential. Traders need to understand order flow and identify algorithmic patterns. This understanding is crucial for effectively interpreting ask size vs bid size. While algorithms can create volatility, they also offer opportunities. Traders can exploit temporary price discrepancies. They can also capitalize on the predictable behavior of certain algorithms. However, success requires a deep understanding of market microstructure and algorithmic behavior. Analyzing ask size vs bid size in this environment demands constant vigilance and adaptability.